- On-Page SEO Checklist PDF
- 1. Find Keywords To Target In Your Content
- 2. Create Short And Meaningful URLs
- 3. Optimize Your Page Titles With Keywords
- 4. Create Engaging Meta Descriptions
- 5. Wrap Your Title in an H1 Tag
- 6. Use Compelling Subheadings Properly Tag
- 7. Give Users What They Want As High In The Content As Possible
- 8. Add Internal And External Links To Related Content
- 9. Cover The Topic Fully
- 10. Align Content With Search Intent
- 11. Demonstrate Your Experience And Expertise
- 12. Add Relevant Schema Markup
- 13. Provide Unique Information
- 14. Add Relevant Images And Engaging Visual Content
- 15. Add Keywords To Your Body Content
- 16. Optimize For Featured Snippets And Other Search Features
- 17. Ensure Content Is Easy To Consume On All Devices
- 18. Check Page Indexing With URL Inspection Tool
- 19. Review Critical Technical SEO Elements
- Learn More About On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing your content to rank higher in organic search engine results. It's called on-page or on-site SEO because it involves optimizing elements on the page. Unlike off-page SEO, it's a process you can fully control.
Use our comprehensive checklist to optimize your content fully and keep search engines and users happy.
On-Page SEO Checklist PDF

Click here to download the On-Page SEO Checklist as a PDF and use it as a reference while performing your on-page SEO audits.
1. Find Keywords To Target In Your Content
On-page SEO starts with keyword research. You must first identify your target keywords to know which search terms to optimize your content.
The process is described in detail in our keyword research guide, but here is a quick summary for easy reference:
Find keywords - by analyzing your niche using a tool, you can create a list of keywords to target in your content. This will include seed keywords, long-tail keywords, trending keywords, and keywords your competitors are using in their campaigns
Analyze keywords - for each keyword in your list, examine the search intent, keyword difficulty, and search volume to determine if it's a good candidate for your website.
Target keywords - use the techniques described in this guide to create targeted pages for each of your chosen keywords.
2. Create Short And Meaningful URLs
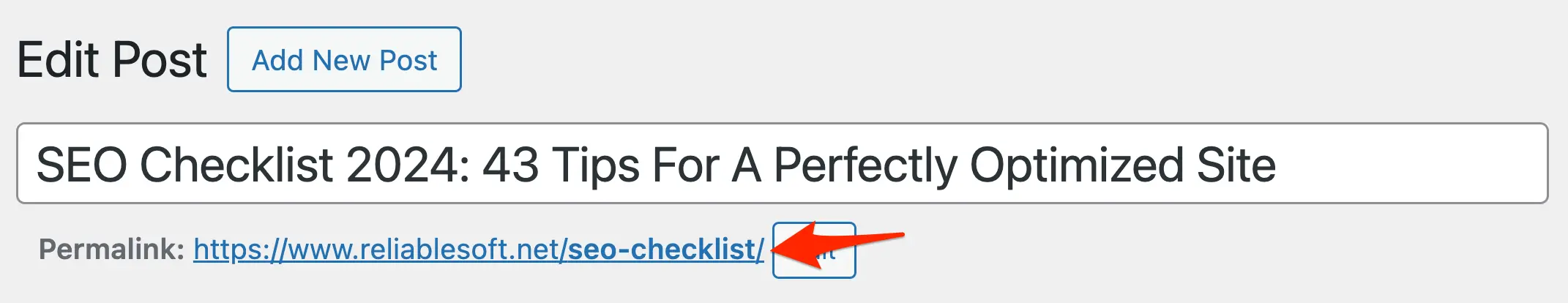
Each page on your website should target a specific keyword. Use that keyword in your URL and keep it short, meaningful, and memorable.
For example, my on-page SEO guide has the title "15 On-Page SEO Techniques (Basic and Advanced)," but the URL includes only my target keyword, "https://www.reliablesoft.net/on-page-seo/".
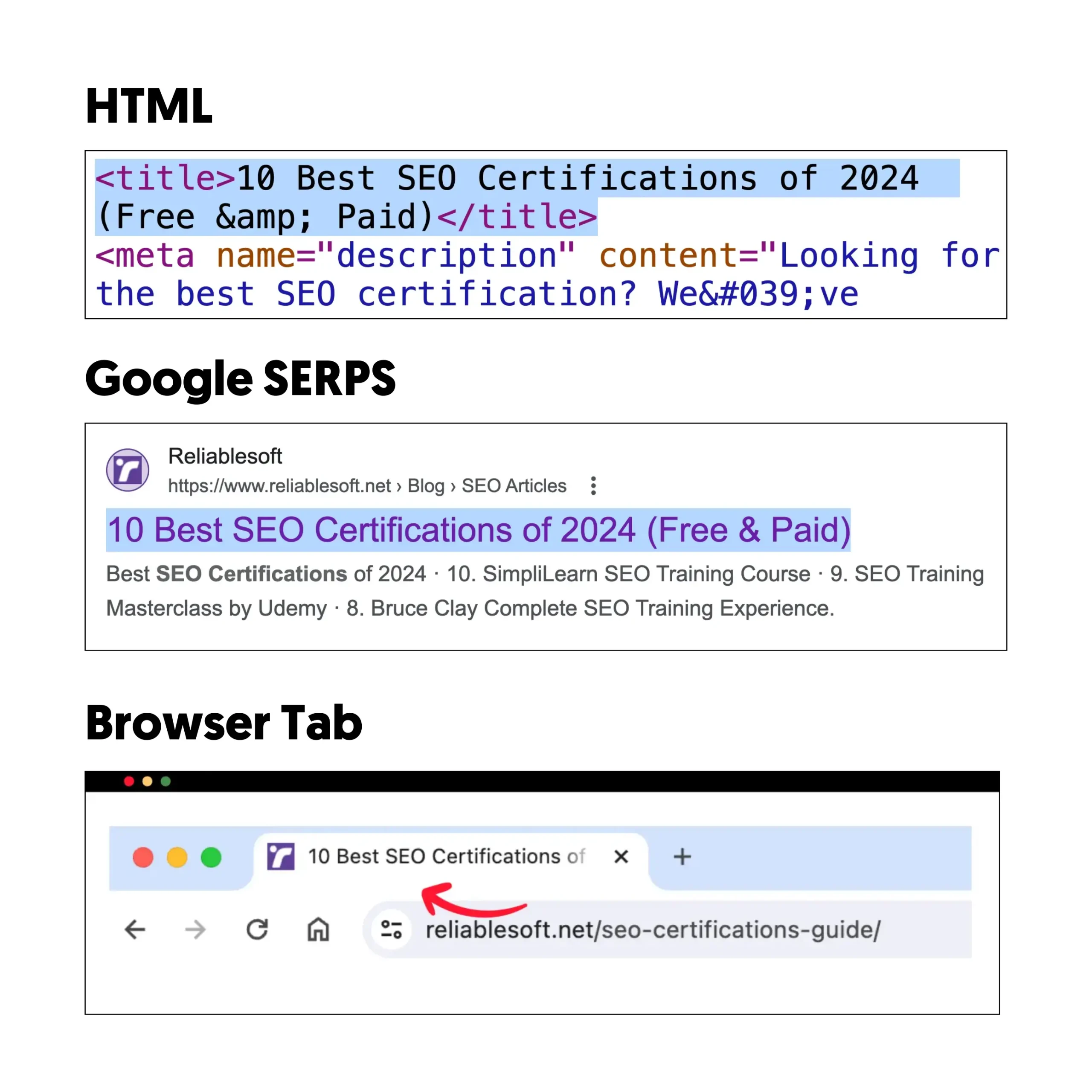
Here is another example. The post "10 Best SEO Certifications of 2024 (Free & Paid)" has the URL https://www.reliablesoft.net/seo-certifications-guide/, which includes the target keyword.
Creating SEO-friendly URLS is a straightforward SEO task. Follow these simple rules:
- Use your primary Keyword
- Use hyphens as word separators
- Use lowercase letters
- Don’t use spaces
- Don’t use dates
3. Optimize Your Page Titles With Keywords
Like the URL, your page titles should include your target keyword. The only difference is that you must make your titles compelling and interesting for users to click.
Whatever you write in the page title tag is shown in Google Serps, browser tab, and social media networks.
Here is your checklist for optimizing your page titles:
Write unique titles for each webpage - SEO 101, but still important. Each page on your site should have its own unique title.
Ensure titles are relevant to the page content - If not, users will return to the search results as soon as they enter your page, increasing your bounce rate and negatively impacting your rankings.
Keep the title length around 50 to 60 characters - this guideline is not strict, but keeping your titles within this range ensures they are seen on desktop and laptop without being cut.
Include your primary keywords - If possible, try to add your keyword at the beginning of the title to increase its relevancy to user queries.
Interesting for users to click - adding numbers (like 15 SEO Tips For Better Rankings), dates (like SEO Checklist 2024), and words like "Best" and "Worst" and increase the organic CTR of your titles.
4. Create Engaging Meta Descriptions
Another important item in your on-page SEO list is creating engaging meta descriptions.
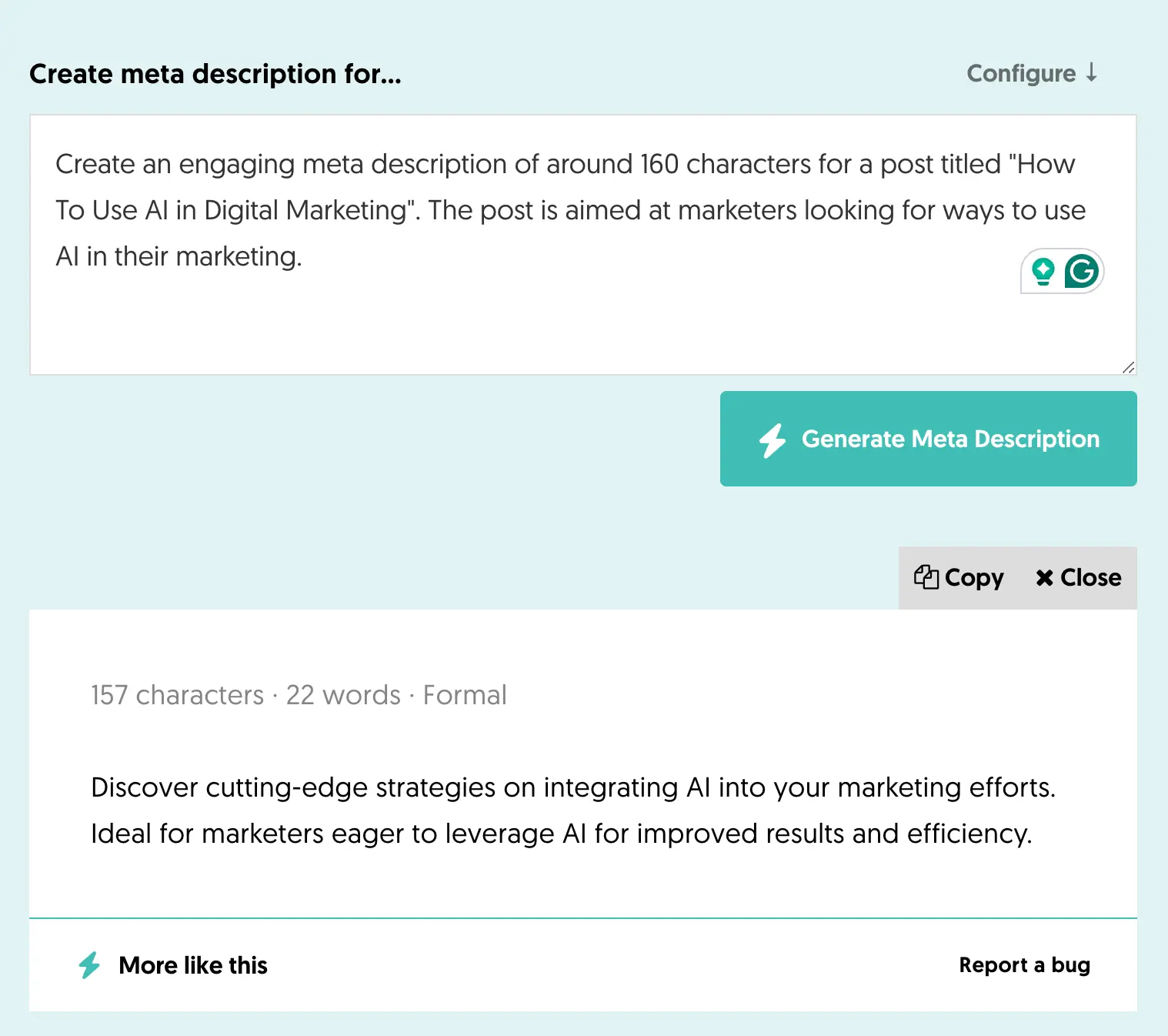
As Google states, a meta description is like a pitch that convinces the user that the page is exactly what they are looking for.
Here is an example from one of my blog posts.
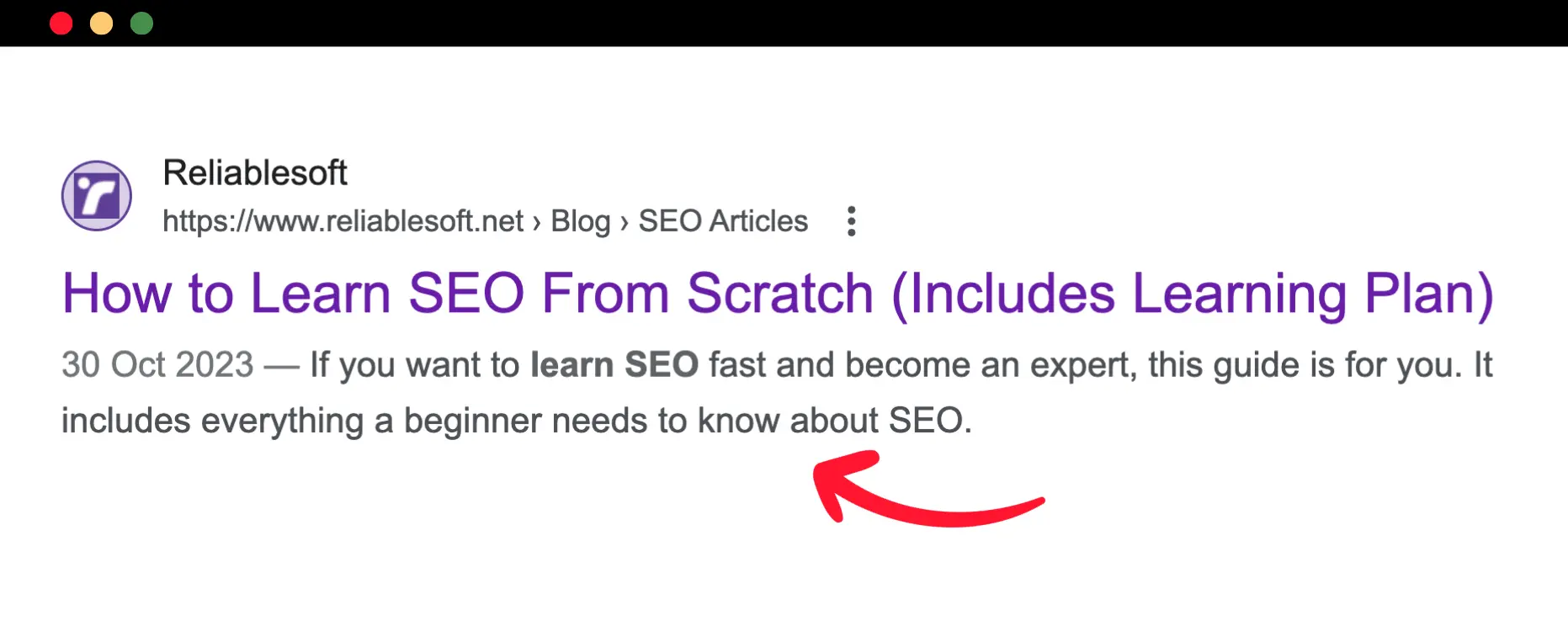
When creating meta descriptions for your pages, have these in mind:
You should provide a custom meta description for all your pages, but it's not guaranteed that Google will show them in the SERPs. In many cases, Google will create a meta description from text found on the page.
Adding your keywords to the meta description will make it more relevant to user queries, and they will be displayed in bold in the search results.
There is no limit on how long your meta descriptions can be, but keeping them around 160 characters ensures they are shown on desktop and mobile without truncation.
Your meta descriptions don't need to be in a sentence format, but depending on the case, they can provide information about the content. For example, for ecommerce pages, you can include the product details like these:
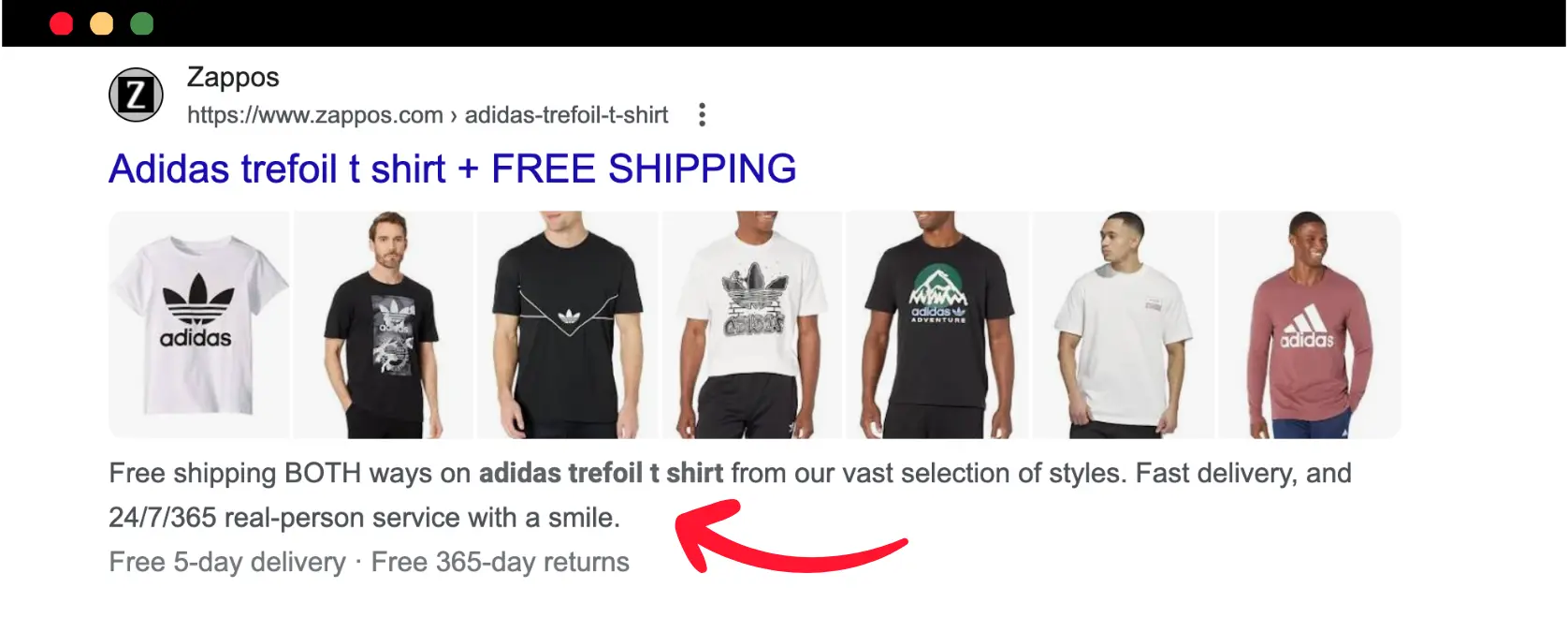
You can safely use AI text generator tools to get ideas for writing engaging meta-descriptions. One example is our free AI meta description generator.
5. Wrap Your Title In an H1 Tag
In most CMS, whatever you write as the title of a page or post is shown in the <title> tag in the HTML and also wrapped into an H1 tag.
To check if this is the case with your website, navigate to one of your pages (using Chrome), highlight the value of the page title, right-click, and select INSPECT.
If the title is enclosed in <h1>....</h1> tags, as shown below, you are good to go. If not, you can ask a developer to make the necessary changes in your website's code to wrap the title in H1.
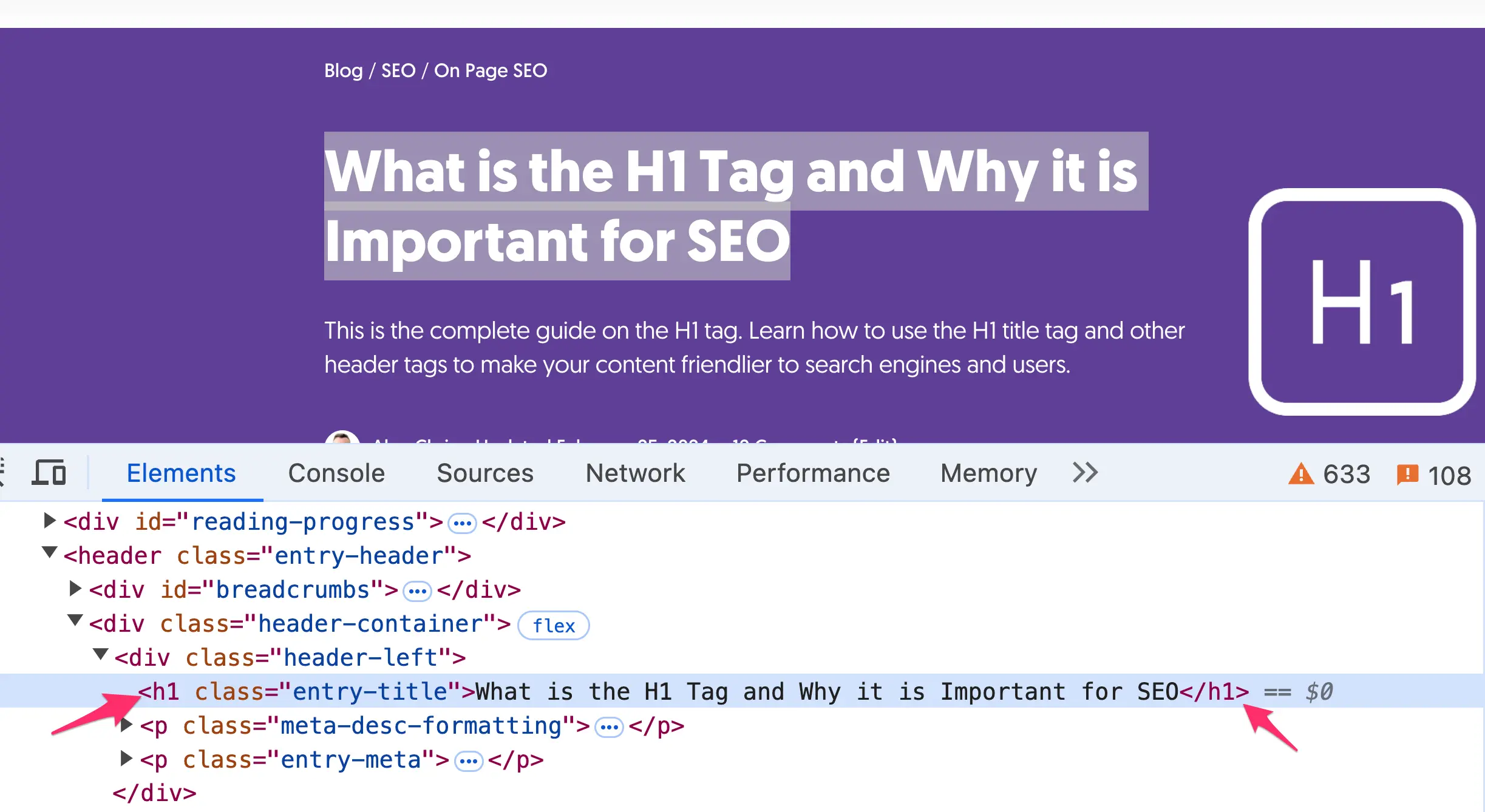
For best SEO practices, having only one H1 tag per page is recommended, but it's not the end of the world if you have more. If it's an easy change, then remove the other instances; if not, don't worry, Google can still understand your content.
6. Use Compelling Subheadings Properly Tag
Besides the main heading (H1), the rest of your page headings should be descriptive and wrapped in <h2> and <h3> tags.
This hierarchical structure makes reading your content easier for users and search engine crawlers.
Here is how it looks visually:

Make your subheadings skimmable by giving users enough information on what to expect in the particular content section.
For example, instead of "Use images," use this heading: "Add high-quality images in your content with relevant alt text."
You can also blend your keywords with meaningful text to create subheadings. For example, if your keyword is 'Technical SEO', a subheading could have the value "Use Technical SEO To Fix Crawling And Indexing Errors"
7. Give Users What They Want As High In The Content As Possible
Here is the thing: Search engines are looking for the fastest ways to get answers to users, and people don't generally like to read a lot of content.
For content creators, this means putting what users (and search engines) want as high in the content as possible. In other words, get to the point as fast as possible.
For example, if you look at the introduction of this post, you'll notice that we kept it to the minimum and went straight to the list of items.
This is particularly important when the content answers a user's question. For example, in this post, we answer "What Is On-Page SEO?" at the beginning of the content.

For more information, read: What Is Above The Fold Content And How To Optimize It.
8. Add Internal And External Links To Related Content
Many people are confused about how links in the content can help SEO. Here is a quick explanation:
You can use two types of links in your content: internal and external.
Internal links are links pointing to other pages on the same domain. Internal links help users learn more about a topic, keep users on your website for longer (which is good), and help search engine crawlers discover more pages on your website.
In addition, internal links help search engines understand how your content is related and which pages of your website are the most important.
External links are links pointing to web pages outside your domain. When they point to high-quality content, they help users discover more useful information, which is good for the user experience.
To use links in your SEO strategy, follow these simple rules:
- Link to relevant pages only (either internal or external).
- Ensure the anchor text you use for the link is relevant and descriptive. Avoid generic terms like “click here.” Instead, use phrases that give an idea of what the linked content is about.
- Regularly check for broken links.
- Use “nofollow” tags for links to which you don’t want to pass SEO value.
9. Cover The Topic Fully
According to Google, one of the criteria for high-quality content is topic coverage. Their guidelines explicitly state that the content should provide a substantial, complete, and comprehensive description of the topic.

This means two things:
- Ensure that your content covers a topic in full. Before writing, check the SERPS for your target keywords and make note of the topics covered by the top-ranking pages.
- Structure your content to answer the main question as high in the content as possible and then provide additional information.
10. Align Content With Search Intent
To have any chance of ranking in the top positions of Google, your content has to align with the search intent. Here is how to do this:
First, identify the intent behind your target keywords. There are four types of keywords:
- Informational (looking for information)
- Navigational (seeking a specific website)
- Transactional (wanting to make a purchase)
- Commercial (researching products).
Use tools like Google’s autocomplete, related searches, and “People Also Ask” sections to understand what users are looking for.
Next, review the top-ranking pages for your target keywords. Analyze their format, style, and content. Is it a blog post, listicle, product page, or video? Ensure your content covers all the topics they cover, and add your unique angle to the content.
For example, when you search for "dog food for sensitive stomach", you'll notice that the top results are product and category pages from eCommerce websites. If you want to rank for this term, you must have the same type of content.
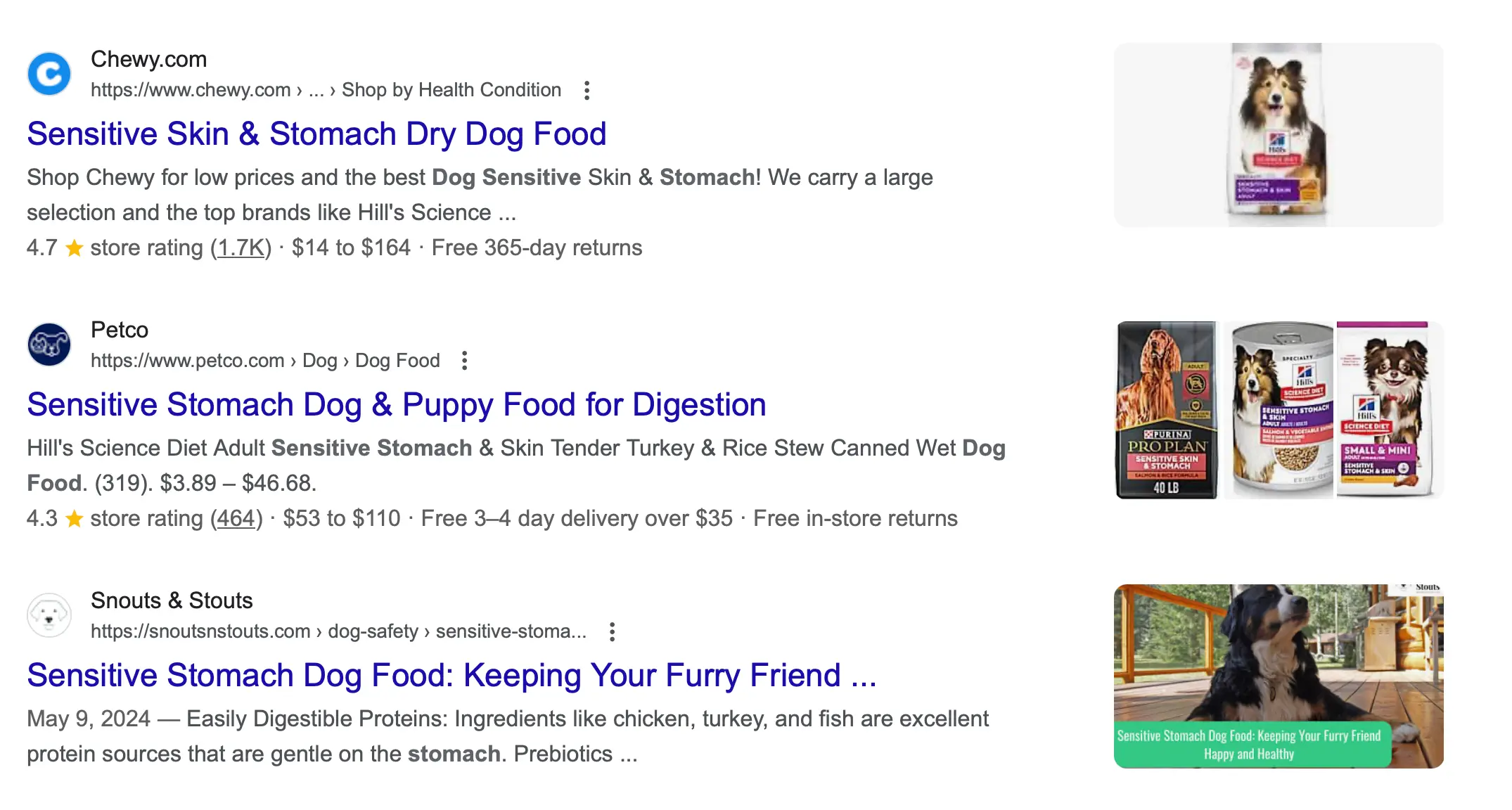
Lastly, structure your content to address the user’s query directly. Use meaningful headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs to make the content easy to read and understand.
11. Demonstrate Your Experience And Expertise
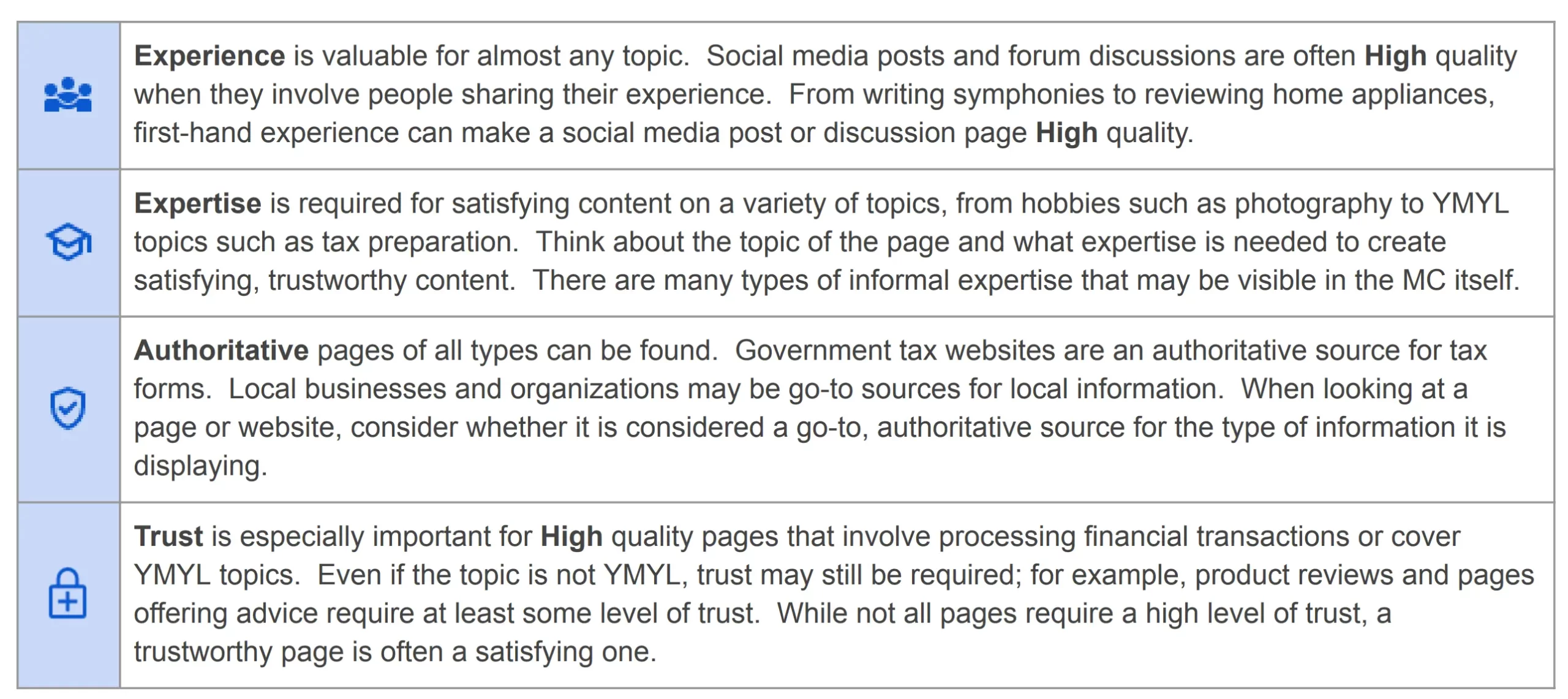
To rank for a particular keyword, you must prove to Google and users that you're an expert. Google, when evaluating the content of a page, looks for signals of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trust) to determine if the content is a good fit for a particular search,
This means you must ensure your content reflects your knowledge and expertise on the topic. Start by showcasing your credentials and experience. Add an author bio at the end of your articles, detailing your qualifications and experience in the field. Link to your professional profiles, such as LinkedIn, to build credibility.
Use data and references from reputable sources to support your claims. Citing studies, expert opinions, and authoritative websites can enhance the trustworthiness of your content.
12. Add Relevant Schema Markup
Structured data (aka schema markup) is another element that can make your content easier for search engines to understand. Schema markup is code added to your HTML that describes parts of your content to search engines more structurally.
First, identify the most relevant schema types for your content (all available schema types supported by Google are listed here).
For example, if you run a recipe blog, use the Recipe schema. If you have a local business, use the Local Business schema. This helps search engines display rich snippets, such as star ratings, images, and other key information, directly in search results.
Next, implement schema markup on your web pages using tools like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or plugins if you’re using a CMS like WordPress.
Once added, test your code using Google’s Rich Results Test to ensure it’s correctly implemented and error-free.
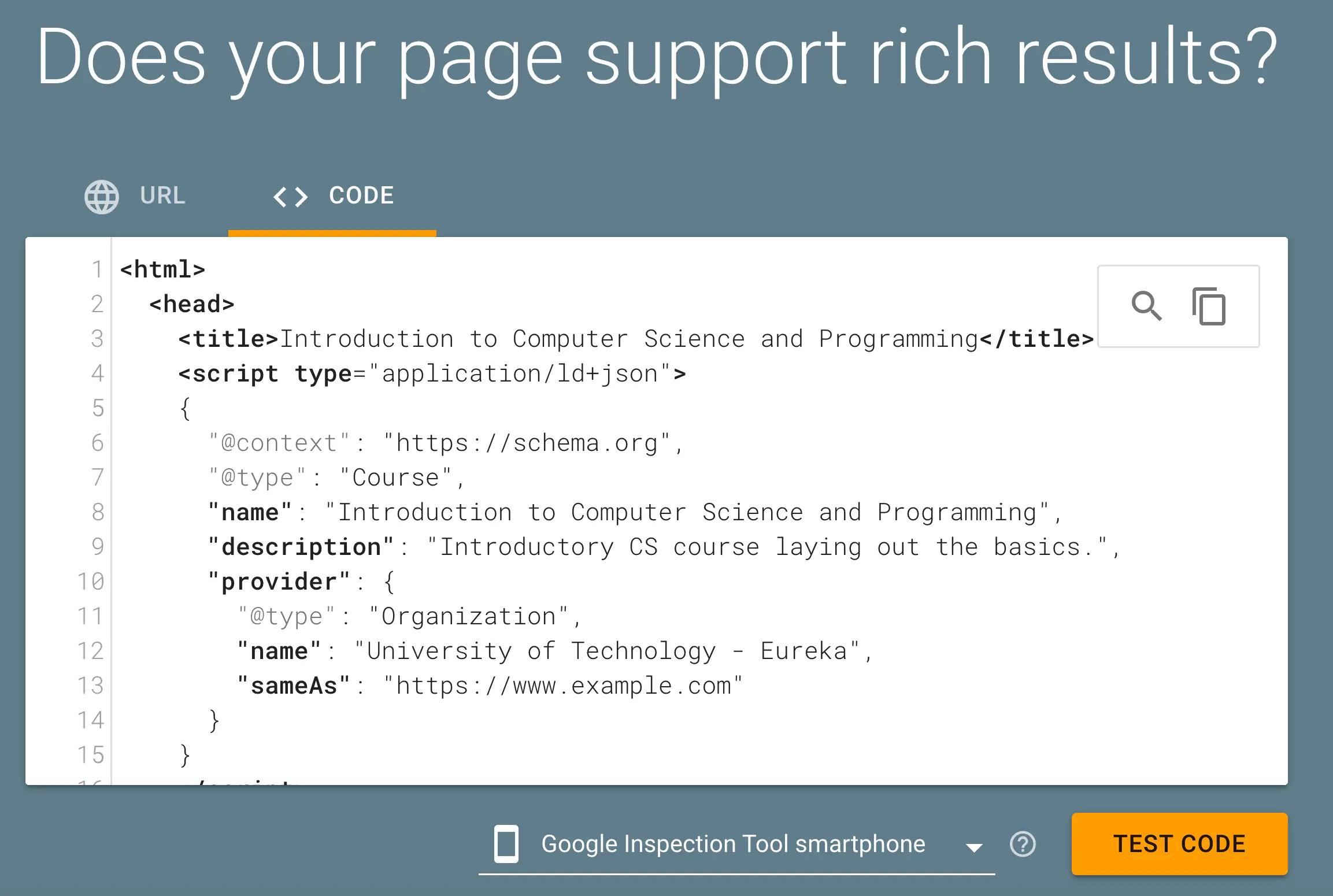
Ensure you regularly review and update your structured data to reflect any changes in your content or schema guidelines.
13. Provide Unique Information
Rewriting and reformating content already available on other websites is not enough to get you one of the top Google rankings.
To get Google's attention, you must cover the essential topics for a keyword and provide unique information and original content.
In their content guidelines, Google states, "If the content draws on other sources, does it avoid simply copying or rewriting those sources, and instead provide substantial additional value and originality?"
In practice, this means the following:
Conduct original research or surveys related to your niche. Blend existing information with your own data and insights that can’t be found elsewhere. This will set your content apart and establish you as an expert in your field.
Offer unique perspectives or solutions based on your personal experience or case studies. Explain how your approach differs from others and why it’s effective. Use specific examples and detailed explanations to add depth and originality to your content.
For example, in our post on the best digital marketing courses, we didn't just list the courses; we also provided screenshots of what the learning environment looks like, showed actual exam questions, and outlined our experience registering for a course. These elements provide value to users and make the content unique and different from what is already available.
14. Add Relevant Images And Engaging Visual Content
Search results and the web, in general, have become more visual. People don't like reading large pieces of text, so it's essential to use relevant images and visuals in your content to make it easier to consume and more engaging.
When adding images to your content, ensure that:
- They are high-quality and relevant to your content.
- Avoid using stock images. They offer no value and can reduce the quality of your content.
- Use original images, screenshots and other elements unique to your content. You can use tools like Canva to create these visuals even if you're not a graphic designer.
- Use descriptive file names and alt text for each image to improve accessibility and SEO.
- Consider adding videos to engage your audience further. Videos can increase users' time on your page, which is a positive signal to search engines.
- Compress and optimize your images to ensure fast loading times and maintain a good user experience.
Use our image SEO checklist to ensure your visuals are optimized using best practices.

15. Add Keywords To Your Body Content
Keyword stuffing and SEO over-optimization are bad practices and should be avoided, but adding relevant keywords to your content is highly recommended.
Here is what you should do:
- Add your target keywords to your body content. Focus on using them in key areas such as the introduction, headings, and conclusion.
- Ensure the keywords flow naturally within the text and add value to your content. Avoid forcing keywords into places where they don’t fit.
- Use long-tail and related keywords to make the text sound more natural instead of repeating the same keywords.
- Check what keywords your competitors are using in their content to get ideas.
For more information, read How To Add SEO Keywords To Your Content.
16. Optimize For Featured Snippets And Other Search Features
One of the ways to get more traffic without creating new content is to optimize your existing content for featured snippets and other search features.
Featured snippets (and other search features) appear above the organic results and receive more clicks and traffic.
To make your content eligible for these, follow these guidelines:
- Add relevant structured data when applicable (as described above).
- Find queries that Google displays featured snippets, local packs, rich results, or other features.
- Change your content to match the featured snippet format.
For step-by-step instructions, read How To Get Google Featured Snippets.
17. Ensure Content Is Easy To Consume On All Devices
One of the biggest mistakes people make when reviewing their on-page SEO is checking their websites on desktops and not other devices. Most users consume content on mobiles, and it's your top priority to make your websites mobile-friendly and ensure the user experience on all devices is the best possible.
This means looking at all the page experience factors, including:
- Page speed and other core web vitals.
- Serving content securely over HTTPS.
- Do not use popups and other elements that distract users from navigating your website.
- Making the content easily distinguishable from ads.
- Making the content easy to read using large fonts and small paragraphs.

For more information, read our Mobile SEO Best Practices guide.
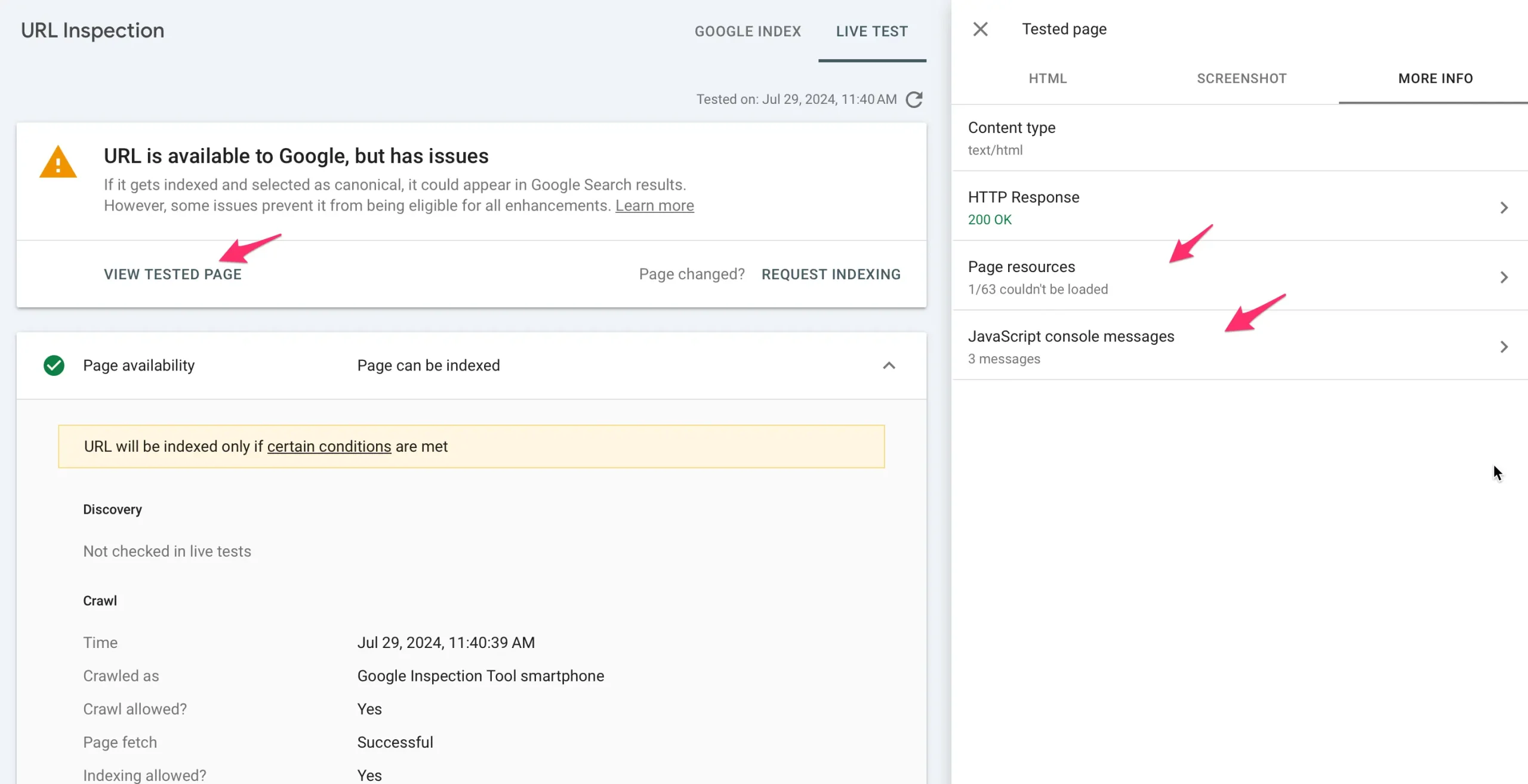
18. Check Page Indexing With URL Inspection Tool
Use the URL Inspection tool of the Google Search Console to ensure that Google can access all the resources a page needs to display correctly. It's very common to accidentally block CSS or JS files through your robots.txt file, which can negatively impact your indexing and the content's ability to rank.
Here is how to do this:
- Log in to Google Search Console and enter the page URL in the top bar.
- Click the Test Live URL button and then the VIEW TESTED PAGE button.
- Click on the Screenshot tab to see how Google renders a page.
- Click the MORE INFO tab and look for errors in the Page Resources and Javascript Console Messages.
19. Review Critical Technical SEO Elements
On-page SEO is critical for ranking in Google, but equally important are some technical SEO elements that can keep your content out of the Google index.
In particular, you need to check for:
- Crawling and indexing errors using GSC.
- Canonicalization and duplicate content.
- Blockings in your robots.txt
- XML sitemaps.
You can find all the relevant information in our technical SEO checklist.
Learn More About On-Page SEO
To learn more about on-page SEO and become an expert, use the following guides:
- Best Google SEO Courses (includes lessons on on-page SEO).
- The Complete SEO Course (covers basic and advanced on-page SEO tactics).
- On-Page SEO Articles (updated regularly with new content).



