What Is Google's Site Search Operator?
Google's site search operator is a powerful tool for finding information on a specific website using Google’s search engine. By focusing your search on one site, you can quickly locate the exact information you need without sifting through unrelated results.
The operator is very easy to use. You just add "site:" in front of the particular domain or URL you want to search. You can then use several other operators to refine your search.
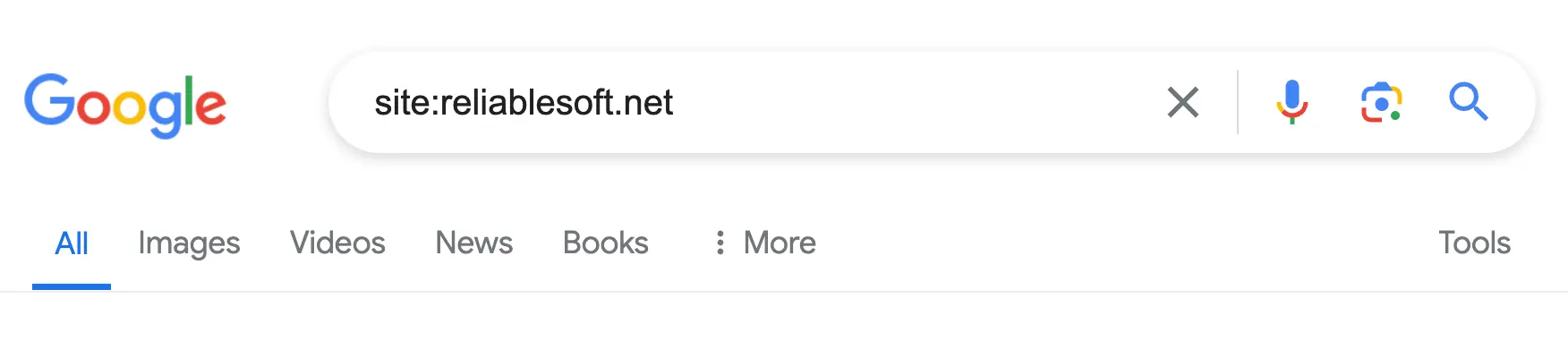
For example, if you type "site:reliablesoft.net" into Google search, the results will only refer to the specified domain (reliablesoft.net).
You can use the Google site search operator for various use cases. The most useful are:
- To check your website for keyword cannibalization issues.
- To find information on a specific website that doesn't have an internal search function.
- To search a website for keywords.
- To check if a domain or page is indexed on Google.
The site search function is especially useful for SEOs and digital marketers as it allows you to check the content of any website, not just yours.
Practical Examples of Google Site Search Operator
Here are some examples of how to use the Google site search operator effectively:
1. Basic Site Search
Use case: To find content on a specific website around a particular keyword. For example, to find articles on SEO from reliablesoft.net
Here is the command to use:
site:reliablesoft.net SEO
Google will return all pages related to SEO from Reliablesoft.
2. Search For a Specific Phrase
Use case: to find content on a website that includes a specific phrase in the page title or content. For example, to find all pages on ahrefs.com that contain the phrase "link building strategies".
Here is the command to use:
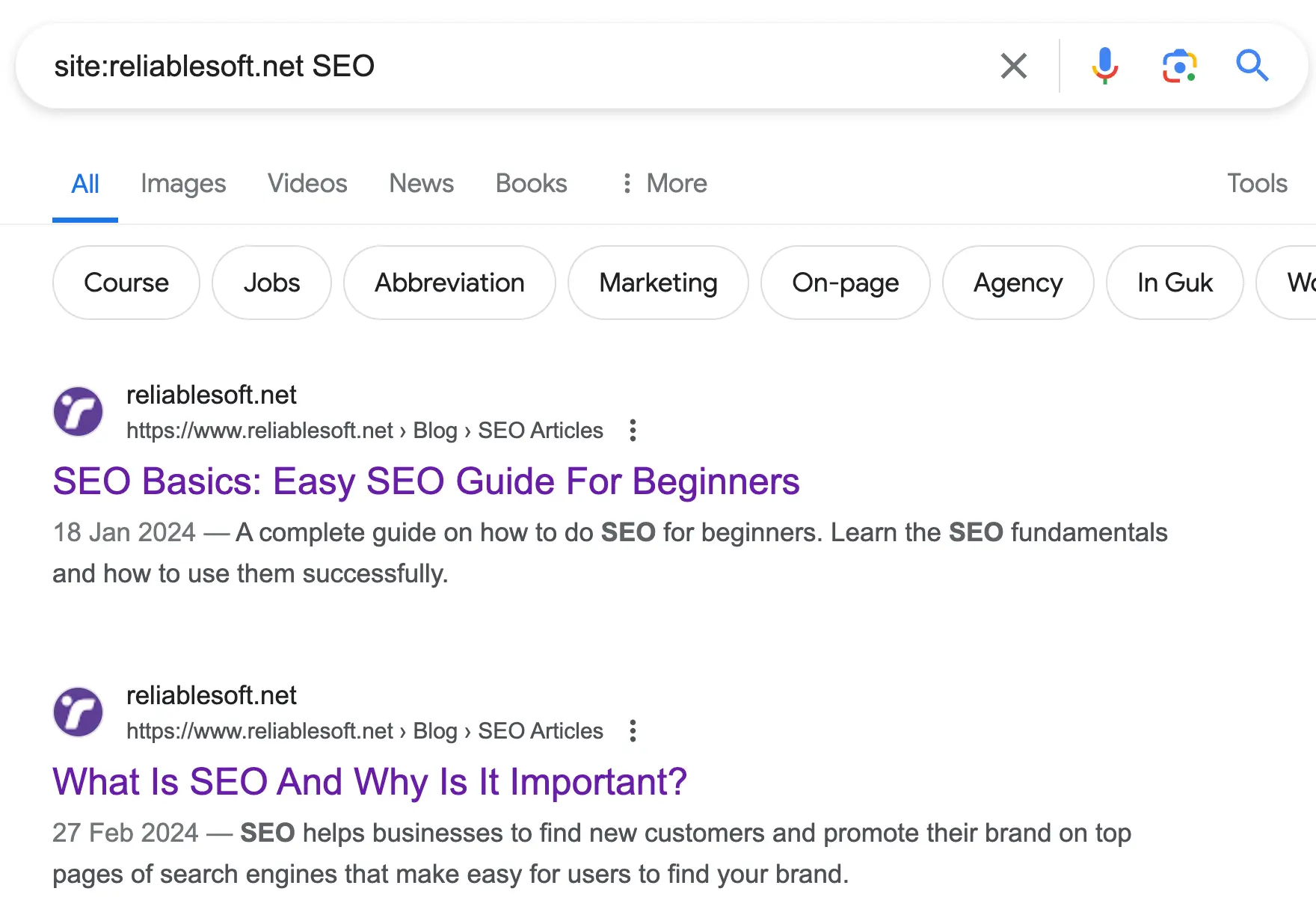
site:ahrefs.com "link building strategies"
Google will show pages on ahrefs.com that specifically mention "link building strategies".
3. Search For a File Type
Use case: Find a specific file type on a website, such as a pdf. For example, you can find any indexed PDF files on neilpatel.com.
Here is the command to use:
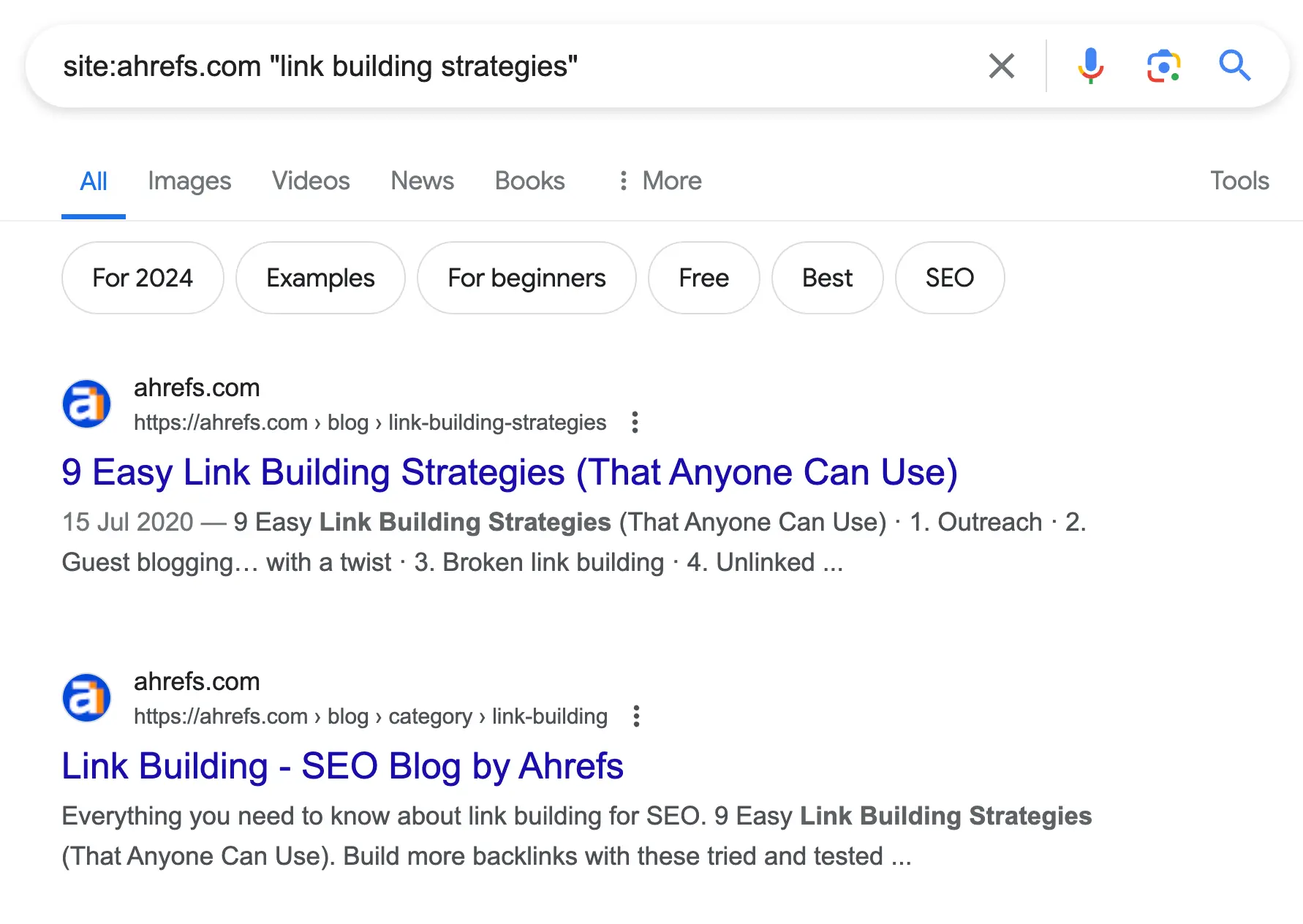
site:neilpatel.com filetype:pdf
Results will include all PDF files available on Neil Patel’s blog.
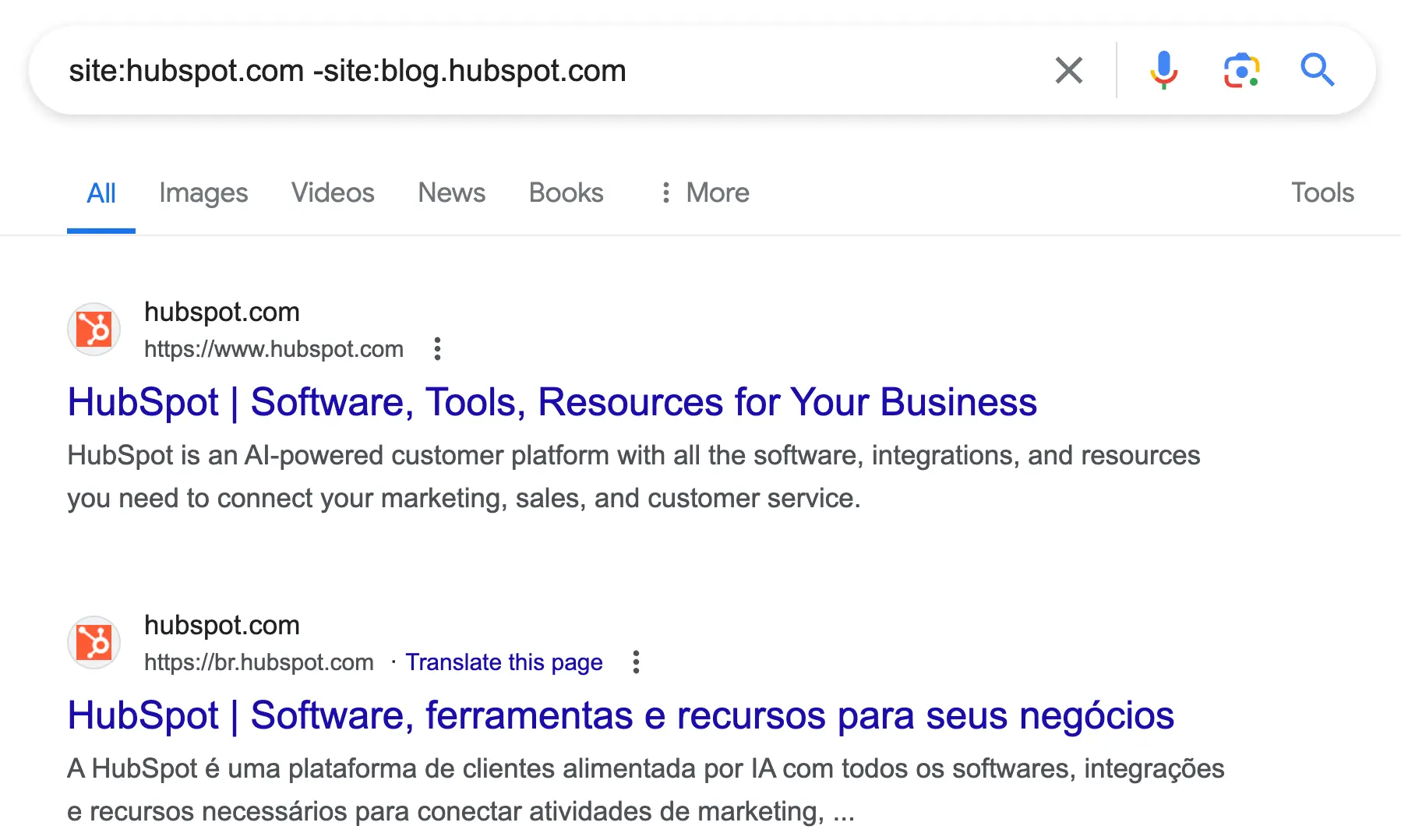
4. Exclude Subdomains
Use case: Search for content on a domain by excluding specific subdomains. This is very useful for big websites with content distributed over different subdomains. For example, to search for content on the HubSpot website by excluding content from their blog.
Here is the command to use:
site:hubspot.com -site:blog.hubspot.com
Google will display results from HubSpot, excluding those from the blog subdomain.
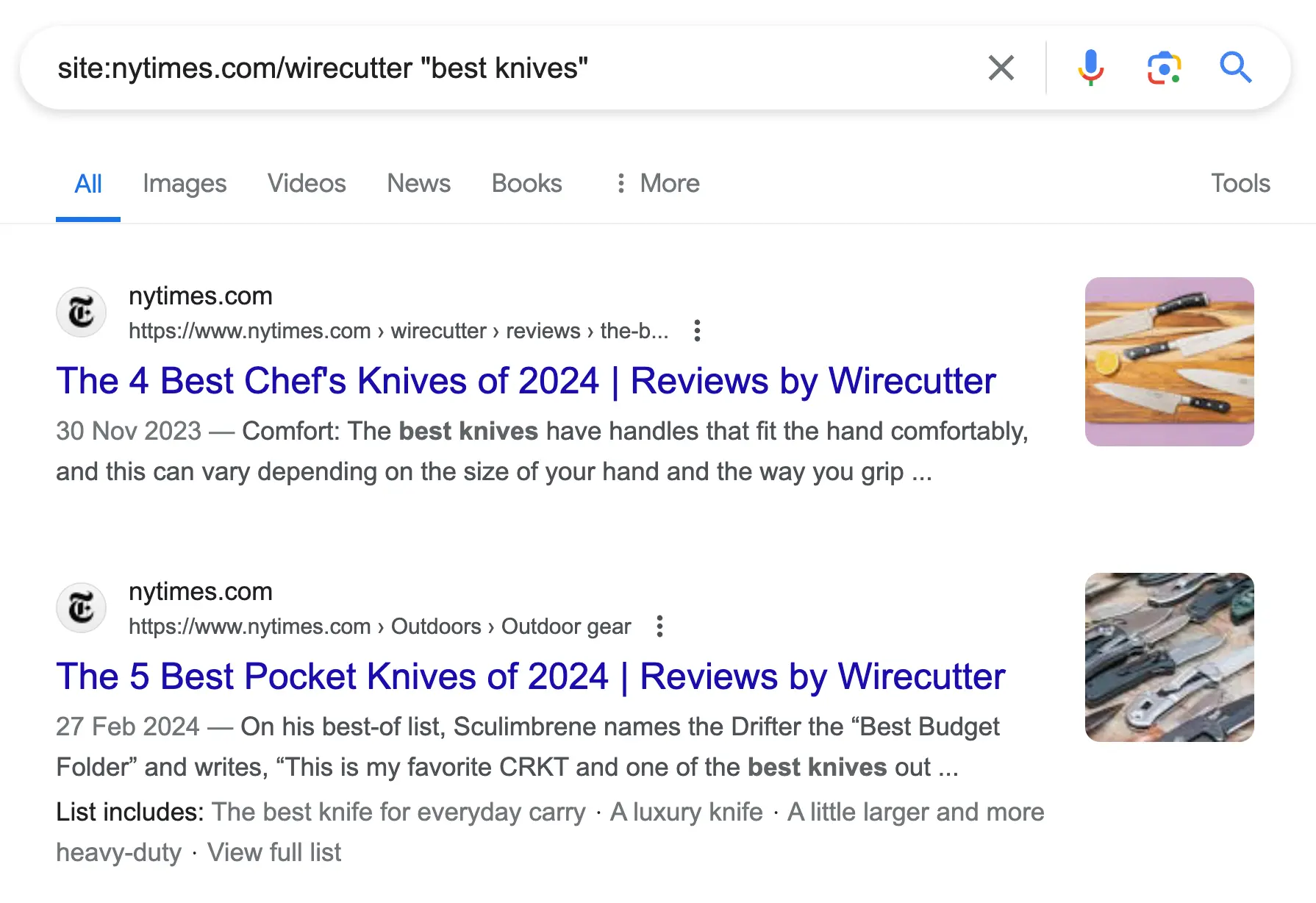
5. Search within a Specific Directory
Use case: To find articles within a specific directory on a domain. For example, see reviews in the WireCutter folder in the nytimes.com domain.
Here is the command to use:
site:nytimes.com/wirecutter "best knives"
Results will be limited to articles found in the WireCutter directory of the New York Times.
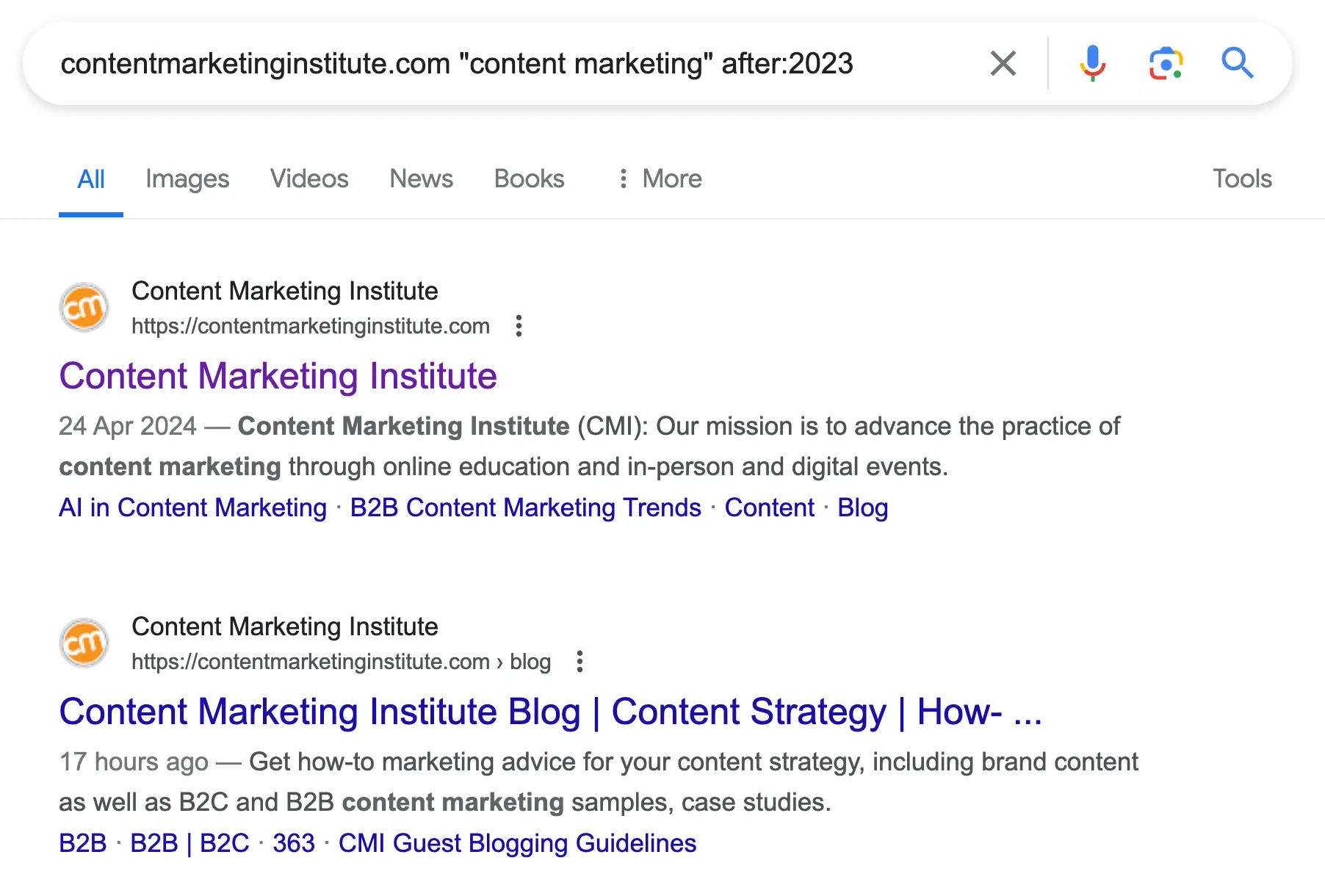
6. Find Content by Date
Use case: Search a website for content published after a specific date. This is particularly useful for finding the latest content published by a website. For example, to find articles on CMI related to content marketing published after 2023.
Here is the command to use:
contentmarketinginstitute.com "content marketing" after:2023
Google will display content related to content marketing from the Content Marketing Institute published after 2023.
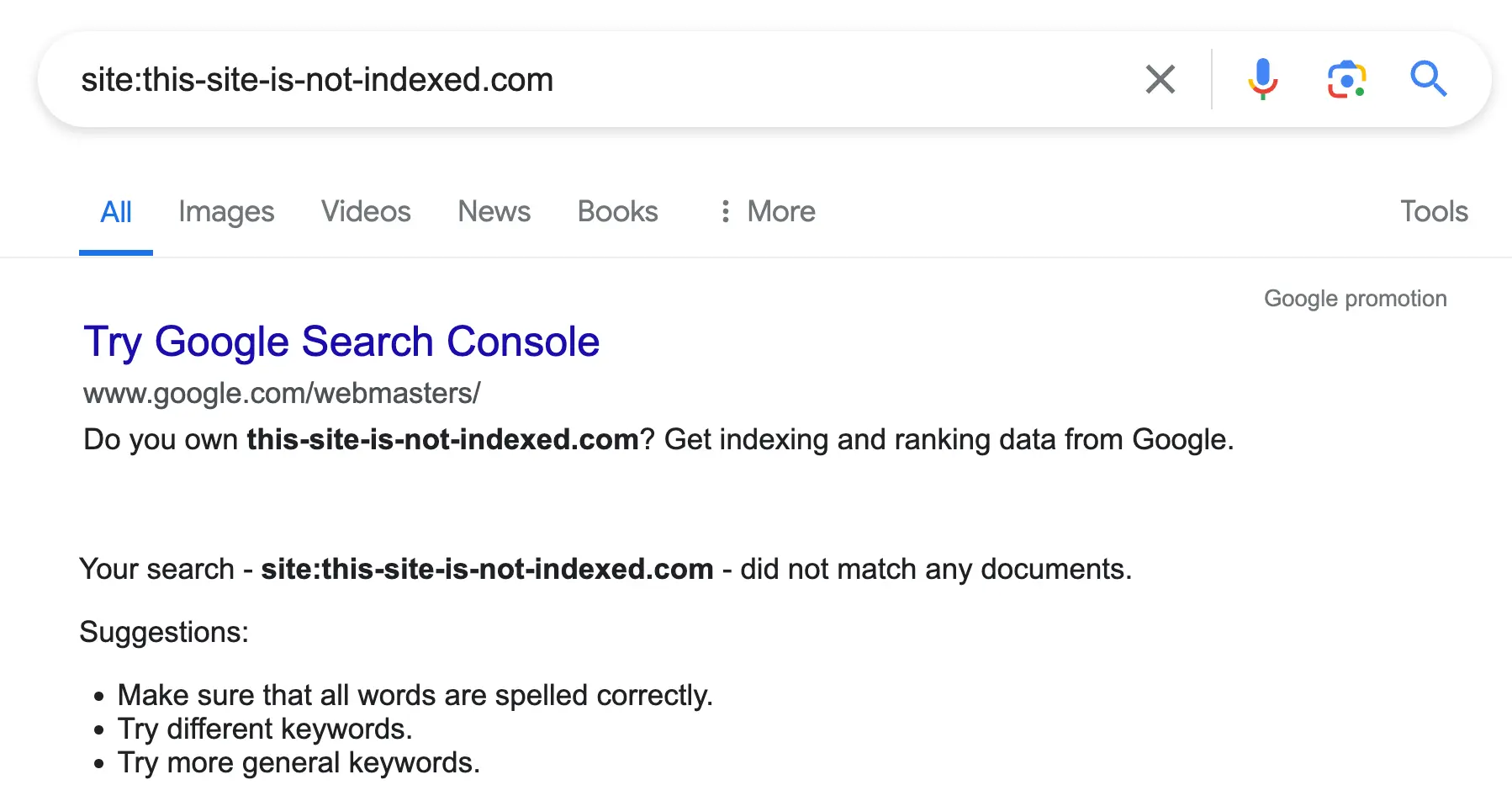
7. Check If a Domain Is Indexed
Use case: Use the site command to determine if Google indexes a domain's pages. This is useful when troubleshooting issues with Google Penalties. If Google de-indexes a website, the command will return no results.
Here is the command to use:
site:the-website-to-check.com
This command will list all pages of your website that Google has indexed.
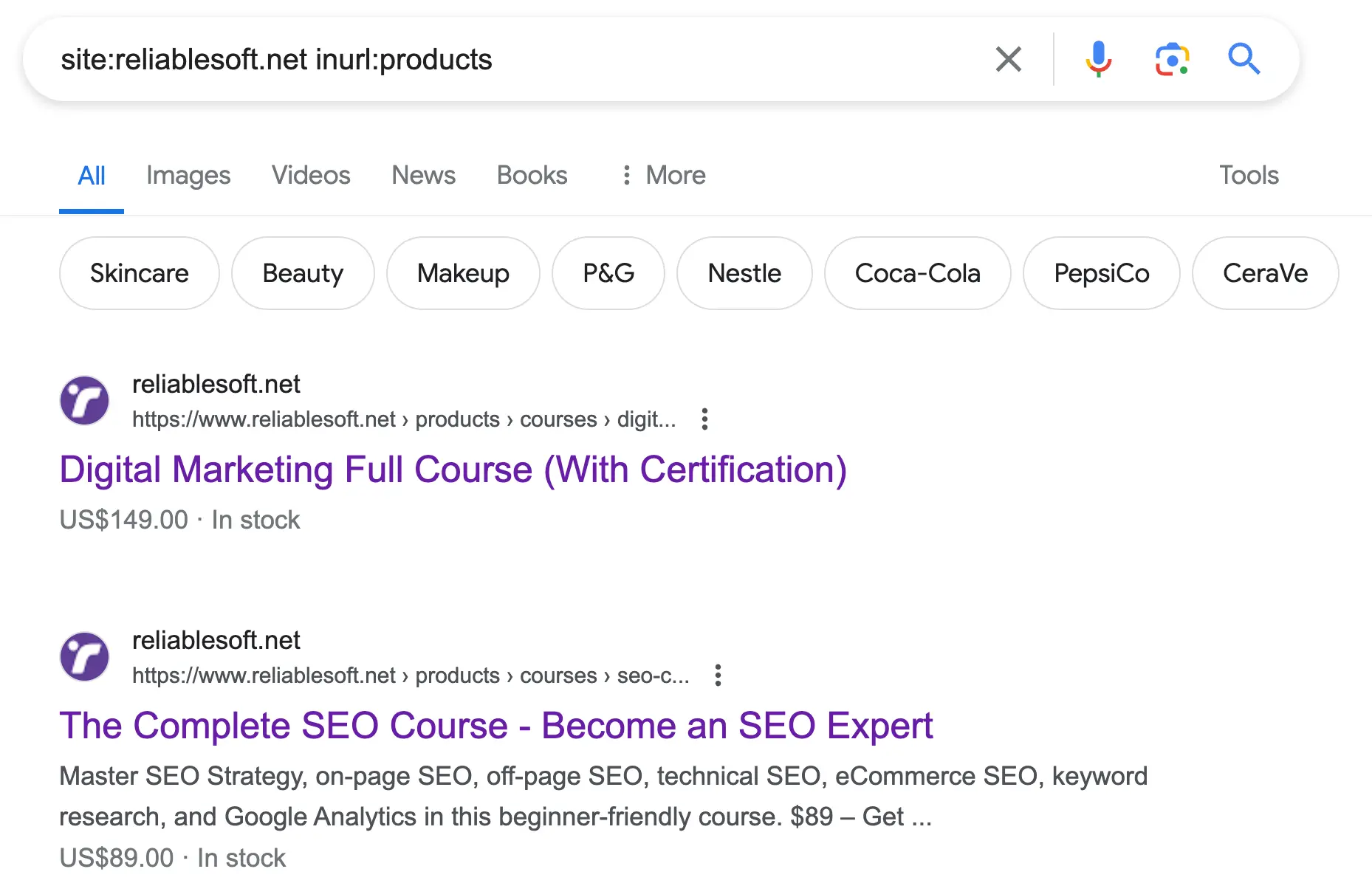
8. Find URLs Containing Specific Words
Use case: You can use the inurl operator with the site: operator to find specific words that appear in URLs. For example, you can search for URLs containing the word 'products' to get a list of all Reliablesoft Academy courses.
Here is the command to use:
site:reliablesoft.net inurl:products
Google will display all URLs that include 'products'.
9. Identify Spam Issues On Your Website
Use case: When troubleshooting spam issues, you can use the site command to search your website for spammy keywords like casino or Cialis and find the affected pages.
Here is the command to use:
site:example.com cialis casino
10. Combine with Other Operators
As you can see in the examples above, the site: command can be combined with other operators to perform more advanced searches.
For example, to find recent PDF guides on SEO from Semrush, you can use the following command:
site:semrush.com SEO filetype:pdf after:2023
Breakdown of the Operators Used
- site:semrush.com - Limits the search to pages from Semrush's website.
- SEO - Searches for the "SEO" keywords within the specified site.
- filetype:pdf - Filters results only to include PDF files.
- after:2023 - Further narrows the search to documents published after the year 2023.
Summary Table
Here is a list of all the examples for ease of reference:
| Command | Use Case |
|---|---|
| site:reliablesoft.net SEO | Find articles for a keyword. |
| site:ahrefs.com "link building strategies" | Find a specific phrase. |
| site:neilpatel.com filetype:pdf | Find specific file types. |
| site:hubspot.com -site:blog.hubspot.com | Exclude subdomains. |
| site:nytimes.com/wirecutter "best knives" | Search in a specific directory. |
| contentmarketinginstitute.com "content marketing" after:2023 | Find content by date. |
| site:the-website-to-check.com | Check if a domain is indexed. |
| site:reliablesoft.net inurl:products | Find specific keywords in URLs. |
| site:example.com cialis casino | Find spammy content. |
| site:semrush.com SEO filetype:pdf after:2023 | Combine multiple operators. |
Limitations of Google Site Search Operator
When using the site search operator, you should be aware of three important limitations:
1. Not all website pages are indexed by Google: Google doesn’t index every page on a website. Some pages might be omitted due to robots.txt restrictions, password-protected content, or other technical reasons. So, if you don't find the content you are looking for, it doesn't mean it does not exist.
2. Returns partial results: The site: operator doesn't show all possible results for a given query but only a sample. You cannot use this to find pages a website has in the Google Index.
3. Random results: The results are presented randomly and not in any order.
Despite these minor limitations, the Google site search operator is a great tool for finding specific content on the web, something every SEO professional should know how to use.



