What Is Website Structure?
A website structure refers to the way your website pages are organized and connected together. It is about the hierarchy of the website, menu structure, and internal linking.
A good website structure is crucial for the user experience and makes the job of search engine crawlers easier, which means better indexing and SEO.
Why Is Website Architecture Important?
The structure of a website is very important both in terms of SEO and usability. It should be user-friendly, easy to navigate, fast, and serve its purpose.
A well-defined site structure is important for SEO for three main reasons:
It helps search engines understand your content better - A good site structure helps search engine crawlers read, index, and understand your website faster, improving your chances of ranking in search engines.
The way search engines work is the following:
- They discover your website on the Web.
- They start crawling your homepage and then follow all links from there.
- They try to figure out the site's structure to understand better how your pages/posts are related and which pages of your site are more valuable than others.
When you have an optimized structure, you make this job very easy for them, meaning more visibility in the search results.
A good structure increases your chances of getting sitelinks in Google search - Sitelinks are links below the description of your snippet in Google Search Results that point to other pages on your website. They are a great way to make your search listings more prominent and increase your CTR (click-through rates).
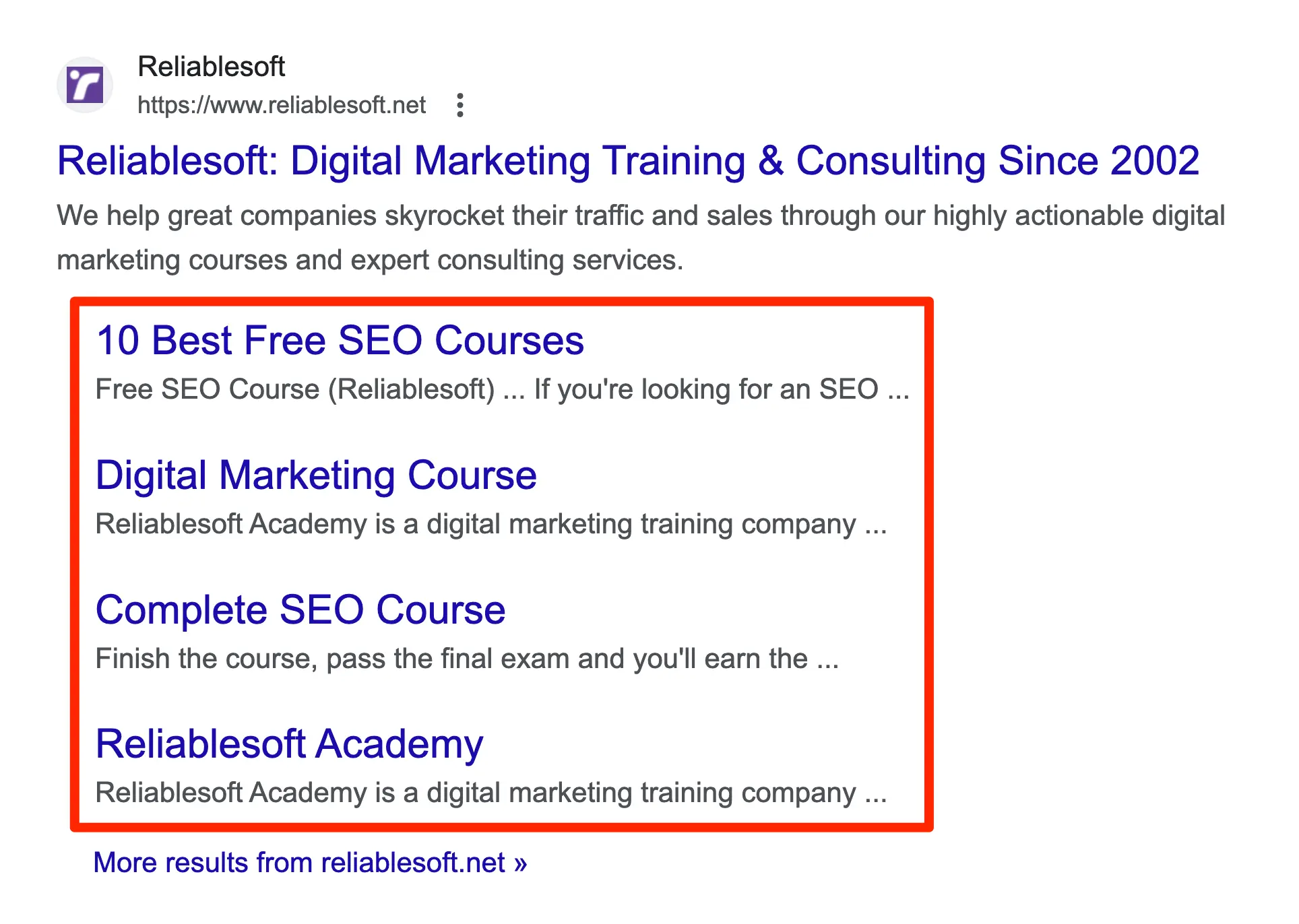
You cannot specify which parts of your website are to be shown as site links since the Google algorithm automatically selects these. The only way to get sitelinks to appear with your listing is through a good site structure.
A good structure provides for a great user experience and lowers bounce rate - A bounce rate is a metric that shows how many people land on a webpage and leave without interacting with the page or site. A high bounce rate is bad for SEO, and the reason is the following:
Google knows when a user clicks on your listing from Google search, visits your page, and then goes back to Google search without interacting with your website. For them, this signals that users are not happy with the results, eventually leading to lower rankings.
When you have a solid site structure, users will find it easier to navigate through your website and find what they are looking for, and this increases usability and time on site and lowers your bounce rate.
What Is a Good Website Structure?
The actual structure of a site is strongly related to the type of content a website offers. If we are to divide website types into groups, we will end up with four major groups:
- Blogs
- Corporate Websites
- News Websites
- eCommerce Websites (Selling either products or services online)
Ideal website structure of a blog
A good site structure for a blog looks like this:
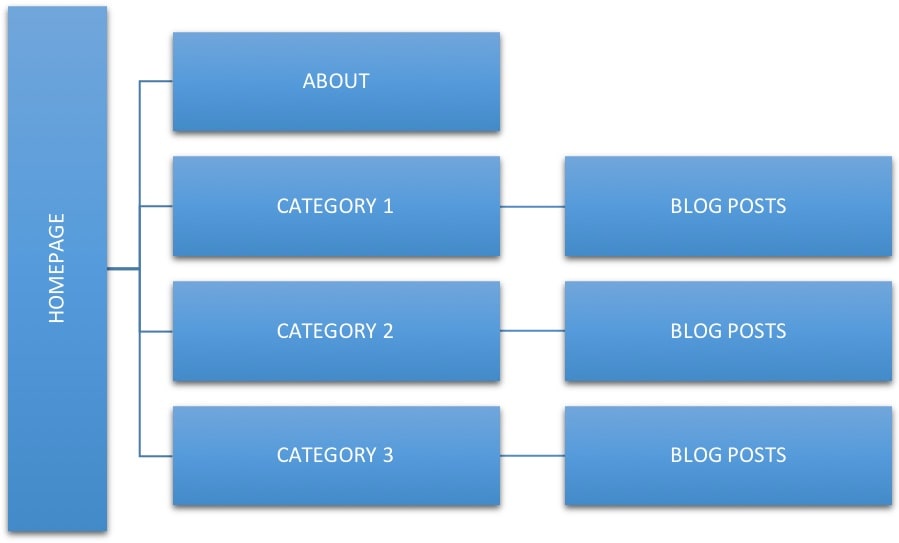
Besides the home page and the other pages like About Us, Contact Us, etc., blog posts should be grouped into categories according to relevancy.
For example, if you have a food blog publishing different kinds of recipes, you can create several categories based on the type of recipes, i.e., Italian recipes, vegetarian recipes, Chinese recipes, etc.
Ideal website structure of a small business / corporate website
The main purpose of a small business / corporate website is to provide more information about the business, its products, services, and departments.
A good website structure for a corporate website is as follows:
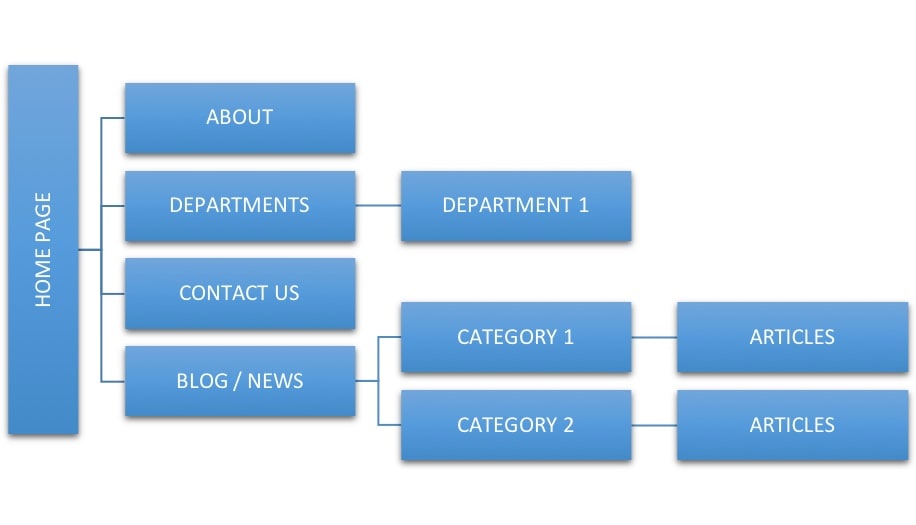
Notice that you have a main category for departments and a main category for the blog with several sub-categories.
Ideal website structure of a news website
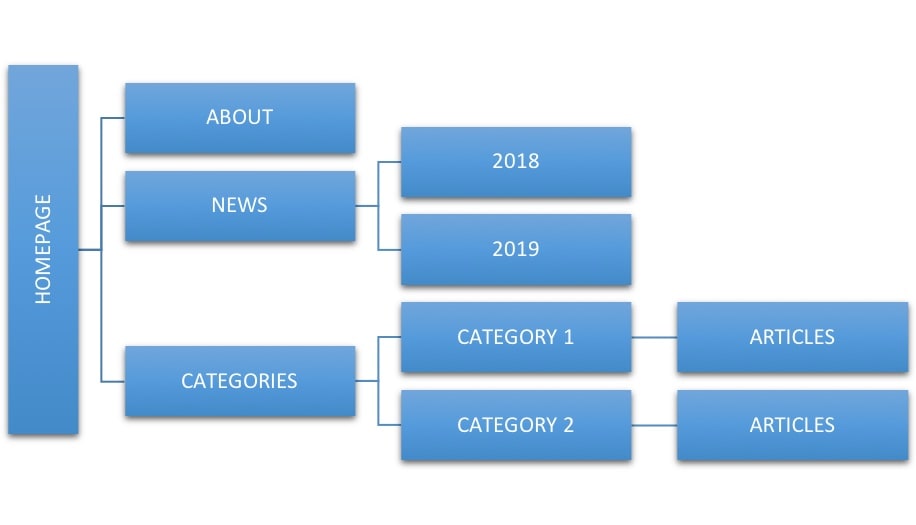
A news website, such as an online magazine, can group content into several categories based on the type of content and when it was published.
This structure can help search engines, and users find what they want by visiting the category of interest or navigating through the content by date.
Ideal website structure for an eCommerce website
The site structure of an eCommerce website can be a bit more complicated than other types of websites, especially when it offers many different products.
In a typical scenario, though, a good structure can be as follows:
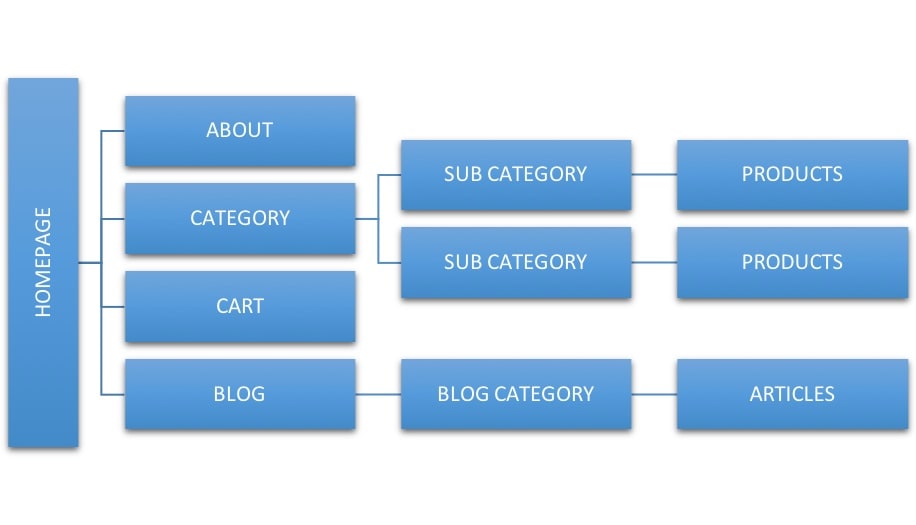
On top of the website structure, we have the homepage and then the content grouped into several categories.
There is no limitation as to the number of categories or subcategories you can create but a rule of thumb is not to create more than 3 levels of depth in your hierarchy.
In other words, each product should be accessed from the homepage in less than 3 clicks. This makes indexing faster and easier to understand by crawlers and it’s also friendlier for users.
How To Structure A Website For SEO
- Use a Hierarchical Website Structure
- Group Related Content Into Categories
- Use HTML And CSS For Navigation
- Use Breadcrumbs
- Create An SEO Friendly URL Structure
- Optimize Your Internal Link Structure
- Provide a User Sitemap
1. Use a Hierarchical Website Structure
The focal point of your website is the homepage, and all other pages should be grouped into categories based on their type.
For example, blog posts should be grouped into categories and placed under the ‘Blog’. News articles can be grouped by published date. If you are offering services, these can be grouped under services.
Try to think what the best grouping from a user’s perspective is. Run some scenarios and try to replicate the steps users take to find a product or article on your website. If you can make this process easy enough for them, it will be for search engines, too.
Your hierarchy should be no more than 2 or 3 levels deep - Don’t overcomplicate your site hierarchy; keep it simple. All website pages must be accessible from the homepage in less than 3 clicks.
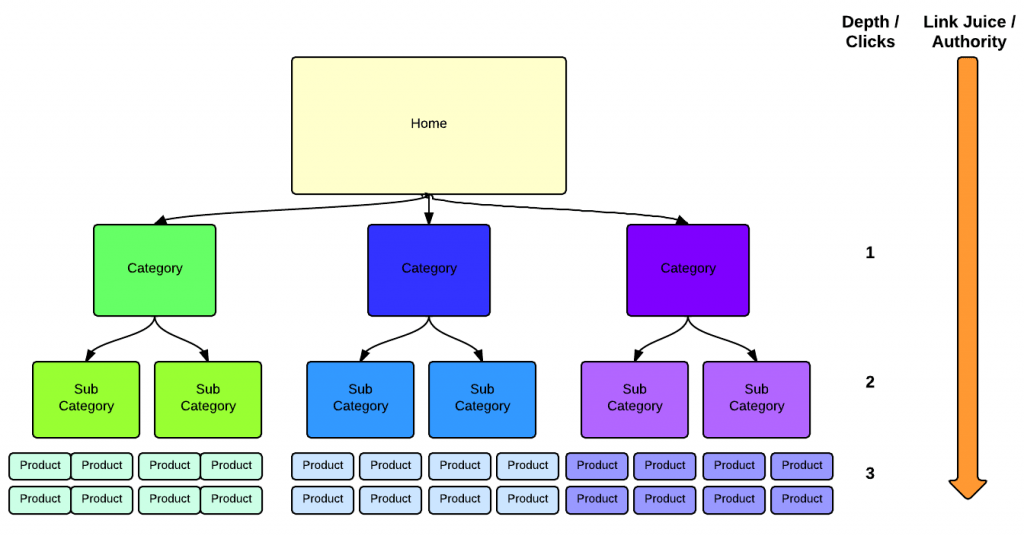
For example, if you are running an online shop, a user should be able to visit a specific product page in less than 3 clicks. This translates to:
- Homepage (1 Click).
- Product Category (2 clicks).
- Product Subcategory (3 clicks).
- Product page.
2. Group Related Content Into Categories
There are some rules to follow when creating categories, either for your products and services or for your blog.
The first rule is that you NEED to have categories. The reason is simple: It makes it easier for users to find the content they are looking for and for search engines to crawl and index a website.
Try to keep your categories the same size. If a category is too big because you have a lot of products or blog posts about that topic, try to break it into two or three categories.
Add your categories to the menu of your website and homepage. Don’t try to hide your categories, but make sure your main categories are accessible from the main menu and linked to from the homepage.
Use categories to create content relevancy. This is true, especially for blogs. One of the reasons for creating categories is to build topic relevancy and help Google understand which topics you want to build authority on.
Optimize your categories for SEO. When you create a new category, do some SEO work on it. In particular:
- Optimize the title and description of the category.
- Write a short introduction.
- Add a relevant image (with proper ALT text).
- Optimize the slug.
- Make sure that is included in your sitemap.
- Add internal links pointing to your category pages.
For example, look at my SEO Articles category. Notice that I have changed the slug of my categories from ‘category’, which is the default value, to ‘articles.’ Why? Because it makes more sense.
For more information on category SEO, you can read:
3. Use HTML And CSS For Navigation
Avoid using Javascript or Ajax when creating your navigation. The best approach to making the lives of search crawlers easier is to use plain HTML tags combined with CSS for formatting.
Also, don’t use images to create navigation links but text. This means that if you want to link to a category page from your homepage, don’t just add an image and link to it but also have a text link.
4. Use Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumb menus are important for SEO. Google has often mentioned the need for a breadcrumb menu on all your pages so users can navigate the site easily.
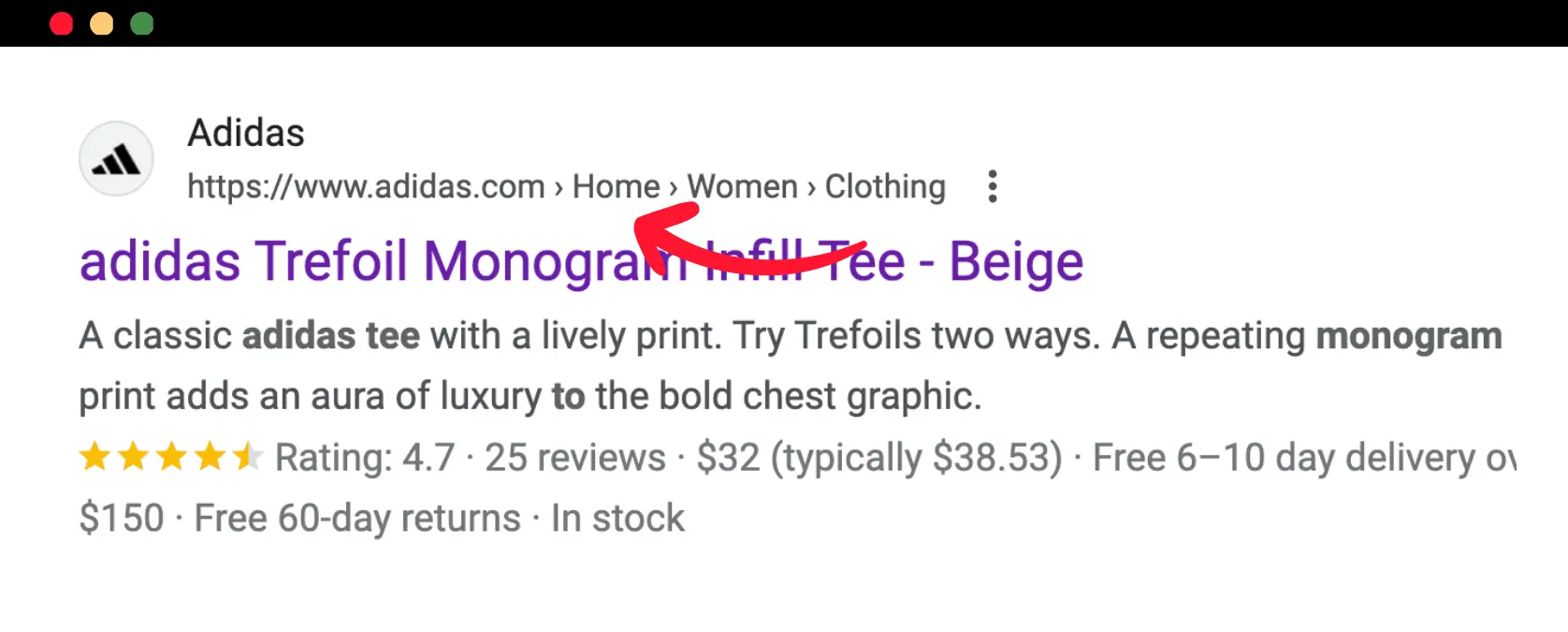
When activating breadcrumb menus on your website, make sure that:
The breadcrumb menu displays your site structure accurately. For example, when you activate a breadcrumb menu on a product page, it should have the following elements:
Homepage > Product Category > Sub Category > Product page
In other words, the menu should display all levels until you return to the homepage.
Add structured data to describe the breadcrumb menu to search engines. There is a special type of markup for breadcrumbs that gives search engines more information about your navigational structure. Google can use this information to enhance the appearance of your search listing on both desktop and mobile.
5. Create An SEO Friendly URL Structure
You should also consider your permalink structure When creating your site structure. Your goal is to create SEO-friendly URLs that match your site structure.
For example:
Let’s assume that you have decided to adopt this site structure for your fitness blog:
- Homepage
- Fitness Category -> Articles
- Diet Category - > Articles
Your permalink structure should be as follows:
- myfitnessblog.com
- myfitnessblog.com/articles/fitness
- myfitnessblog.com/articles/diet
IMPORTANT:
Don’t confuse the logical structure of a website with the URLS of the category pages and the actual URLS of single pages.
In the above example, the URL of a single blog post could be myfitnessblog.com/how-to-lose-weight.
Notice that the category name is not included in the URL because It doesn’t have to be included. It’s friendlier to users and search engines to keep your URLs short and precise. Google can understand the category of the article from your sitemap and breadcrumb menu.
6. Optimize Your Internal Link Structure
One of the ways to make your site structure stronger is to make good use of internal links.
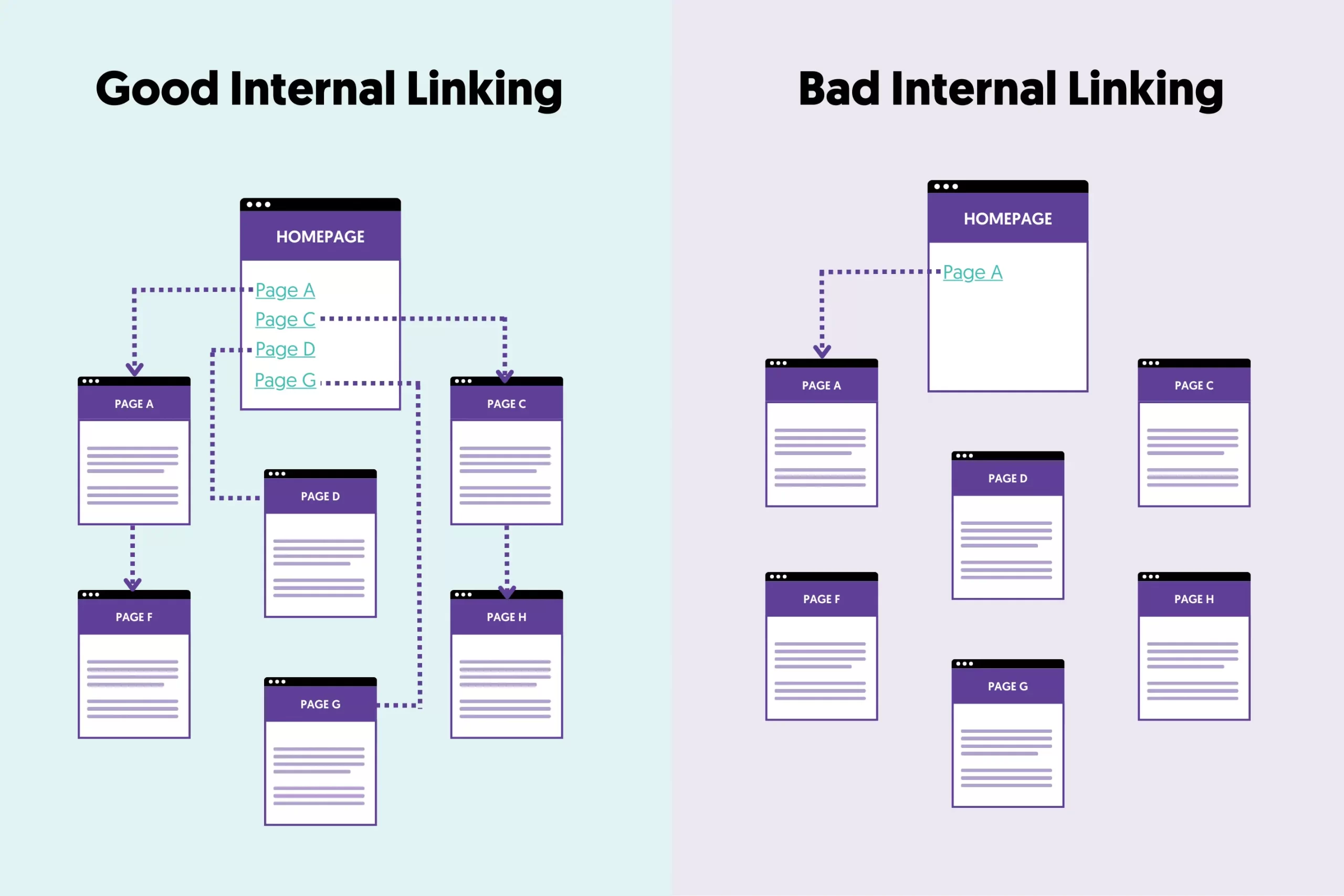
Internal linking is a very important aspect of SEO for 5 reasons:
- It’s a way to lower the bounce rate and increase time on-site.
- It’s a way to help search engines discover more pages from your website.
- It’s a way to pass ‘PageRank’ from strong pages to other pages and make them stronger.
- It’s a way to give search engines clues about the valuable pages of a website.
- It’s a way to implement your site structure.
When creating internal links, have these rules in mind:
Create internal links pointing to your category pages. This will help crawlers index those pages and give them a good idea of how your website pages are related (which helps with topic relevancy).
Identify your most valuable pages (others refer to this as pillar content or cornerstone articles) and link to them from other related pages of your website. At any point, these pages on your website should have the greatest number of internal links.
From your category pages, make sure that you link to the most valuable pages of that category. See how I have organized by SEO Articles category page where the most valuable posts are displayed on top.
You can use optimized anchor text for your internal links. For example, if you want to link to a category on your website that displays athletic shoes, you can safely use the following anchor text: “Athletic shoes” when linking to that category. Unlike external links, Google will not punish you for using optimized anchor text for internal links.
Ensure that ALL website pages can be reached through internal links. Google will probably ignore a page with no internal links, so ensure all your website pages have internal links pointing to them.
7. Provide a User Sitemap
This differs from the XML Sitemap you must create and submit to search engines. In your website’s footer, you can include an HTML sitemap that shows the website hierarchy to users.
Here is a nice example from HP
How To Change Your Website Structure Without Affecting SEO?
If you already have a website that ranks in Google, one of the challenges you will face is how to change your site structure without losing your existing rankings.
While there are a number of actions to follow to protect your rankings, there is always a risk involved when changing either the content or structure of an existing website. So, you need to have a good plan to follow to minimize the risk.
Some guidelines to help you out:
Before changing anything make sure that you have the full picture in your mind as to what you want to achieve.
Don’t just go and create a new category because you realized it’s a good idea but first think how your overall structure should look like and then start making changes.
Use 301 redirects in case you are renaming or removing categories or changing URLs.
A 301 redirect instructs search engines that the URL of the page has changed. Search engine crawlers will update their index accordingly.
For example, if one of your category pages has the following URL:
example.com/category/seo
and you change it to
example.com/articles/seo
then you should add the following 301 redirects in your .htaccess file:
Redirect 301 /category/seo example.com/articles/seo
Submit your updated sitemap to Google.
Once you are done making changes, log in to your Google search console and submit your updated sitemap to Google. You can optionally request a ‘Fetch as Google’, to force Google to process your changes faster.
Conclusion
A good site structure is more important than ever nowadays. We used to create flat websites with many pages targeting specific keywords in the past, but that’s no longer the case today.
Things have changed. Competition is intense in all niches, and with the introduction of machine learning, mobile-first index, and voice search, it’s important to give search engines more clues about the topics (and not just keywords) you want to rank for. And the best way to do this is by having a well-defined and solid site structure.
A website site structure should be hierarchical and easy to use. The starting point is the homepage and all other pages should be grouped into related categories.
Users should be able to reach any site page by following links on the homepage.
Website categories need to be SEO-optimized and added to the navigation menu. Internal links should highlight the most valuable website content to users and search engines and help them identify how the website is structured.
If you haven’t done an audit of your site structure yet, then this is a task to add to the top of your SEO checklist.



