What Is Keyword Research?
Keyword research is the SEO process of discovering which words or phrases users type into a search engine when looking for information, products, or services online. By knowing the exact search terms, you can provide them with relevant content that satisfies their intent.
Keyword research is important for SEO because:
- If you don’t know the search phrases people use in Google, you risk optimizing your website for the wrong keywords.
- Without analyzing the potential of a keyword, you don’t know if it’s a keyword you want to rank for.
- Keyword research will help you understand your industry and identify your true competitors.
- With keyword research, you get to know the size of your potential audience, a metric useful in setting marketing goals and creating growth plans.
You can follow a three-step process to perform keyword research:Step 1: Find Keywords
- this includes tools and techniques for finding keyword ideas.
Step 2: Analyze Keywords - determine the best keywords for your campaigns using various metrics.
Step 3: Target Keywords - ways to use your chosen keywords in your campaigns.
Step 1: Find Keywords
The first step is to find potential keywords for your campaigns. You can use several techniques combining manual methods and keyword research tools.
Get To Know Your Niche
Knowing who you have to compete with will help you create a realistic keyword list and an SEO strategy that can get you results.
Go to Google and start typing search terms related to your niche. Visit all websites that come up on the first page of Google and take note of things like:
- Their posting frequency (how often they update their website with new content).
- Type of content they publish (text, videos, etc.).
- How their website is structured (what they have on their homepage, menus, etc.).
- Find out their domain authority.
The main idea behind this exercise is to identify your main competitors and get new ideas about topics/keywords you can target.
What is important to understand before doing keyword research for SEO purposes is that there is a big difference between the keywords you would like to achieve high rankings and the keywords you can actually rank high on Google.
If your website is new, some keywords might be impossible to target (usually, these are highly competitive keywords), so it’s good to know this from the beginning to adjust your keyword strategy to go after keywords that you have more chances of reaching the first page of Google.
Create Topic Buckets
Once you finish the above, it’s time to get more specific by writing down topic ideas. Do your brainstorming and write down anything that comes to mind related to your niche, industry, and products.
Put yourself in the position of the Google searcher and try to think what search terms they might type in Google.
If needed, revisit the websites noted above and closely examine their page titles. This can give you more ideas about topics related to your niche that you might not have considered.
Group your ideas to form topic buckets. Each topic bucket should include related ideas.
Let me give you an example of how this works.
Let’s say you are in the digital marketing niche and want to find keywords to help you get clients for your digital marketing agency.
Your target market is small businesses and startups looking for different services related to digital marketing. Your topic buckets might include the following:
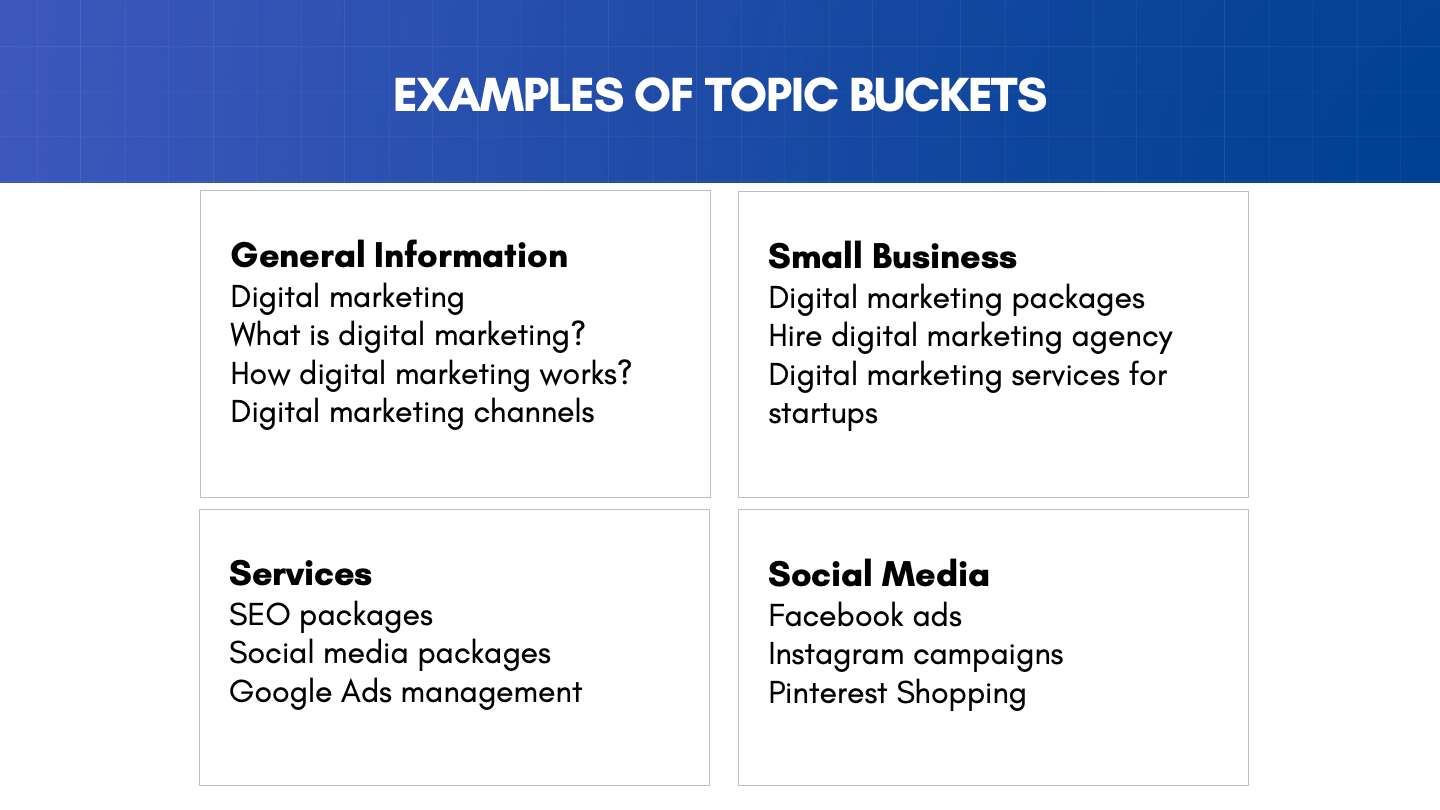
- General Information Bucket. This bucket includes ideas related to general questions about digital marketing.
- Small Business Bucket. This bucket includes search terms that a small business owner might use in Google when looking for digital marketing agencies.
- Services bucket. This bucket includes search terms for specific marketing services like SEO and social media marketing.
If this is your first time doing keyword research for your website, you may have many topic buckets. This is perfectly fine.
Remember that this is an ongoing process and not something you must complete 100% on the first go. To begin with, write your basic ideas and move on to the next step.
Find Seed Keywords
Now that you have a list of ideas grouped into topic buckets, the next step is to find seed keywords.
Seed keywords are broad keywords that relate to your main topic and can be used as a starting point for your keyword research.
For instance, in the 'General Information Bucket,' your seed keyword might be 'digital marketing.' In the 'Small Business Bucket,' it could be 'small business digital marketing.'
To do that, we need the help of keyword research tools. I will demonstrate the process using Semrush, but you can use your favorite tool to go through the process.
If you don’t have a Semrush subscription, you can take advantage of our exclusive offer and get a 14-day free subscription to SEMrush Pro.
Login to SEMRUSH and go to the Keyword Manager.
Enter your ideas (from your topic buckets) and start your analysis.
Semrush will group the keywords by seed keyword.

Find Long Tail Keywords
As you work through the list of your seed keywords, you will realize that most (if not all) are highly competitive.
In other words, when you search for these keywords on Google, you find hundreds of websites competing for one of the top 10 positions.
If you have an established website, this may not be a big issue, but starting now is a huge problem.
What should you do? Adjust your keyword research strategy and start looking for less competitive keywords, i.e., long-tail keywords.
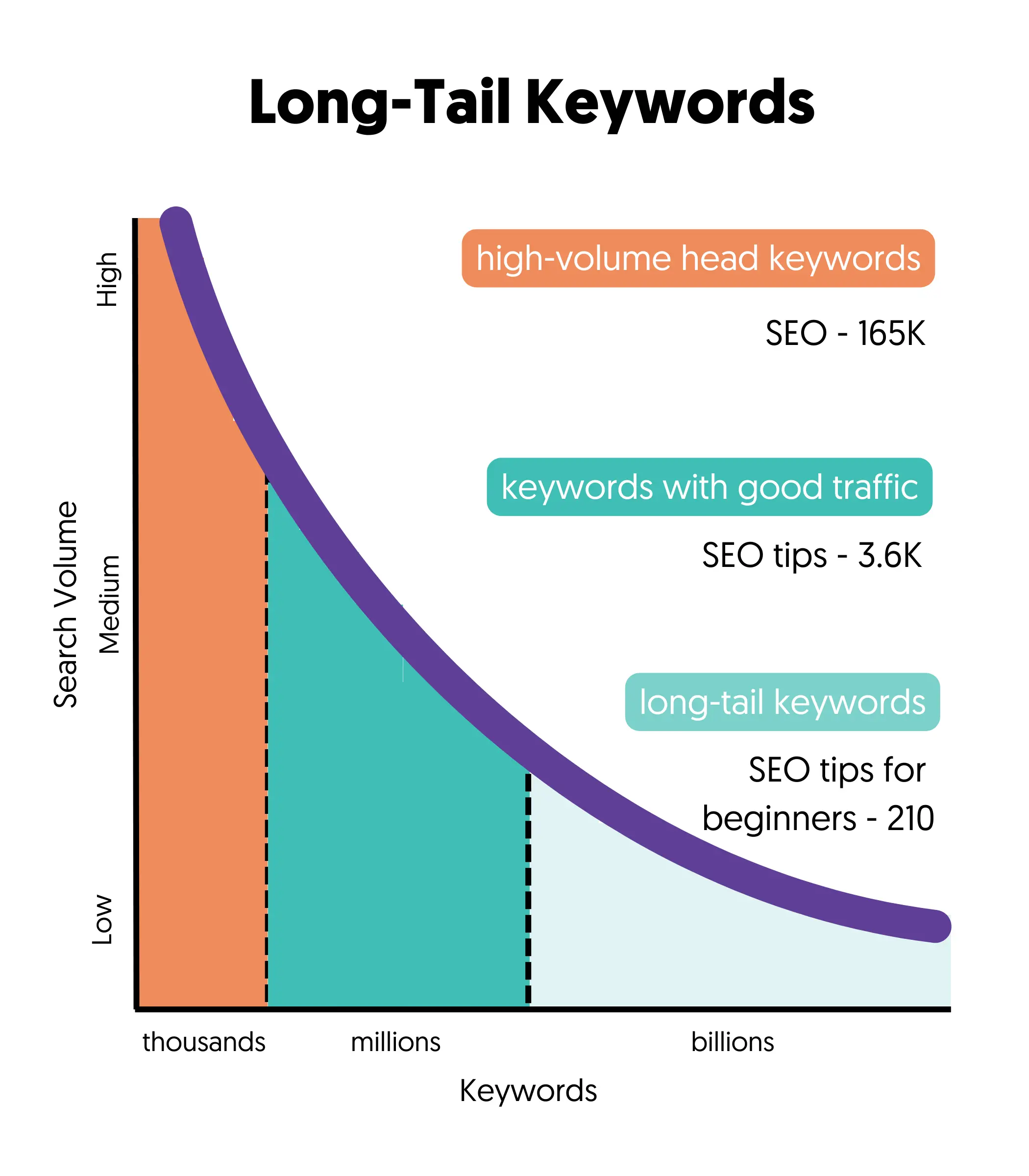
Long-tail keywords make up 70% of all searches, and it’s your only opportunity to start ranking high on Google for keywords that can bring targeted traffic to your website in a relatively short time.
You might think that the issue with long-tail keywords is that they have less search volume, and while this is true, less is better than nothing.
In other words, there is no point in spending your time and effort on popular keywords that it’s impossible to rank. Better start with the low-hanging fruit and build your way up.
Once you achieve high rankings for several longtail keywords, you also increase your chances of ranking for seed keywords.
How do you find long-tail keywords? There are several ways to find long-tail keywords.
You can manually search Google and look for the ‘People also ask’ or ‘related searches’ section. You can also go to Wikipedia and Amazon and see what people are searching for.
The fastest way is to use two Semrush functions, the ‘Keyword Magic Tool’ and the ‘Topic Research’ tools.
Revisit the Keyword Magic tool and use the ‘Advanced Filters’ to search for keywords that have 4 words or more. Just enter the number 4 into the ‘Words Count’ box and click Enter.
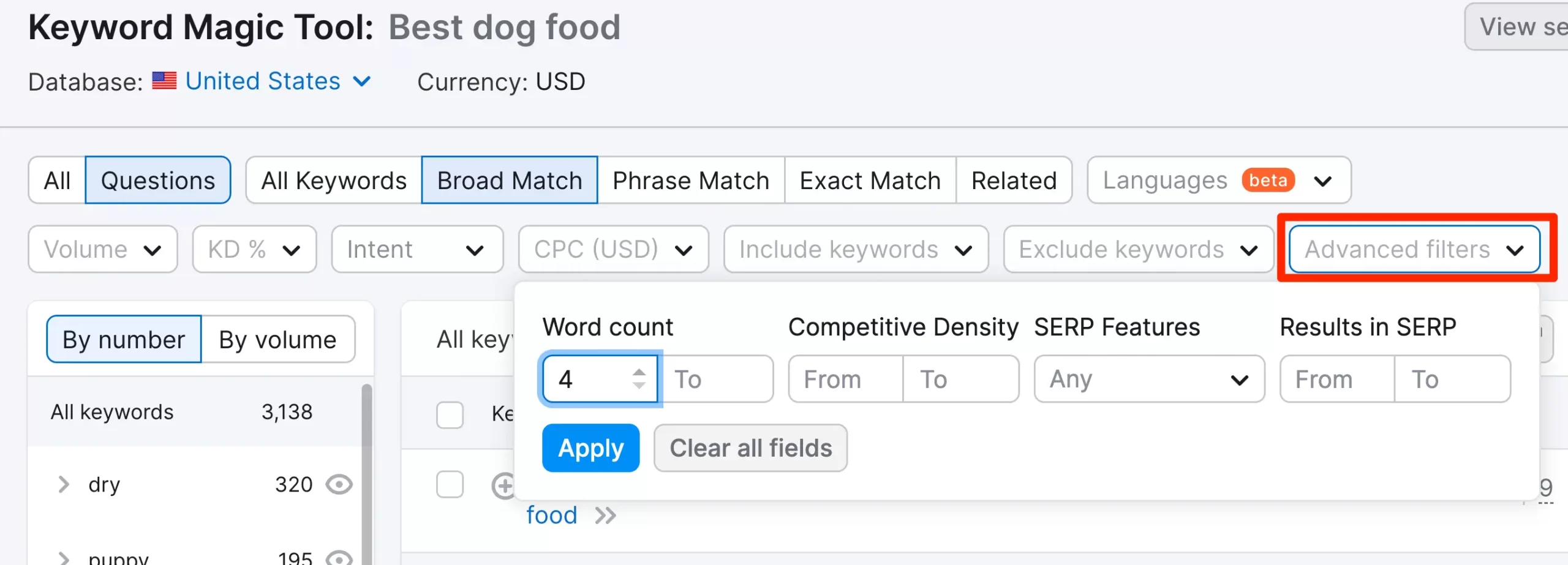
Now, you see more than 4 words. Select the keywords that match your business, examine their search intent by analyzing the Google results, and add them to your main list.
Another way to find longtail keywords is to use the ‘Topic Research’ tool. Select the topic research option from the menu, type your ideas, and click GET CONTENT IDEAS.
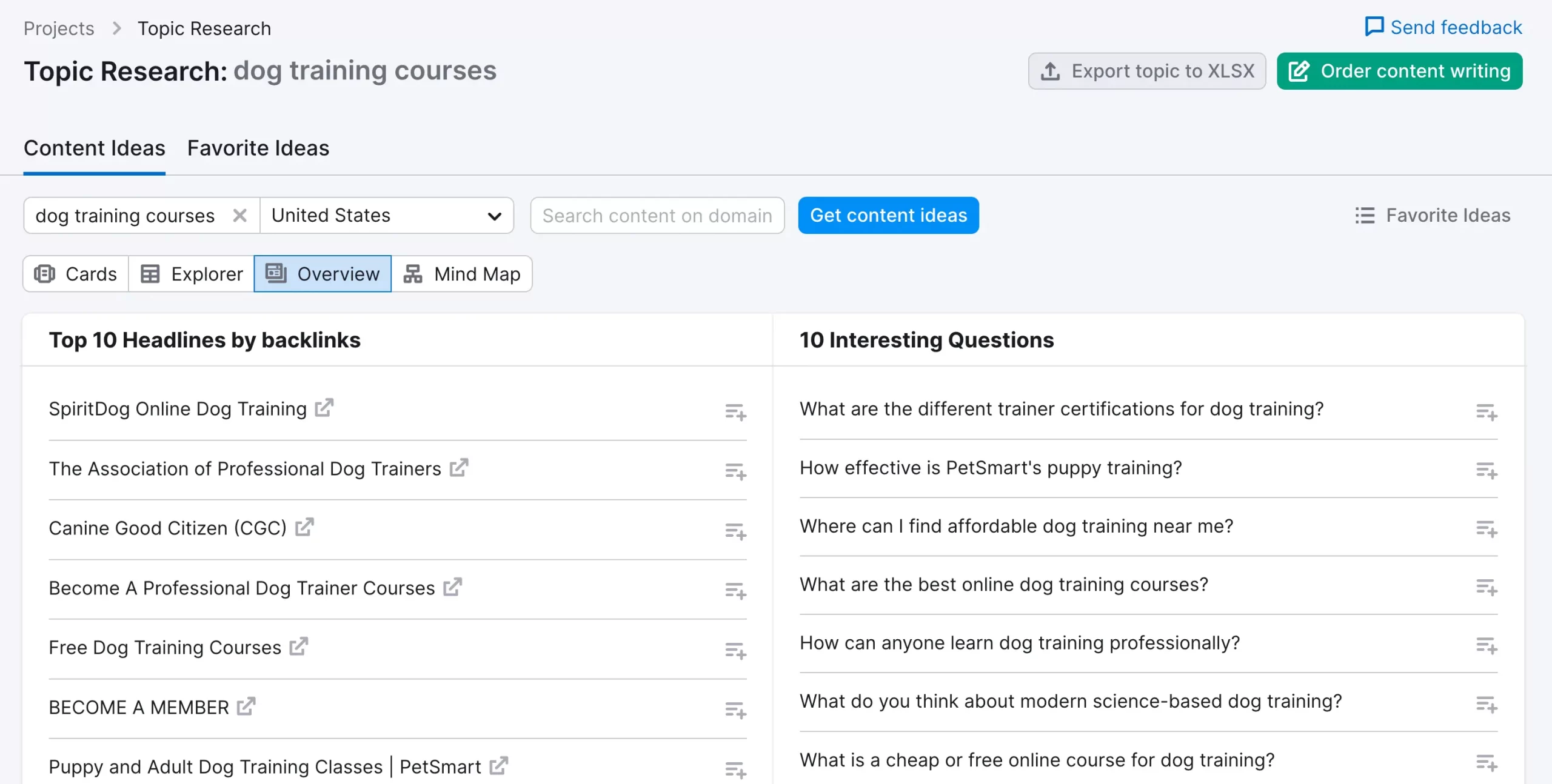
Look for the ‘Interesting Questions’ section and find questions about your business and products.
Find Your Competitor's Keywords
While doing your keyword research, you created a list of websites that are your direct competitors. You visited their websites and analyzed their content; now it’s time to learn for which keywords they are ranking and the amount of traffic they receive from Google searches.
Go to SEMRUSH, select ORGANIC RESEARCH from DOMAIN ANALYTICS, and type in a competitor’s URL.
What you see are the keywords your competitors are ranking. Click on VIEW ALL ORGANIC KEYWORDS to go to the full list and use the advanced filters to find keywords with a decent search volume, excluding brand-related keywords and keywords that do not fall into your line of business.
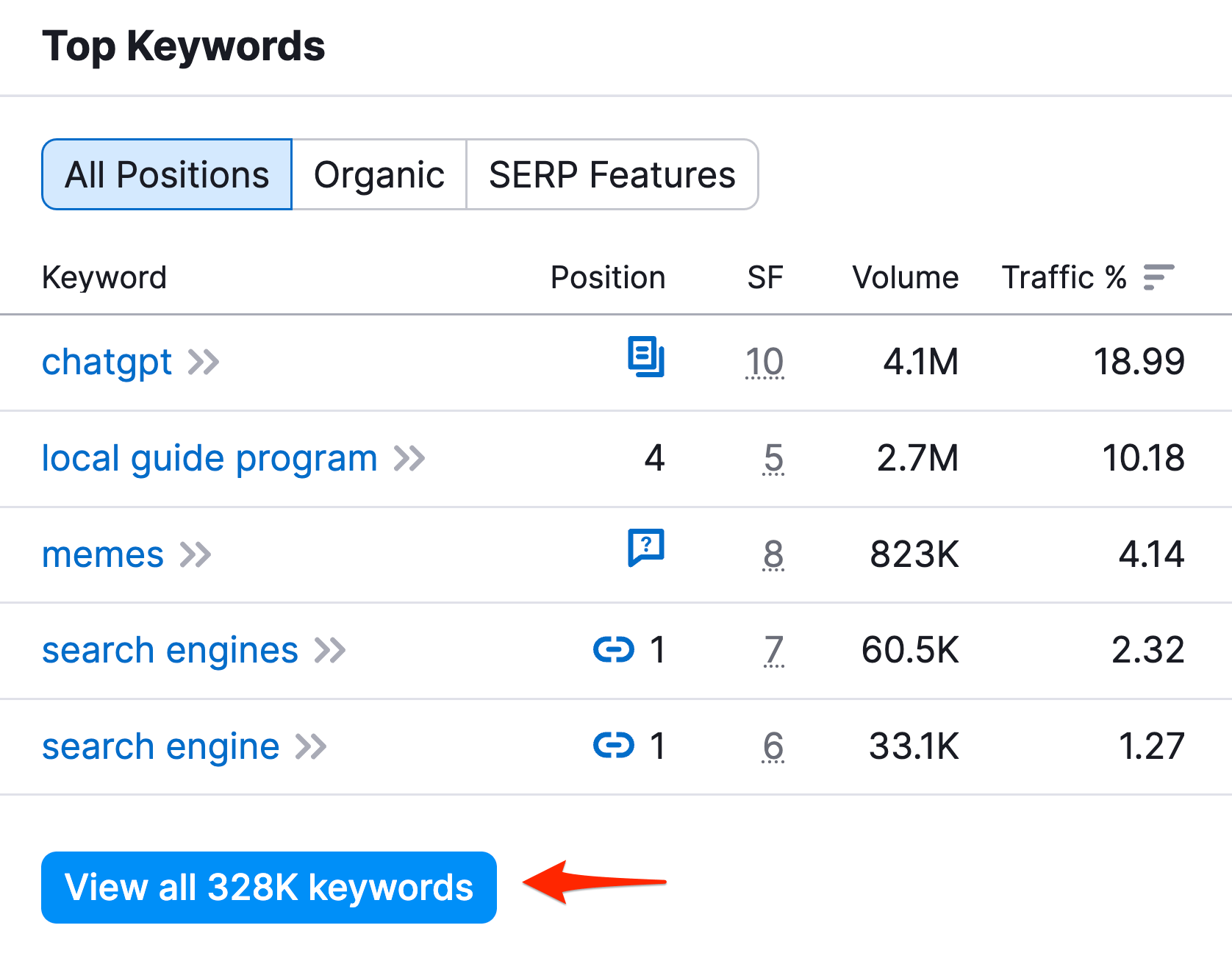
This exercise aims to find keyword ideas you might not have thought of before and use them to enrich your keyword list.
You can also follow the procedure above to determine which keywords a competitor’s page ranks.
In other words, instead of using the domain in the search box, type in the URL of a specific page.
What you see now are all the keywords that the particular page ranks, the monthly search volume, and whether they generate traffic to the website.
Find Trending Keywords
Besides the above steps, you must monitor your niche for trending and new keywords that rise to the surface.
It’s a fact that 30% of the queries entered into Google monthly are NEW and keywords that Google has never seen before.
This means that the keyword tools won’t show a big search volume for these keywords or not show them at all.
Most probably, they’re keywords your competitors are unaware of, so this gives you a competitive advantage since you can rank for them faster.
I personally use this method a lot, and it works great for almost all niches and industries.
Google Trends is the tool to use for this exercise. Go to Google Trends and enter your seed keywords.

Filter the results by area (if you are targeting specific areas), categories, and Google search channels.
Look for the RELATED QUERIES section and drill down to get more details for a specific query.
A piece of advice: don’t give up too soon on this tool; try different filters and different keywords/topics, and you can find some great keywords to target before everyone else does.
Add in your calendar a reminder to repeat this exercise at least once every 3 months.
Step 2: Analyze Keywords
After finding keywords, the next step is to analyze them to choose the ones that are the best fit for your business.
Examine Search Intent
The search intent is simply the type of information users are looking for when they perform a search. For some keywords, the search intent is obvious, but for others, it needs more investigation.
For example, their intent is clear when searching for ‘SEO packages for small businesses, but searching for ‘SEO’ is vague.
The best way to determine a keyword's search intent is to type the keywords in Google and examine the first page of the results.
Google is doing a great job of understanding the user’s intent, so what they show on the first page is very close to what users seek.
You need to do this exercise to find and eliminate from your list keywords that have a different intent than what you are offering. You don’t want to waste your time targeting keywords that won’t get you the right type of traffic.
For example, I initially added the keyword ‘Freelance Digital Marketing’ to my list. When you search for this keyword on Google, you will see that most of the results are resources for becoming a freelancer.
Since I aim to find keywords to get clients, this keyword is not a good fit. The searcher's intent is not to hire a freelancer but to learn how to become one.
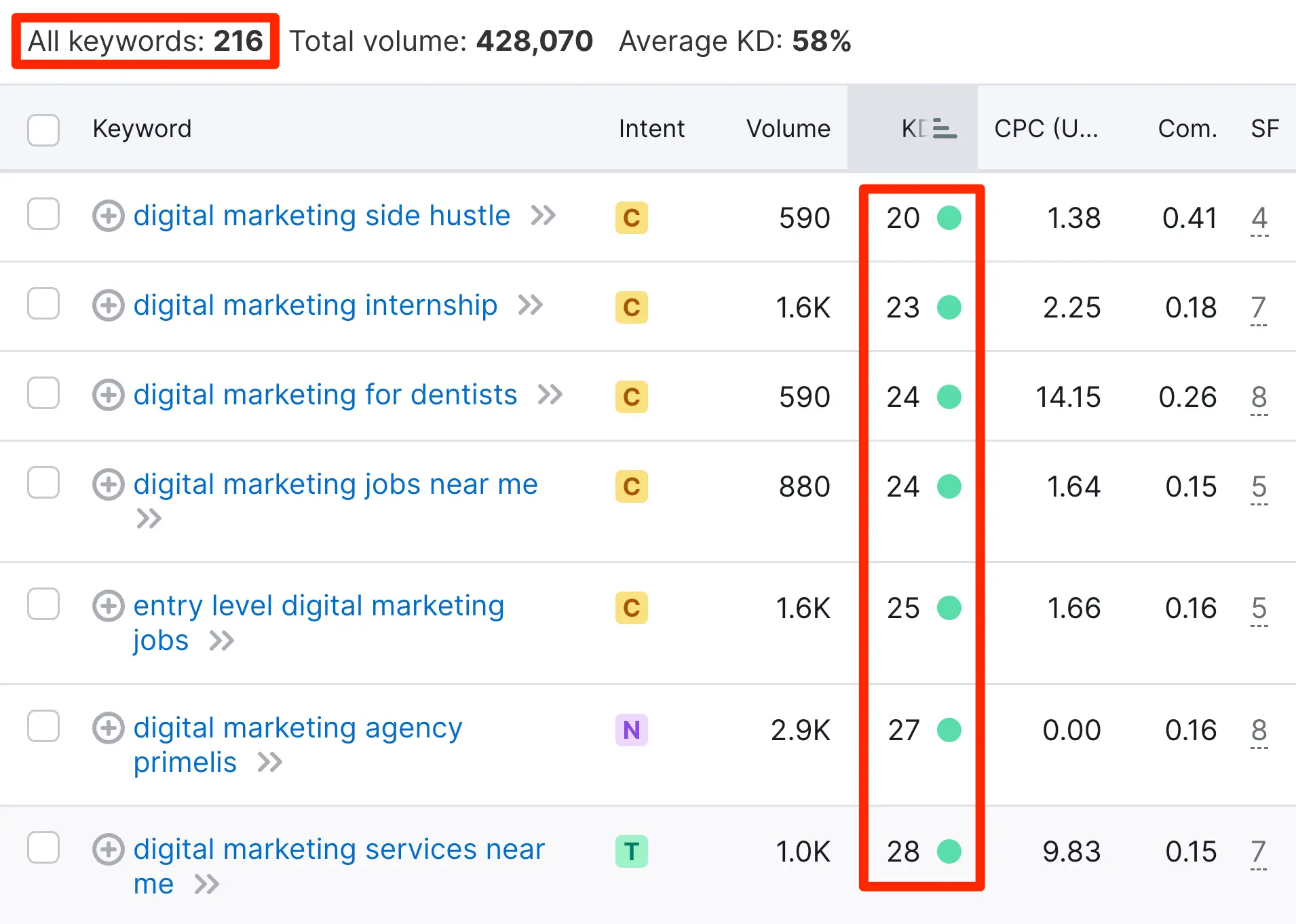
Keyword Difficulty
Keyword difficulty (KD) estimates how difficult it would be to rank well in Google organic search for that keyword. It is given as a percentage; the higher the percentage, the more difficult it is to rank high for the specific keyword.
Each tool has its way of calculating keyword difficulty, but in general, the lower the value, the better.
In all Semrush reports, you can see the keyword difficulty of a keyword. The column is marked as KD%.
When analyzing your keywords, you should look for keywords with a low keyword difficulty but a decent monthly search volume.
Domain Authority
I’ve mentioned this several times, but it’s time to make it more specific. When you search for a keyword on Google and notice that big and well-known websites occupy the first 10 positions, it is very difficult for a small business website or blog to get there.
For example, when searching for ‘Digital Marketing,’ you’ll see websites like HubSpot, Moz, Wikipedia, and other giant websites.
This means that although ‘digital marketing’ is a term I would like to rank for, Google tells me that this is not possible, so I take that term out of my list and instead look for variations (long-tail search terms) that are possible to target.
Step 3: Target Keywords
Once you reach this point, you should already have a list of keywords (both seed and long-tail keywords) you would like to rank for.
Go through the keywords one by one and decide whether to keep or remove them from your list by answering the following questions:
- Is the keyword search intent in sync with your marketing goals?
- Is the keyword difficulty low compared to other keywords?
- Does Google rank normal websites in the first 10 positions or only big and well-known websites?
- Is there a decent search volume (above 50) for that keyword?
- Can you provide good content for that keyword?
If the answer to all the questions is YES, then keep that keyword in your list; otherwise, if the answer to any of the above is NO, remove it.
Once you have your final list of keywords, you should use them in your campaigns. This is explained in detail in the SEO writing guide. The most important guidelines are:
- Use your focus keyword in the page title
- Use your focus keyword in the page URL
- Use your focus keyword in the page title tag and H1 tag
- Use Long-tail keywords in your H2 and H3 headings
- Use related keywords in the image ALT Text
- Use related keywords and synonyms in your copy
Keyword Research Tools
To perform keyword research, you need the help of tools. There is a lot of data to analyze, and it’s impossible to do manually.
These are the tools that I use and recommend.
Semrush (Paid)
This is my favorite tool for keyword research, and I use it daily for all digital marketing tasks. It’s not free, it comes with a monthly subscription but worth’s every cent.
For keyword research, you can use Semrush to do topic research and find seed keywords, long-tail keywords, and related keywords.
If you don’t already have a SEM tool subscription, Semrush is the way to go.
Before selecting SEMRUSH, I tested several other tools, but none has the functionality of Semrush at this price range.
You can register for a 14-day free trial and test it yourself.
Google Keyword Tool (Free)
The Google keyword tool is a free tool provided by Google that allows you to do keyword research for PPC (Google Ads) purposes, but you can also use it to do keyword research for SEO.
The tool is free, but you need an active Google Ads account to use it.
Go to Google Ads and register for a free account. Then, create a Google Ads campaign, but do not activate it. Keep it paused, and access the tool by selecting TOOLS and then KEYWORD PLANNER.
UberSuggest (Free)
Another free keyword research tool that is worth exploring is Ubersuggest. You can use it to do both topic and keyword research.
While the tool is free, the only disadvantage is that it does not allow you to create an account to save your reports or keywords, and this means that every time you want to do keyword research, you need to start from the beginning.
This is not the case with SEMRUSH, where you have an account and all your lists/data are saved and always accessible.
Google Search Console (Free)
While the primary function of the Google search console is to optimize your website for technical SEO, it’s the tool to optimize your pages after publication.
Keyword research is an ongoing process, and the best tool to use to find out the actual keywords your pages are ranking is the Google Search console.
Why this is an important step? When you optimize a page for a keyword, it does not always go as planned. Google may rank the page for different keywords, and the way to 'correct this' is to find out which keywords the page has more chances of ranking for and add those keywords to your content.
Here are the steps to follow:
- Create an account and verify your website.
- Access the ‘Search Performance Report’
- Look at the 'search terms' and ‘positions’ columns
- Identify keywords that are not included in your content.
- Change your content to add those keywords naturally
- Re-submit your page to Google.
Google Trends (Free)
As explained above, another tool you can use to find out about new and trending keywords is Google Trends.
Go to Google Trends and perform several searches using different filters to discover what is trending in your industry.



