- 1. Setup Google Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools And Analytics
- 2. Check And Verify Your Robots.txt File
- 3. Create And Submit An XML Sitemap
- 4. Check For Google Penalties And Manual Actions
- 5. Install and Configure Yoast SEO (or other SEO plugin)
- 6. Identify And Evaluate Your Target Keywords
- 7. Group Keywords Into Topic Clusters
- 8. Optimize Title Tags, Meta Descriptions, And Page Content
- 9. Add Alt Text To Images
- 10. Promote Your Website With Off-Page SEO
- Learn More About SEO
When you start SEO on a new website, you don't need to configure everything from day one. However, you must perform some basic SEO settings to ensure your website can start ranking in Google.
1. Setup Google Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools And Analytics
The first thing to do is configure three important tools to use through the SEO process.
Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster tools will help you track your website’s search performance and identify important issues related to crawling and indexing. Google Analytics will give insights into what users do once they visit your website.
Here is what you have to do:
Google Search Console: Verify your website by adding the provided HTML tag to your website’s header or uploading an HTML file. Once verified, check the "Page Indexing" report to ensure all pages are indexed without issues.
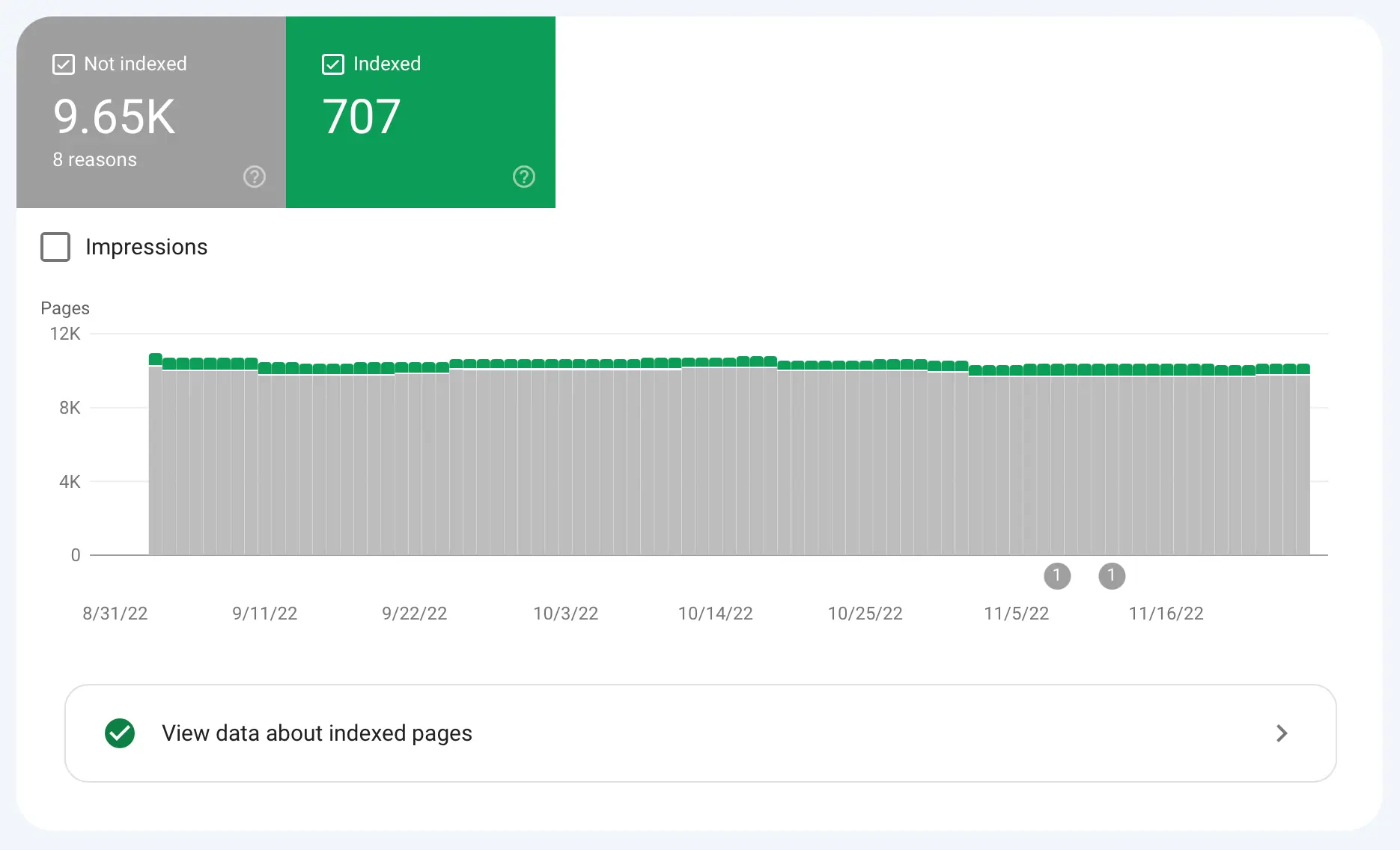
Bing Webmaster Tools: Similar to Google, you can verify your site using a meta tag or file upload and check indexing reports in Bing as well.
Google Analytics: Set up Google Analytics to track your website’s traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates. Link it to Google Search Console for deeper insights into how search affects your traffic.
2. Check And Verify Your Robots.txt File
The next step is to check and verify your robots.txt. Robots.txt is a file in your website's root directory that gives search engines instructions on which pages of your website they are allowed to crawl and add to their index.
You must ensure your robots.txt file isn’t blocking any important pages you want to rank.
Here is what you have to do:
Navigate to "yourdomain.com/robots.txt" to see if you have a robots.txt file. If the file is not found and you get a 404 error, it might be because you're using a virtual file (usually the case on WordPress) or you don't have one.
Either way, use the instructions here to manually create a robots.txt file.
If you have a robots.txt, review its contents to ensure you have no false blocking. In a typical scenario, the contents of the file should be like this:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
Read our robots.txt and SEO guide to learn how to optimize the rules in robots.txt based on your specific needs.
3. Create And Submit An XML Sitemap
One way to index your content faster is to create and submit an XML sitemap to search engines.
An XML sitemap is a file in a specific format that lists all the important pages search engines should know about. It also includes other information like images, videos, and the date the page's content was last updated.
Here is what you have to do:
- Use a plugin or your CMS built-in functionality to create a sitemap for your website.
- Optimize your XML sitemap using best practices.
- Submit your sitemap to Google and Bing.
4. Check For Google Penalties And Manual Actions
Even if your website is new, you should check for Google penalties and manual actions. Google manual actions are imposed on websites when they violate Google guidelines, and algorithmic penalties occur because of the Google ranking algorithm changes.
Here is what you have to do:
First, check for any manual actions.
- Log in to Google Search Console and navigate to the "Manual Actions" report under "Security & Manual Actions".
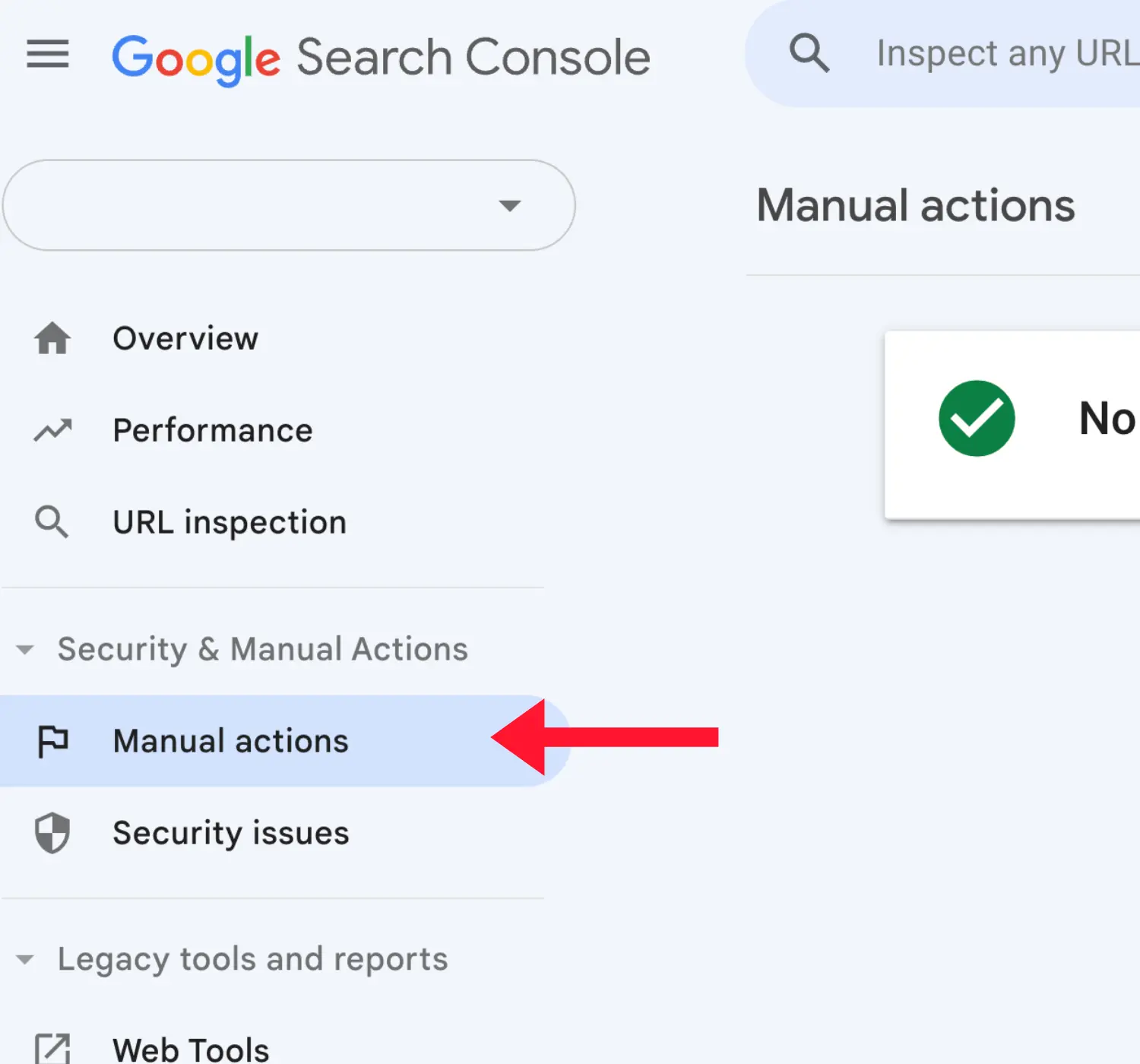
Then, check if your website was affected by Google ranking updates:
- Log in to Google Search Console and navigate to the "Search Results" report.
- Select "Last 16 Months" from the Date menu to view your Googe organic data for the last 16 months.
- View the graph, look for any surges or drops in traffic, and note the dates.
- Compare that with the dates Google released an algorithmic update.
5. Install and Configure Yoast SEO (or other SEO plugin)
Once you get past the above basic SEO checks, which are part of technical SEO, it's time to start working on your on-page SEO, and the first action is to install and configure an SEO plugin.
An SEO plugin will help you optimize your meta tags and images and control which parts of your website you want to appear in Google search. Some plugins also allow you to configure your robots.txt file and optimize your XML sitemap.
For WordPress websites, the best option is Yoast SEO. Other alternatives are Rank Math and All-In-One SEO.
6. Identify And Evaluate Your Target Keywords
Any website's success depends on its content quality and the keywords it targets. A website, especially if it's new, cannot rank for any keyword, so it is crucial to identify and evaluate the keywords you want to rank for from the beginning.
If you choose too competitive keywords or keywords that don't contribute to your business goals, your SEO will fail.
Here is what you have to do:
Conduct Keyword Research: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to find relevant keywords that align with your business goals. Focus on long-tail keywords with lower competition and decent search volume, as these are easier to rank for as a new website.
Evaluate Keyword Difficulty: Check the competition level for each keyword. Tools like Ahrefs and Moz offer a keyword difficulty score that helps you understand how challenging it will be to rank for a particular term. Avoid targeting highly competitive keywords at the start.
Analyze Search Intent: Ensure the keywords you choose match the intent of your target audience. For example, if someone searches for “best running shoes,” they’re likely looking for product recommendations, so your content should address that need.
Prioritize and Create Content: Focus first on keywords with lower competition and high intent to drive conversions. Create cornerstone content around these keywords to build your web presence in your niche.
7. Group Keywords Into Topic Clusters
Your keyword list from the previous step should probably contain many keywords for which you ideally want to rank. To increase your chances of ranking for the terms you want, you should group related keywords into topic clusters.
This SEO technique will help you establish topical authority for certain topics and make ranking easier. Topic clustering is also a great way to position your brand as an authority resource in your niche.
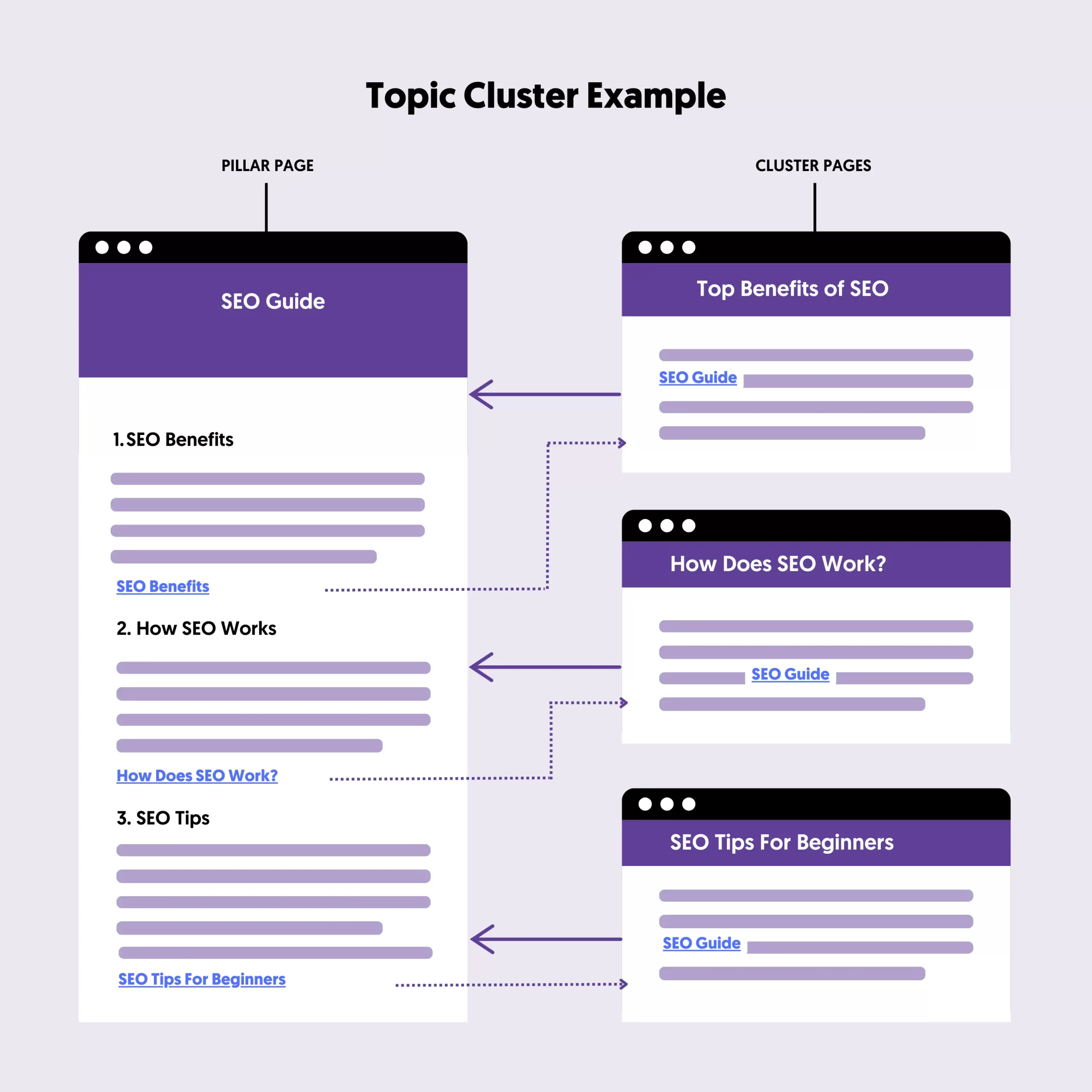
Here is what you have to do:
Organize Keywords by Theme: Review your keyword list and identify themes or topics that naturally group together. For example, if your keywords include “best running shoes,” “running shoes for flat feet,” and “trail running shoes,” these can all be grouped under a broader “running shoes” topic.
Create Pillar Content: Create a comprehensive pillar page for each topic cluster that covers the main topic in depth. This page should serve as the central hub of information on that topic.
Develop Supporting Content: Write blog posts or pages targeting each cluster's related keywords. These supporting pieces should link back to the pillar page, and the pillar page should link to them. This internal linking structure reinforces the entire cluster's relevance to search engines.
Optimize for User Experience: Ensure your pillar page and supporting content provide valuable, easy-to-navigate information. This helps with SEO and enhances the user experience, making visitors more likely to stay on your site and consume more content.
8. Optimize Title Tags, Meta Descriptions, And Page Content
Another on-page SEO task you need to complete from the beginning is optimizing your page meta tags and content.
By crafting engaging and SEO-friendly page titles, compelling meta descriptions, and adding relevant keywords to your content, you help search engines and users understand your content better.
Here is what you have to do:
Write Unique Title Tags: Ensure each page has a unique and descriptive title tag that includes your primary keyword. Keep it under 60 characters to avoid truncation in search results. The title should be compelling enough to encourage clicks while accurately reflecting the page’s content.
Craft Compelling Meta Descriptions: Write meta descriptions summarizing the page content in 155-160 characters. Although meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings, they can significantly influence organic ctr. Include your primary keyword and a clear call-to-action to entice users to click.
Integrate Keywords Naturally: Add your target keywords to the page content, especially in headings (H1, H2) and the first 100 words of your text. Avoid keyword stuffing—ensure that the content reads naturally and provides value to the reader.
Optimize for Readability: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and subheadings to break up the content and make it easy to scan. Add internal links to other relevant pages on your site to improve navigation and help search engines understand the structure of your site.
9. Add Alt Text To Images
Adding images to your content makes it easier for users to consume and can also assist your SEO. Ensure that any images or visuals are high-quality to look good and compressed so they won't slow down the page's loading time.
Here is what you have to do:
Write Descriptive Alt Text: Add alt text to each image that accurately describes the image content and includes relevant keywords where appropriate. This helps search engines understand what the image is about, improving your chances of ranking in image search results.
Keep It Concise: Alt text should be concise, ideally under 125 characters. The primary goal is to describe the image for users who rely on screen readers.
Test Image Load Speed: Use tools like PageSpeed Insights to ensure your images are properly compressed and don’t negatively impact page loading times.
For more information on image optimization, review our image SEO guide.
10. Promote Your Website With Off-Page SEO
Everything discussed so far about technical and on-page SEO relates to SEO rules you can fully control and fall within the boundaries of your website. To achieve high rankings in Google for competitive keywords, you also need to work on your off-page SEO.
Off-page SEO refers to techniques for improving rankings using tactics beyond website content, such as link building, social media marketing, brand mentions, and online reviews.
Here is what you have to do:
Build High-Quality Backlinks: Focus on acquiring backlinks from reputable websites in your industry. Reach out to industry influencers, guest post on relevant blogs, and create linkable assets that others will want to link to.
Engage in Social Media Marketing: Actively share your content on social media platforms where your audience is most active. Respond to comments and participate in relevant discussions to engage with your followers.
Monitor and Manage Online Reviews: Encourage satisfied customers to leave positive reviews on platforms like Google Business Profile, Yelp, and industry-specific review sites. Respond to positive and negative reviews to show that you value customer feedback.
Earn Brand Mentions: Get your brand mentioned on other websites, forums, and social media platforms. Even if these mentions don’t include a direct link, they can still positively impact your online reputation and search engine rankings.
For more information, read our guide on link-building best practices.
Learn More About SEO
What you have learned above are the fundamentals of SEO. It's the first step in optimizing your website for search engines, but that's not the end of the story.
To succeed with SEO, you need a comprehensive strategy that utilizes all available SEO and content marketing techniques to achieve the best possible results.
Use the guides and resources below to continue your learning:



