What Is An SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is the process of evaluating the SEO performance of a website. The main goal of an SEO audit is to identify issues and find new opportunities to help you achieve higher rankings in search engine results. It usually covers indexing, technical SEO, keyword research, on-page SEO, and competitor analysis.
To perform an SEO audit, you'll need the help of Google Search Console and SEO audit tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, or others.
Why is SEO Audit Important?
A search engine optimization audit (SEO Audit) will help you identify problematic areas that need improvement with an action plan to correct them. It's also a great way to keep your website up-to-date with the latest developments in search marketing and on top of the competition.
I recommend doing regular SEO audits (at least twice a year) to ensure your website is up-to-date with the latest developments.
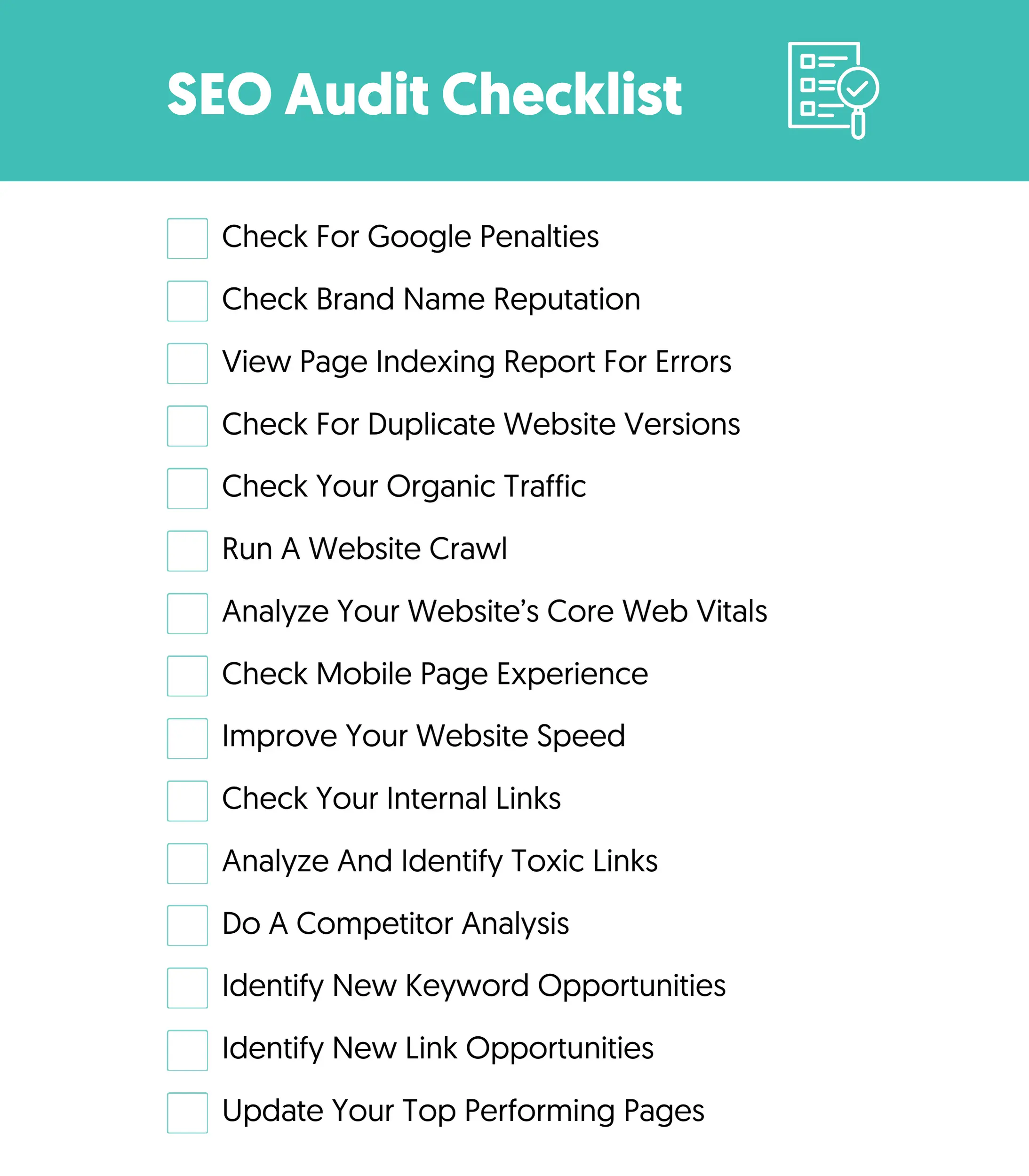
How To Do An SEO Audit (15 Steps)
Follow our SEO audit checklist to review your website:
- Check For Google Penalties
- Check Brand Name Reputation
- View Page Indexing Report For Errors
- Check For Duplicate Website Versions
- Check Your Organic Traffic
- Run A Website Crawl
- Analyze Your Website's Core Web Vitals
- Check Mobile Page Experience
- Improve Your Website Speed
- Check Your Internal Links
- Analyze And Identify Toxic Links
- Do A Competitor Analysis
- Identify New Keyword Opportunities
- Identify New Link Opportunities
- Update Your Top Performing Pages
1. Check For Google Penalties
The first step is to check whether your website is penalized by Google. Your rankings will be negatively affected if your website is under a manual or algorithmic penalty.
You should find out when the penalty was imposed and why your website was penalized. Then, you should create an action plan to correct the issues and remove the penalty.
There are two easy ways to check for Google penalties.
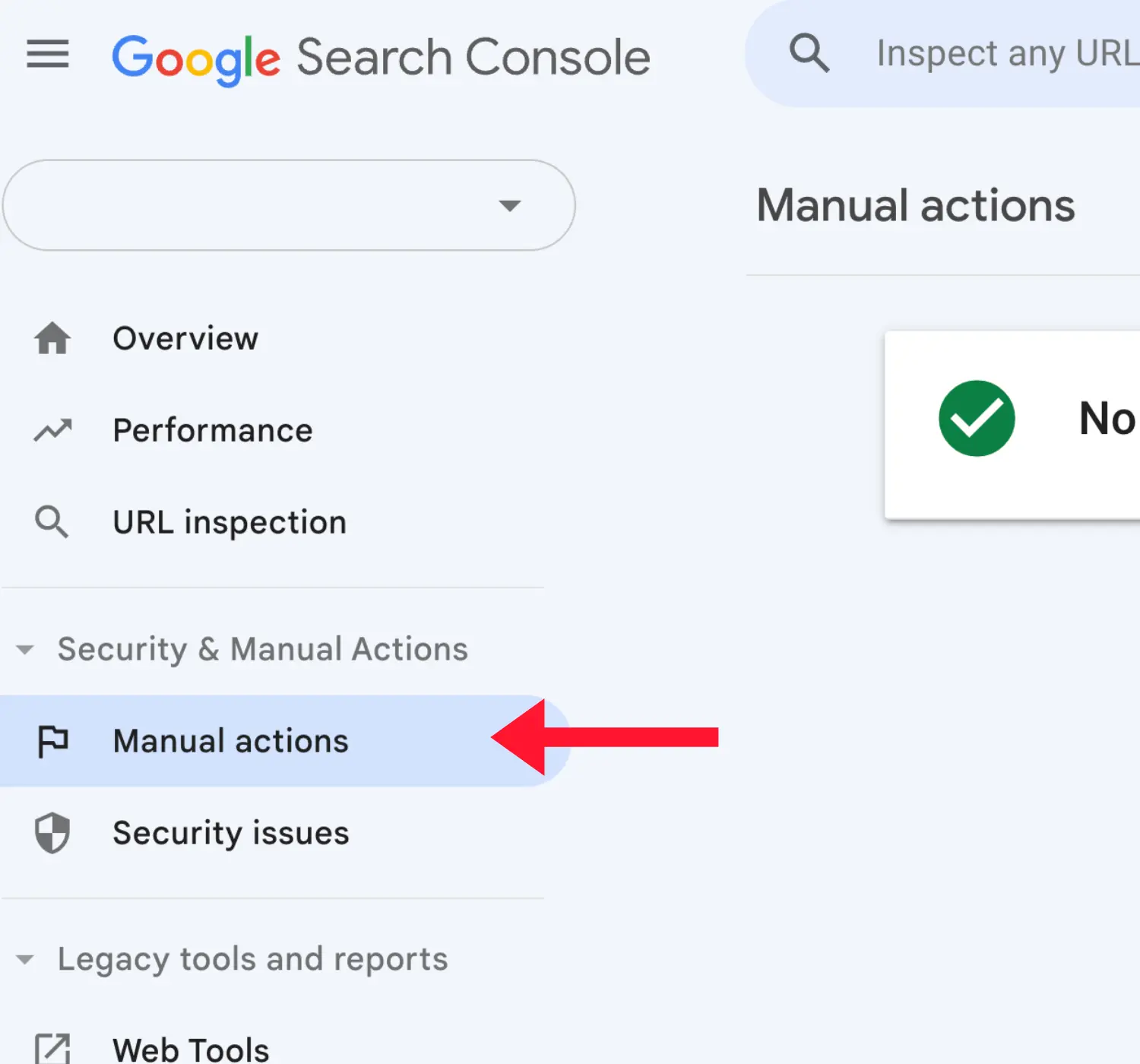
First, log in to the Google Search Console and select ‘Manual Actions’ from the left menu. If a manual action is imposed on your website, you can see the reason(s) here.
The second way is to compare your Google organic traffic for the dates Google released an algorithmic change.
A sudden drop (or increase) in organic traffic is a clear sign that your website was affected by the changes.
Login to Google Analytics and go to Life Cycle > Acquisition > Traffic Acquisition.
Click the dropdown menu above the table and select "Session source/medium".
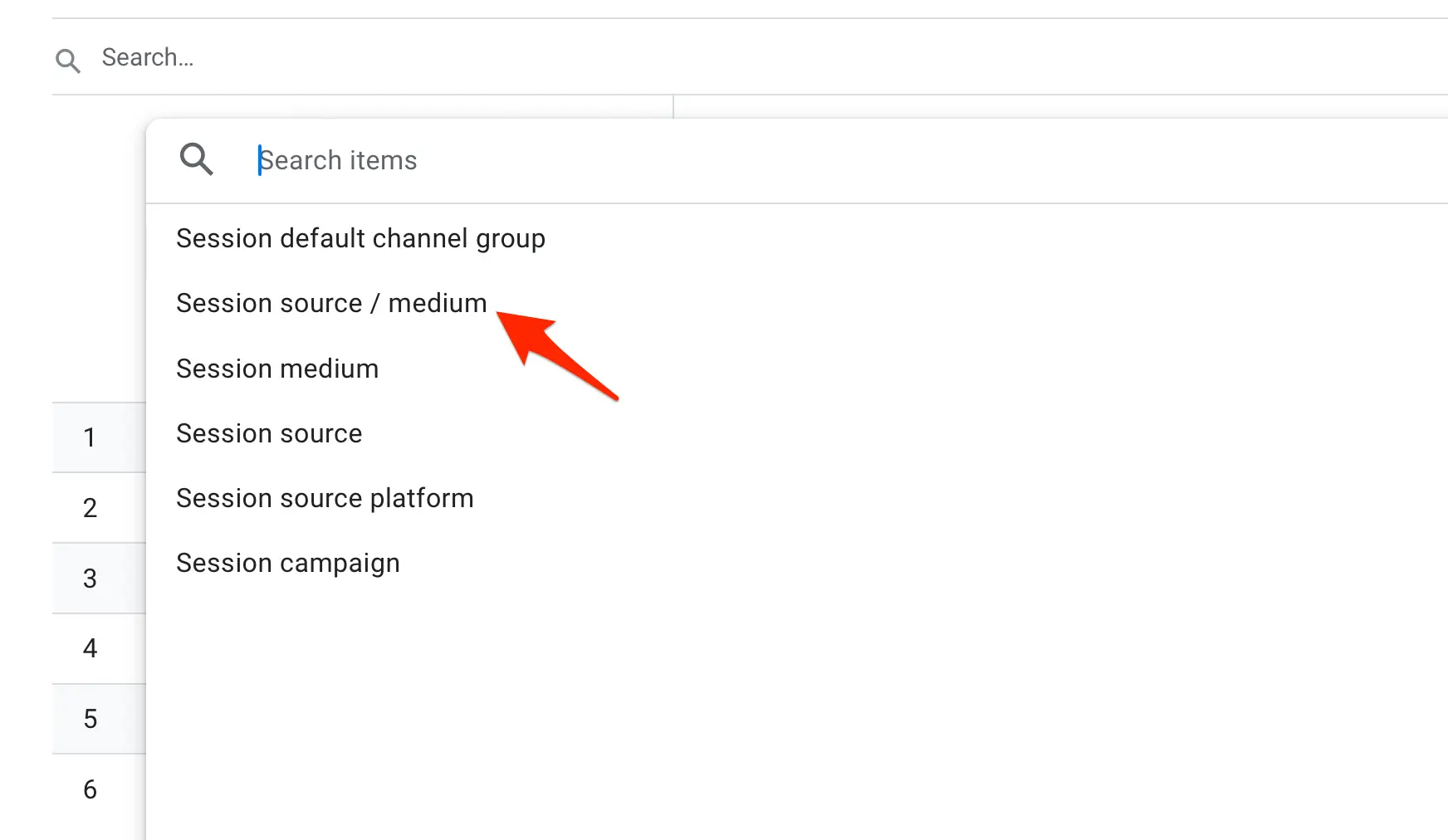
Type "google / organic" in the search box and click Enter. The report now shows your Google Organic Traffic only.

Use the date filters to view your traffic for the last few months.
Compare the dates on which you see significant changes in traffic with the dates Google released an algorithmic change.
What to do if you are under a Google penalty?
If the above tests indicate that you are in trouble, the best approach is to find as many details as possible about the Google updates and adjust your SEO audit accordingly.
For example, suppose a site is penalized by Google because of thin content. In that case, you should audit the quality of your content and either improve, redirect, or remove pages that don’t meet the quality standards.
2. Check Brand Name Reputation
The second step is to search for your brand name on Google and review the results.
Things to check:
- Does your homepage come up first in the results?
- Does Google show sitelinks along with your listing?
- Are the descriptions below your homepage and other pages accurate?
- Does Google show a knowledge graph entry (Google Business Profile Listing) on the right panel for your brand?
- Is the name and other information on your GBP page correct?
Scroll down to the bottom of the results, particularly the "related searches" section.
Things to check:
- Are the ‘related searches’ relevant to your brand?
- Do you see any related searches you can utilize by creating dedicated pages? Typical examples are ‘brand name reviews.’
What to do if you don’t get the expected results?
If you don’t get a nice listing, as explained above, then this means that there are several issues with your website.
The best approach is to fix these issues before proceeding any further by:
- Reviewing and optimizing your site structure
- Review your homepage SEO
- Claim your Google Business Profile page and ensure all information is accurate and correct.
3. View Page Indexing Report For Errors
The next step is to check for indexing errors. This crucial part involves checking if Google can crawl and index your pages.
Use Google Search Console's Page Index Coverage report to see which pages are not being indexed and why.
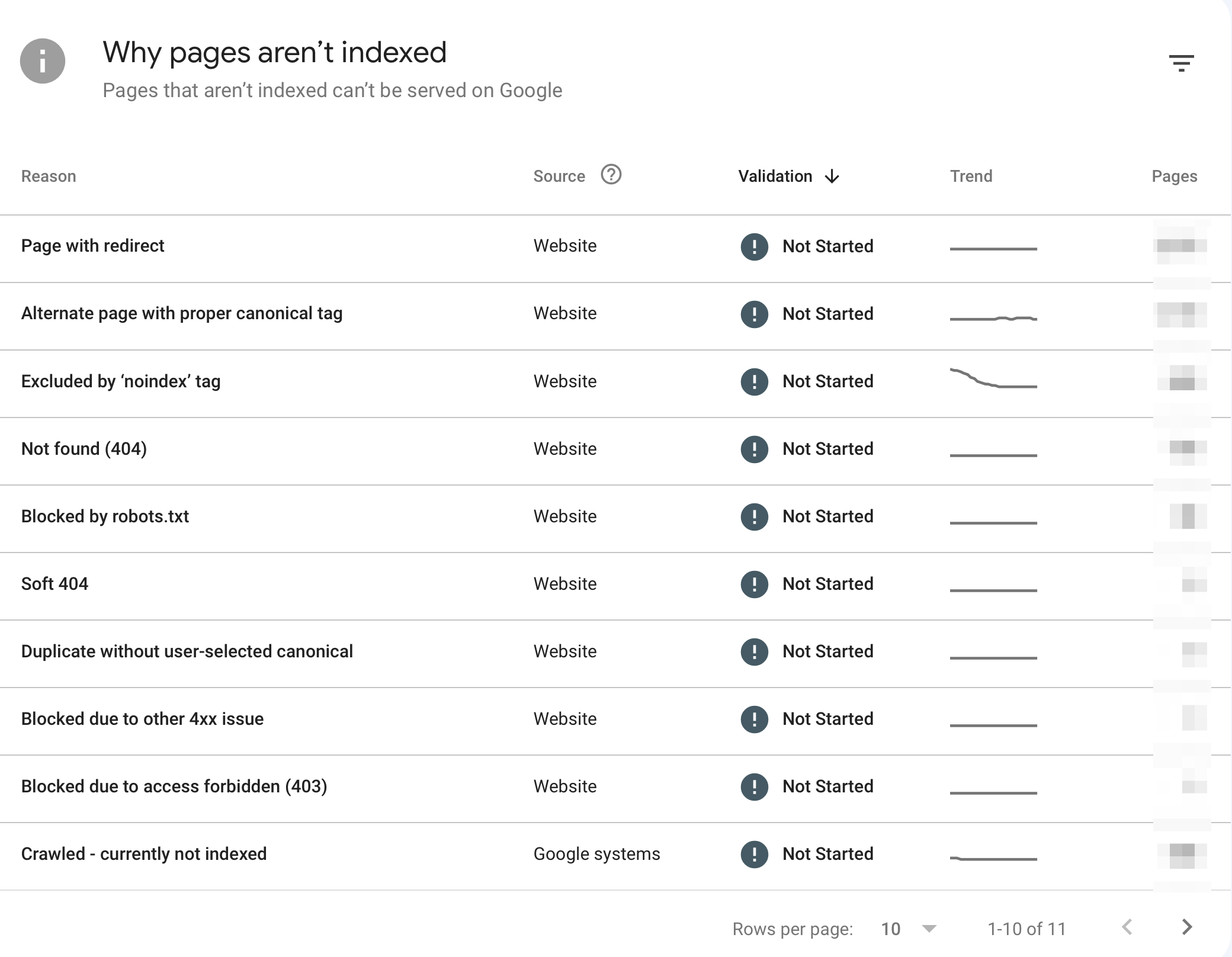
Look for common problems like Soft 404, Not Found (404), and Excluded by 'noindex' tag.
Remember that some errors, like (page with redirect) are expected. Also, it's normal that not all pages of your site are indexed by Google. Review all errors and follow Google's instructions to ensure your website has no serious problems.
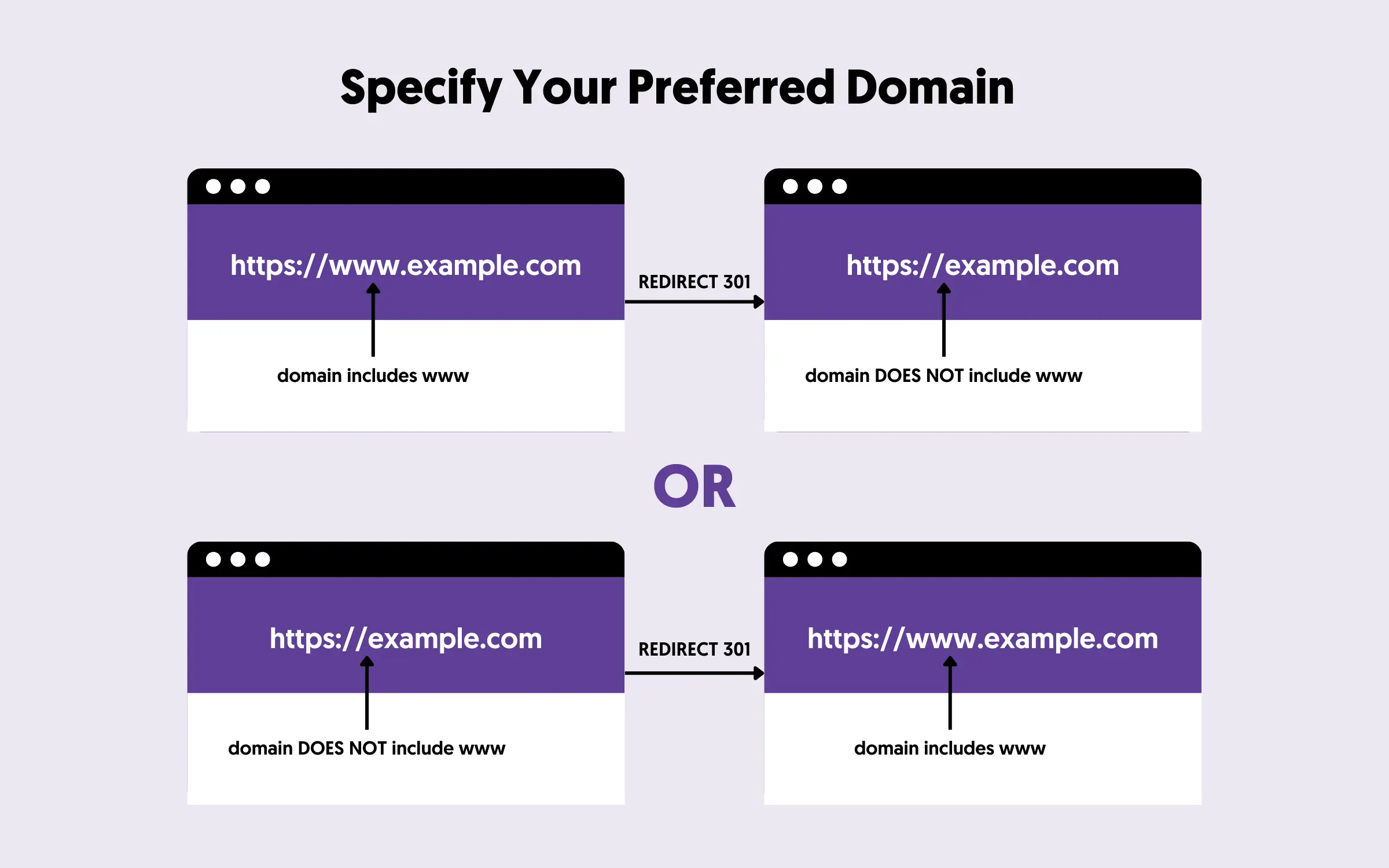
4. Check For Duplicate Website Versions
Many webmasters don't realize that a website can be assessed in four different ways (with/out https and with/out www in the URL) :
- http://example.com
- https://example.com
- http://www.example.com
- https://www.example.com
While this is okay for users, search engines may consider them different websites. This means you may have problems with indexing, duplicate content issues, and loss of page rank.
To test your website is configured correctly, open a browser window and check that all website variations redirect to the same version. If not, you should decide which domain format to use and add the necessary 301 redirections.
For more information, read our guide here.
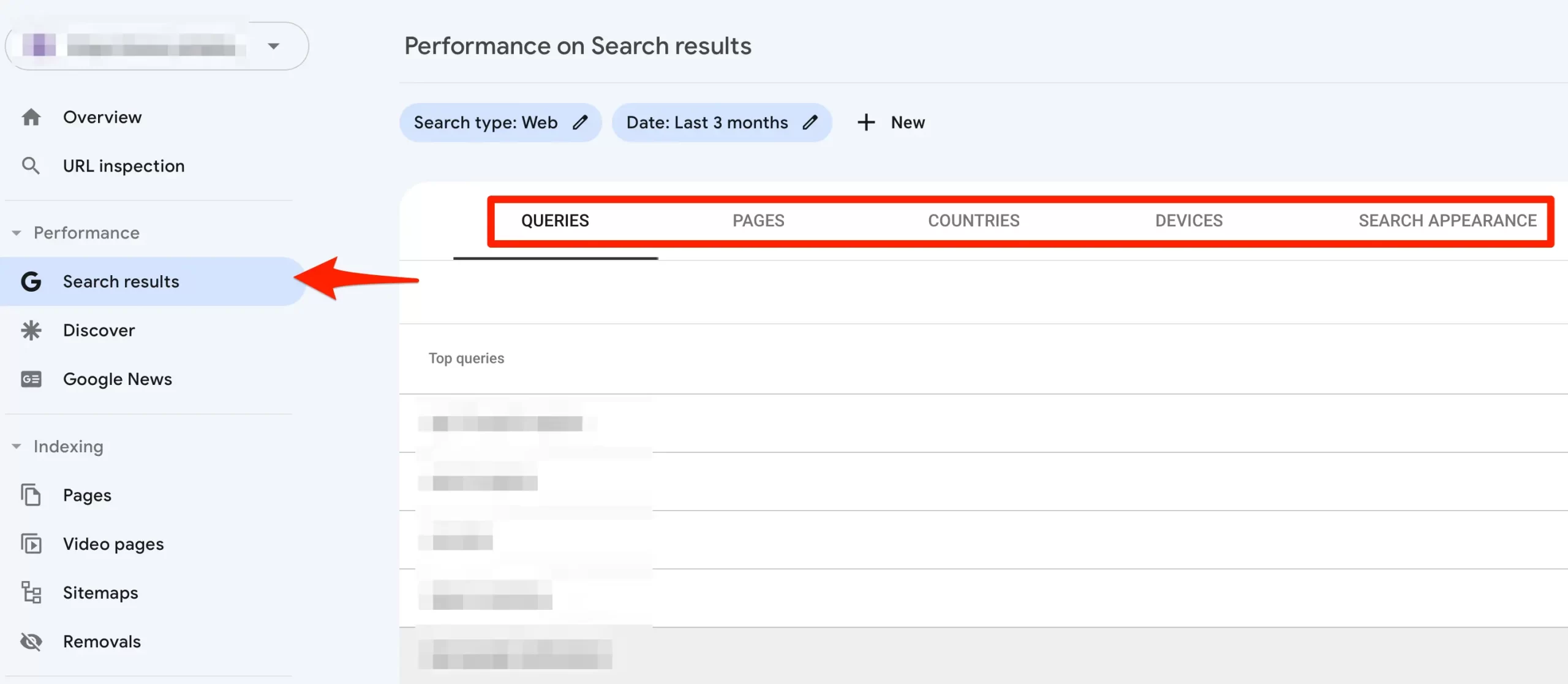
5. Check Your Organic Traffic
The next step before doing a deeper analysis is to check your organic traffic. Login to Google Search Console and view the "Search Results" report.
This will give you an idea of how much traffic your website gets from Google. You can see the keywords, pages, devices, countries, and more information.
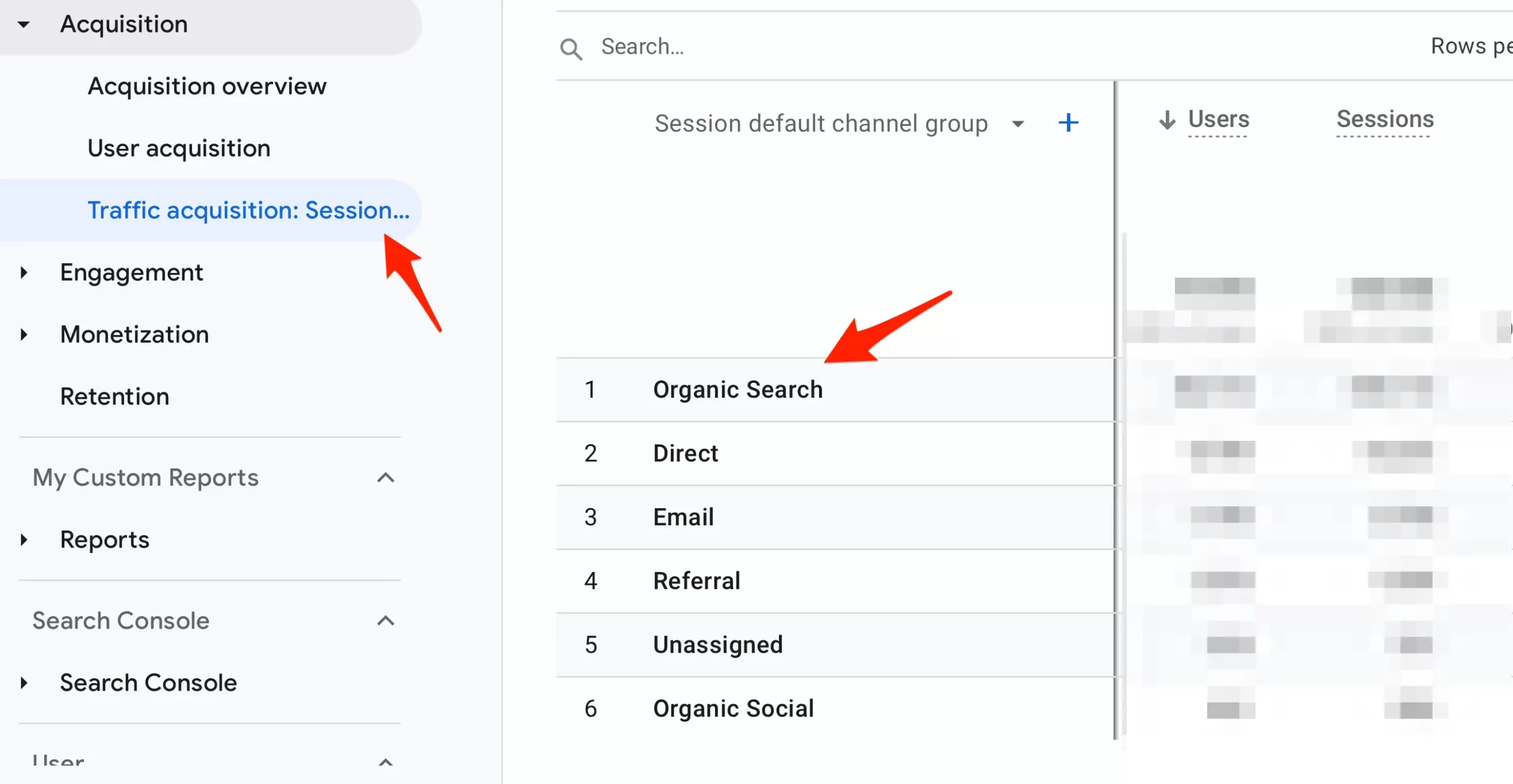
Another way is to use Google Analytics to view traffic from all search engines.
Login to Google Analytics and go to Traffic Acquisition under Acquisition. Look at the "Organic Search" data, which includes users, sessions, views, and more information.
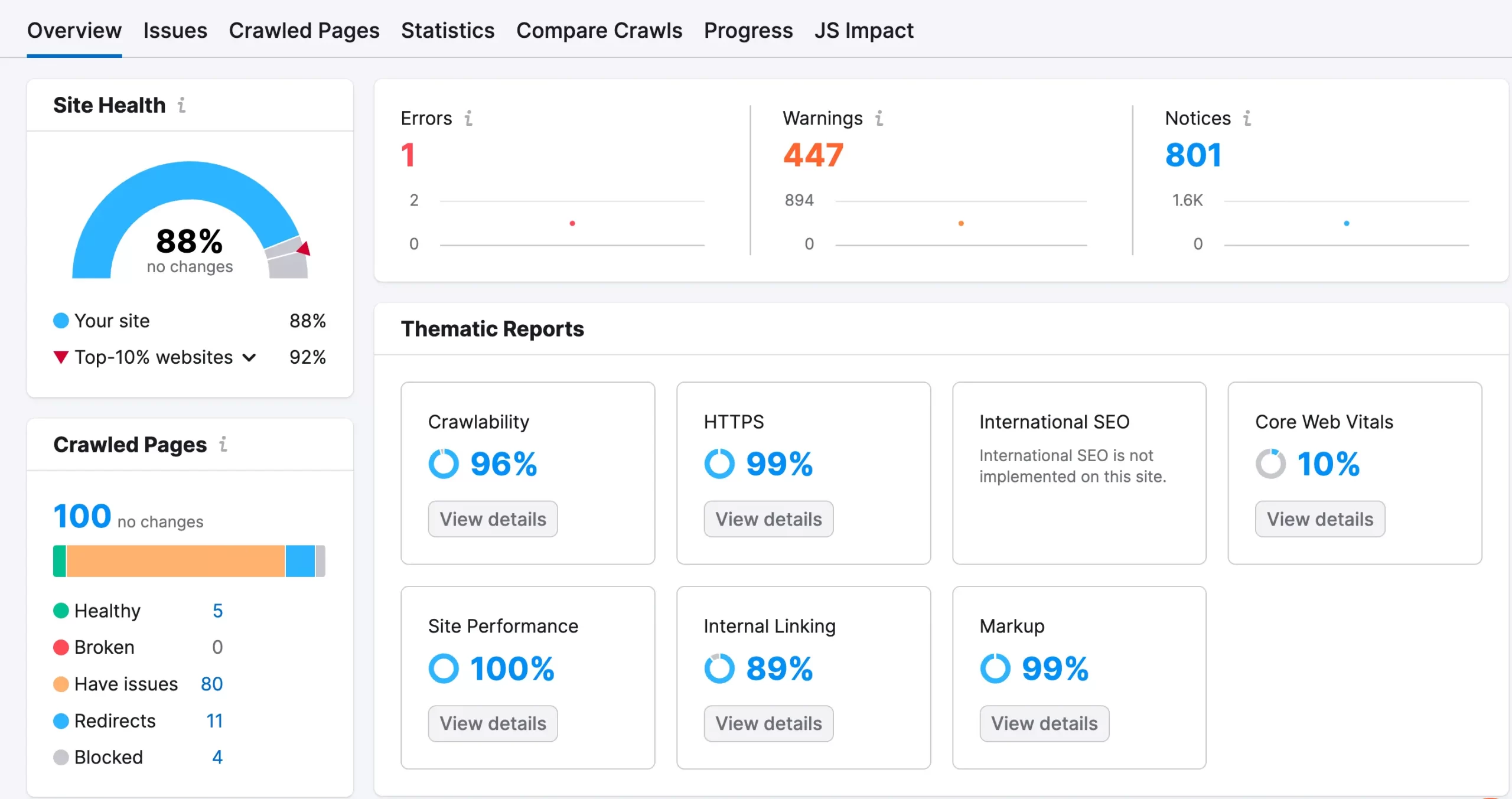
6. Run A Website Crawl
The next step is to use a site audit tool like Semrush Site Audit, Ahrefs Website Audit, Screaming Frog, or others to identify potential issues with your SEO.
Running a comprehensive website crawl is like giving your site a thorough health check-up. It uncovers issues that might not be easily noticeable but are critical for SEO performance.
SEO audit tools simulate how search engines crawl your website and report on several issues like: broken links, page load issues, missing title and meta tags, sitemap problems, structured data issues, and much more.
Here is an example of what the SEO audit dashboard of Semrush looks like:
7. Analyze Your Website's Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals is a set of specific metrics that Google considers essential in a webpage's overall user experience.
Start by using tools like Google's PageSpeed Insights to analyze these vitals.
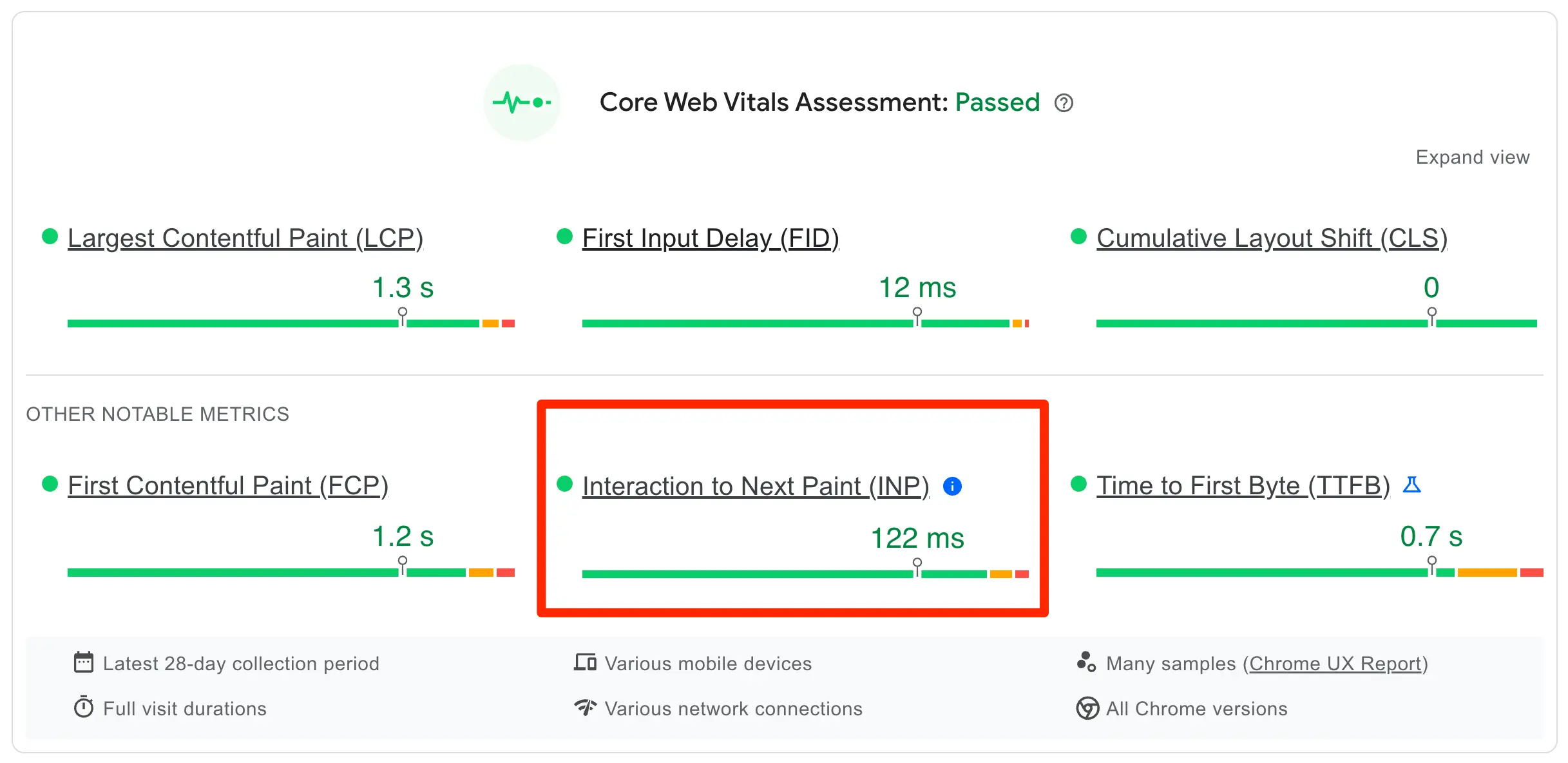
For Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures loading performance, ensure that the largest content piece on your page loads within 2.5 seconds. If it takes longer, you might need to optimize your server, use a content delivery network, or optimize your images and file formats.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) measures interactivity; aim for an INP of less than 200 milliseconds. This can be achieved by reducing the impact of third-party code, minimizing JavaScript execution time, and more.
Lastly, Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures visual stability; strive for a CLS score of less than 0.1. To improve this, ensure images and embedded videos have dimensions, and avoid inserting new content above existing content unless in response to a user's action.
8. Check Mobile Page Experience
One of the mistakes people make when doing SEO audits is to check the desktop version of a website, forgetting that Google is using the mobile version for crawling, indexing, and ranking.
As part of your review, you should check your website on mobile and ensure that the user experience is the best possible. This means:
Secure Pages: Ensure your pages are served securely over HTTPS.
Mobile Usability: Check how well your content displays on mobile devices. This includes evaluating layout, text size, and menus.
Lighthouse is an effective tool for identifying a range of improvements related to mobile usability, which is a critical aspect of the page experience.
Avoiding Intrusive Interstitials: Intrusive interstitials can make content less accessible to mobile users. Ensure your website does not use pop-ups or ads that interfere with the main content, as these can negatively impact the user experience and your site’s SEO performance.
9. Improve Your Website Speed
From my experience talking to clients, handling website page speed is one of the most challenging tasks, at least for non-technical users.
Unfortunately, it is also one of the most important SEO factors that must be addressed successfully. Study after study outlines the importance of page speed (especially for mobile) and how it can affect your rankings and conversion rates.
Your website should load within the core web vitals score outlined above. Here are some actionable tips to follow:
- Compress all your website images using tools like Optimizilla or Squoosh (by Google). These tools can dramatically reduce the size of an image without sacrificing quality.
- If you have a lot of images, consider using a CDN.
- Minimize HTTP calls by using sprites and browser caching.
- Minify your CSS and HTML to make their size smaller.
- Use a caching plugin or page speed service to serve cached pages to users.
- Remove unnecessary JavaScript from pages.
- Update to the latest version of PHP.
- Update your website and software to the latest versions.
If the above list does not make much sense to you, you better hire a developer or SEO expert to do the work for you. It will not cost you a lot, and you have to do it to improve your SEO rankings and conversions.
10. Check Your Internal Links
Linking your pages together is useful to both search engines and users.
Check and make sure that you are indeed linking related pages together by considering these 4 factors:
- You are not only using keyword anchor text for the internal links, but you use both the full page title and non-keyword anchor text.
- The pages you want to rank better in search have the greatest number of internal links.
- The pages you want to rank better in search are linked from your home page.
- You have between 2 – 10 internal links per page.
11. Analyze And Identify Toxic Links
As part of the SEO Audit, you should analyze your backlink profile and identify any toxic links that might impact your rankings.
You can check your incoming links using a backlink checker tool or the Google Search console's ‘Links to your site’ report.
While reviewing your backlinks, answer the following questions:
- How many unique domains are linking to you?
- Which of these domains are considered trusted domains?
- How many links are pointing to your home page, and how many links to your internal pages?
- Which of your pages have the most incoming links?
- What percentage of the links are keyword-based?
- What is the ‘toxic score’ of each link?
Depending on the answers, you may have to take some corrective actions and adjust your action plan accordingly.
For example, if only a few domains link to you, you must get links from related domains. Your task is to create a list of possible websites for guest blogging or blogger outreach campaigns.
If you don’t have links from trusted domains, you need to get in touch with the leaders in your niche and let them know that you exist (it’s easier said than done, but if you get noticed by the big fish, you have more chances of surviving in the pot).
If all the links point to your homepage, you must ensure you get links to your internal pages.
If all the incoming links are keyword-based (and Google did not penalize you yet), you need to urgently change them by making them more natural by using your domain name only, your full post title, and things like ‘click here,’’ link,’ etc.
For step-by-step instructions, read: how to remove bad backlinks from Google.
12. Do A Competitor Analysis
The next item on the list is benchmarking your SEO performance against competitors. This is necessary because the performance of your competitors impacts your chances of achieving higher rankings for related keywords.
Here is how to perform an SEO competitor analysis:
Identify Your Competitors: Begin by figuring out who your competitors are. Go to Google, search for your primary keywords, and see which websites rank in the top positions of Google. Tools like Semrush or Ahrefs can also help you identify these competitors by showing who ranks for keywords similar to those on your site.
Analyze Their On-Page SEO: Examine your competitors’ on-page SEO strategies. Look at their title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, and keyword usage. This can give you insights into how they are optimizing their pages and what you might be missing.
Review Their Content: Evaluate your competitors' content quality, depth, and type. See what content they use to engage their audience and how well it's performing.
Track Their Performance Over Time: Keep an eye on how your competitors' strategies evolve. This can help you stay ahead of the curve and adapt your strategies proactively.
13. Identify New Keyword Opportunities
SEO Auditing is not only for finding and fixing errors but also for spotting opportunities to grow your website. One of the ways to do this is to identify new keywords that can generate targeted traffic.
A key strategy is to analyze your competitors' keyword profiles. A keyword research tool can reveal what keywords your competitors are ranking for, but your site is not. This can uncover untapped niches or long-tail keywords that you might have overlooked.
Another effective method is to review your existing content's performance using Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Look for patterns in user queries and the performance of existing pages.
This analysis can help you identify topics that your website has a high Google trust and topical authority, making it easier to rank new content.
For example, you might find that a blog post about "beginner gardening tips" is unexpectedly attracting traffic for the keyword "easy plants to grow." This indicates that your audience is interested in this specific topic and that Google considers you a good resource for it.
You can use this information to create more content focused on easy-to-grow plants and drive more traffic to your site.
14. Identify New Link Opportunities
Identifying new link opportunities is critical in an SEO audit, as backlinks are a key ranking factor for search engines.
Begin by examining your competitors' backlink profiles using a backlink checker tool. Look for patterns in their backlinks, such as specific websites or types of content that frequently link back to them.
Next, consider what type of content could be valuable for others to link to. Typical examples include case studies, statistics, and original research.
Reach out to websites with relevant content and suggest where your content could add value to their users and what you can give them back in return.
15. Update Your Top Performing Pages
Another common SEO mistake an SEO audit can help you fix is losing rankings for your top-performing pages. It's normal for webmasters to concentrate on publishing new content, but you should take action to protect your existing rankings from dropping.
Use Google Search Console to find your high-ranking pages and create a plan to update them regularly by:
- Improving your on-page SEO - Enhance elements like title tags, meta descriptions, and header tags to ensure they are keyword-rich and relevant to the content.
- Adding new high-quality visuals - Incorporate relevant images or custom-made visuals to make the content more engaging and shareable.
- Optimizing for Google featured snippets - Structure your content with clear, concise answers to common questions, targeting the 'position zero' snippet spot in search results.
- Optimizing content to match changing user intent - Update the content to align with the latest trends and user queries, ensuring it remains relevant and useful.
- Updating statistics - Refresh any data or statistics in your content to reflect current information, enhancing credibility and relevance.
- Checking for broken links - Regularly audit and fix any broken links (external and internal) to improve user experience and maintain the integrity of your site's structure.
Next Steps
The above SEO audit checklist covers the technical SEO, on-page SEO, and off-page SEO checks you need to make to improve your SEO. You can go deeper by enrolling in a technical SEO course and visiting the resources below.



