- The Beginners Guide To SEO
- What Is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
- Why Is SEO Important?
- SEO Starts With Indexing
- Step 1: Keyword Research
- Step 2: Content Quality
- Step 3: User Experience Factors
- Step 4: On-Site Optimization
- Step 5: Technical SEO
- Step 6: Off-Page SEO
- Step 7: Mobile SEO
- Step 8: Local SEO
- Step 9: SEO Performance
- Get Started With SEO
The Beginners Guide To SEO
This comprehensive SEO for beginners guide will help you get started with SEO. It has been written specifically for people who want to learn the basics of SEO and build a strategy to get higher rankings and organic traffic.
The guide was prepared by an SEO expert with over 20 years of experience ranking websites on top of Google and teaching about SEO.
What Is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
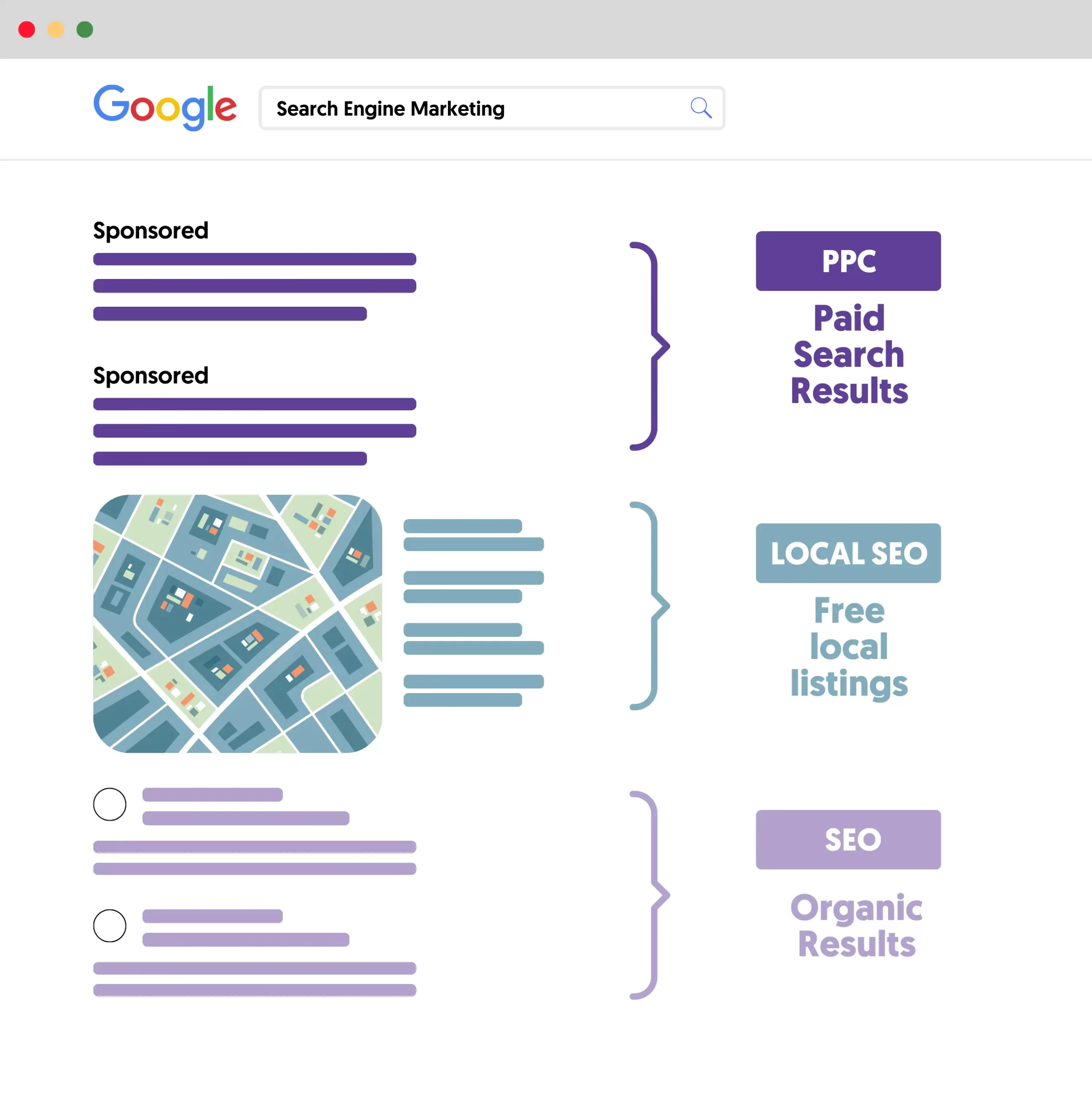
Search Engine Optimization is the process of optimizing a website to rank higher in Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) in search engines like Google.
When you search on Google or Bing, you get a list of related ads at the top of the page and then the organic results. With SEO, you can optimize your website and content to get maximum visibility in organic listings.
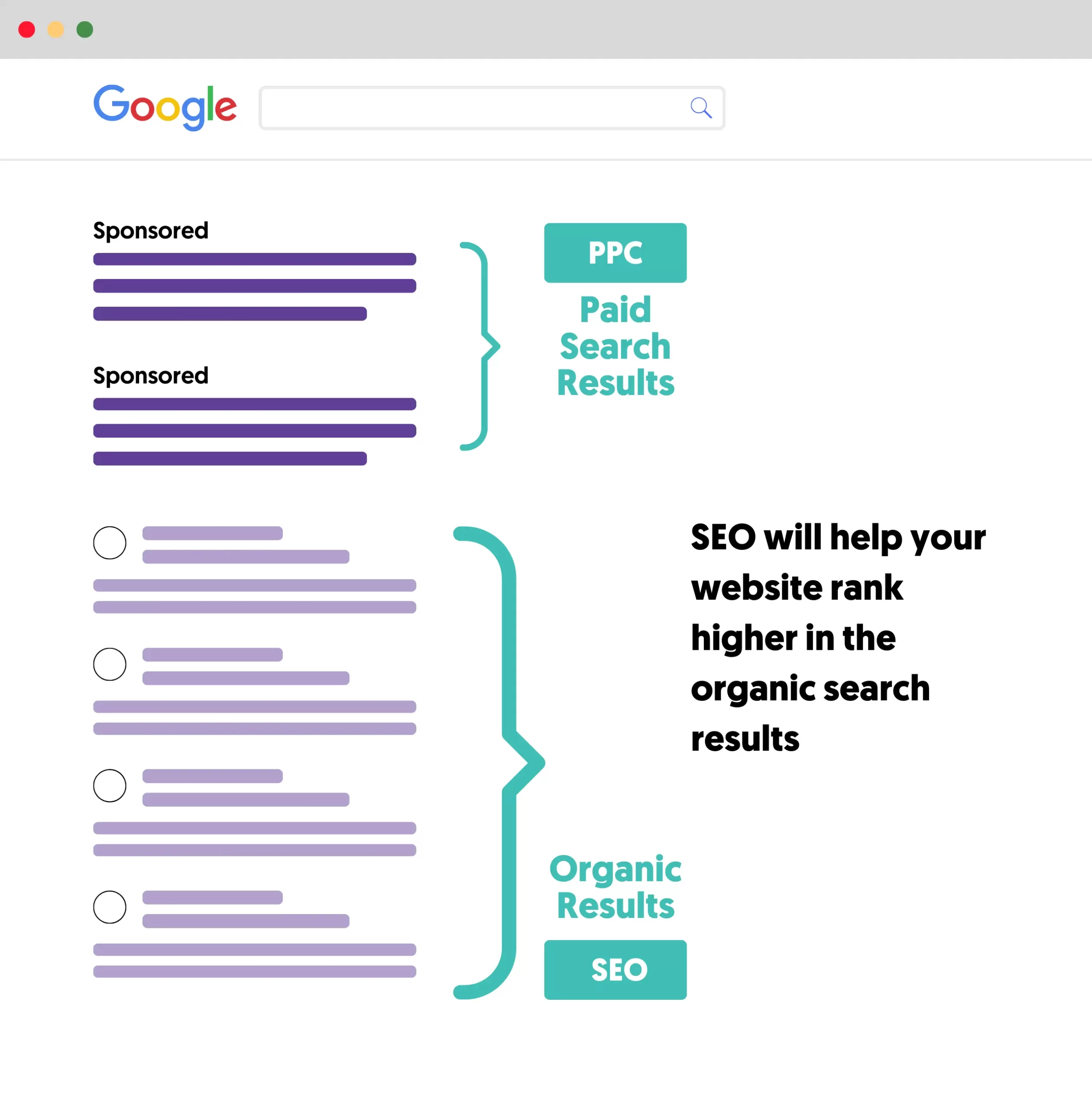
Organic results are not limited to text results, but they may include rich snippets, images, videos, related questions, and other elements intended to help the user find the best possible answer or solution to their query.
SEO will tell you how to configure your website so that search engines can understand your content and rank it as high as possible for the search terms that matter to your business.
Why Is SEO Important?
SEO is important because most users will click a result closest to the top of the page and will not scroll down for further options.
This means you won't get enough traffic if your website does not appear in one of the 5 positions of the results or one of the search results features (rich snippets, featured snippets, etc.).
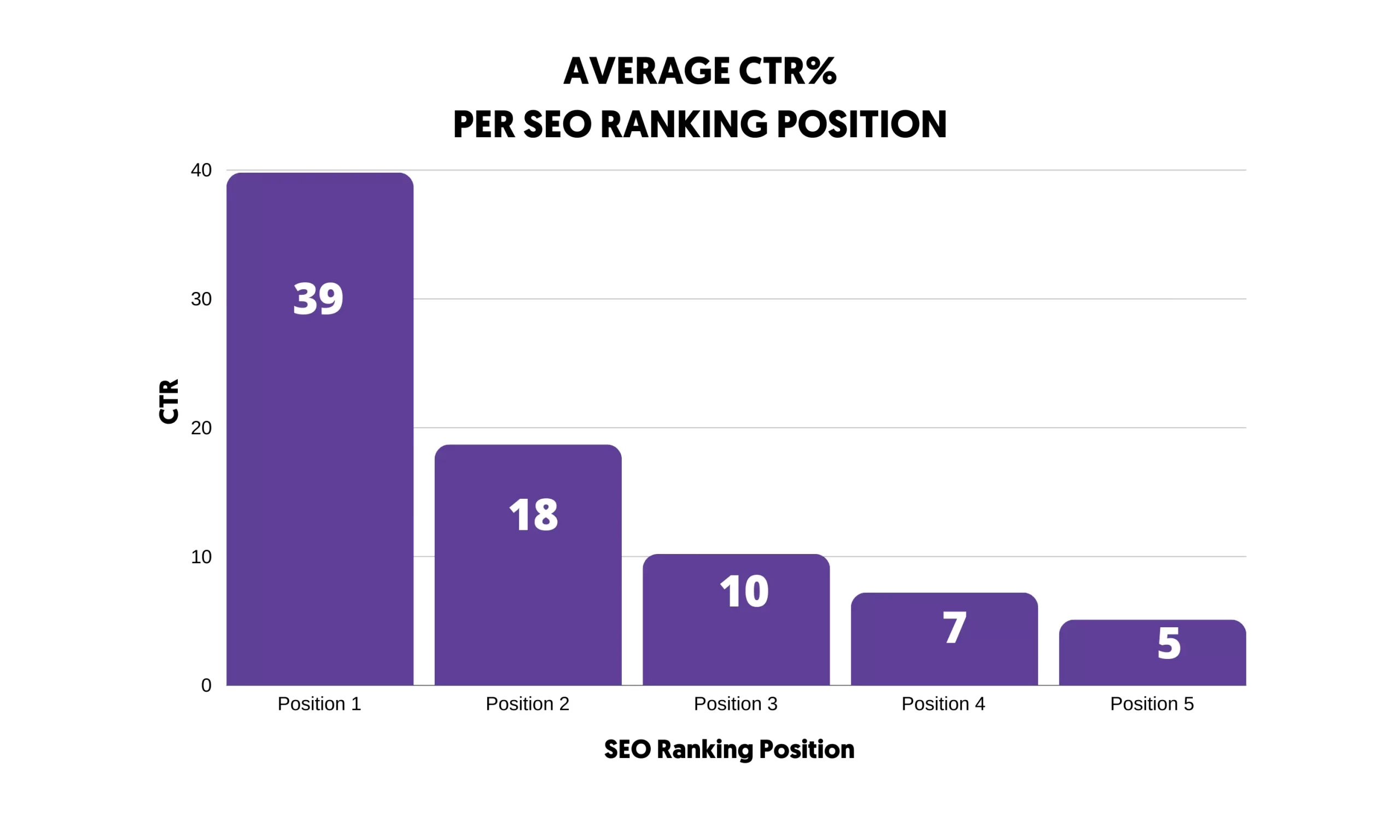
To get serious traffic from Google and other search engines, your website must consistently appear at the top of the organic results for related keywords.
Besides the traffic gains, other benefits of SEO include the following:
- Brand Awareness - brands appearing on top of the results are more trusted by users than brands that don’t have a presence in the search results.
- Usability - when you follow good SEO practices, you’ll create a website that offers users a great experience, with additional benefits like increased conversions.
- Sociability - websites on top of Google are more likely to be shared on social networks and gain extra traction and traffic.
- Gain a Competitive Advantage - with SEO, you can outrank your competitors and become a leader in your industry.
SEO Starts With Indexing
The first step of SEO is to ensure that Google can crawl and index your website. A misconfiguration at this stage will keep your pages out of the Google index, minimizing your chances of getting rankings and traffic.
To understand how indexing works, let's quickly review how search engines work. In a nutshell, search engines crawl the web to find and index all available public pages. Then, they organize this information so that the ranking algorithms can access it.
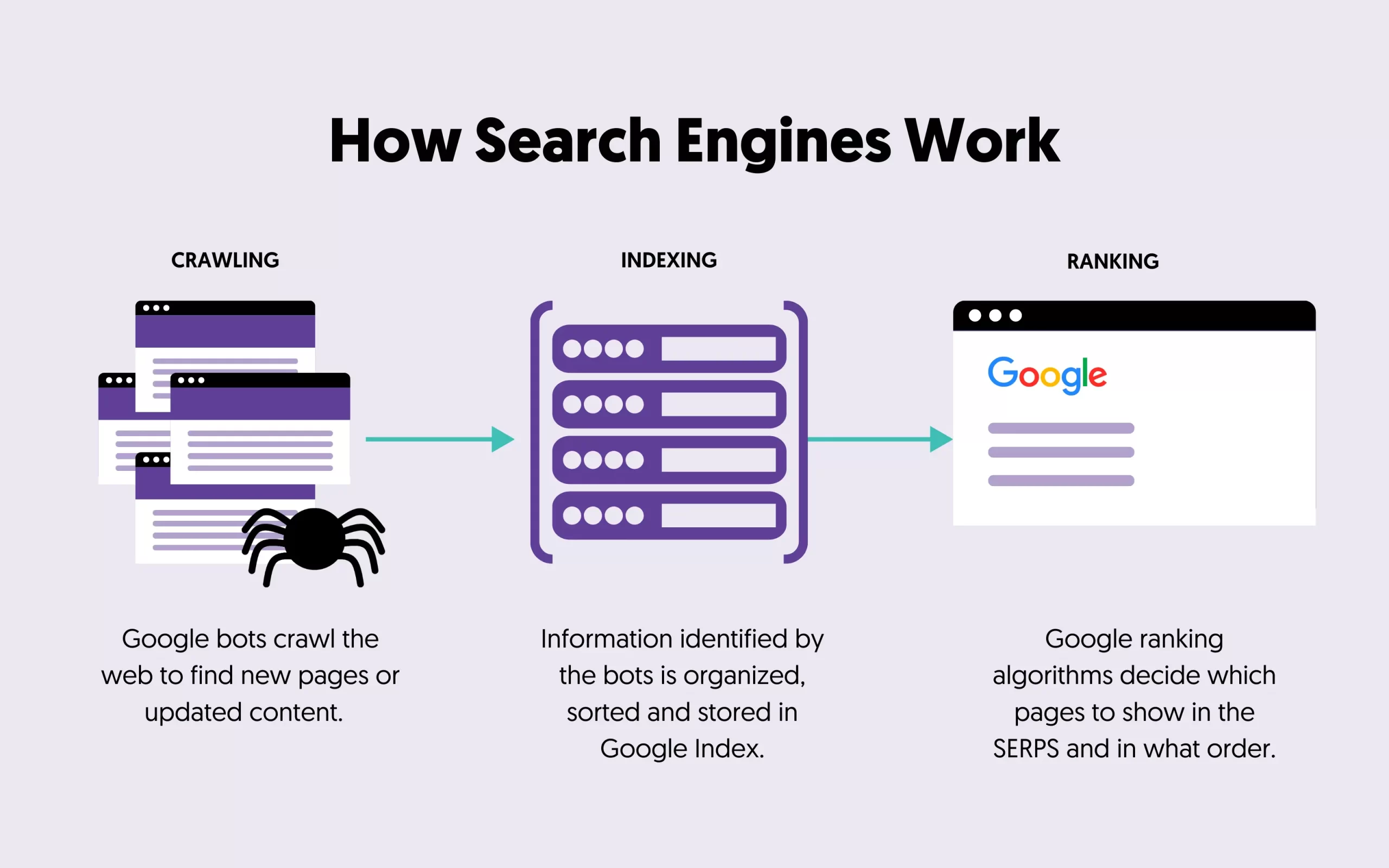
Your job as an SEO is to ensure that the Google bot can index all the important pages of your site, and you can check that using the Google Search Console.
After adding your website to Google Search Console, view the Page Indexing Report and look for the “Why pages aren’t indexed” section. This gives you a list of all pages of your website that are not in Google’s index.
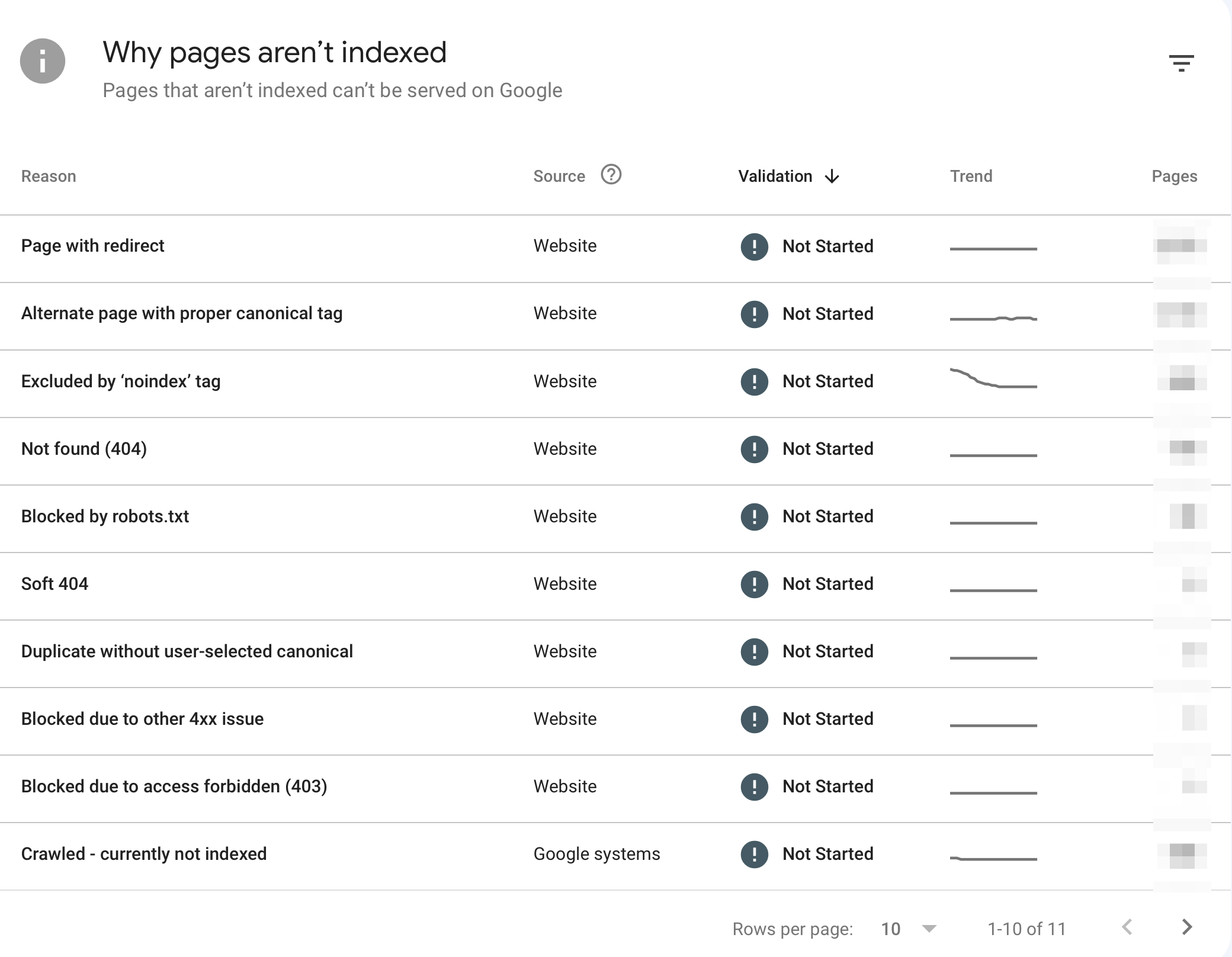
Click on the errors to see which pages are affected, and use the INSPECT URL button to find out why a page is not indexed.
While it’s normal for Google not to index all your pages, you should pay special attention to Not Found (404) and Soft 404 errors, which may affect the user experience.
Once you confirm there are no critical issues, you can get into the SEO fundamentals.
Step 1: Keyword Research
Keyword research will help you find which keywords (words or phrases) users type in search engines that are relevant to what your business or website is offering.
You must do this from day one to provide users with the right content to satisfy their intent. Here is an overview of how the keyword research process works.
1. Start with a broad topic or idea: To begin, identify a broad topic or idea related to your business, website, or blog. For example, if your website is about fitness, your broad topic might be "exercise," “weight loss,” or "health and fitness."
2. Find relevant keywords: Use tools like Google's autocomplete feature, related searches, people also ask, and your knowledge to brainstorm potential keywords related to your broad topic. Make a list of all the potential keywords that come to mind.
3. Conduct keyword analysis: Use a keyword research tool like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or Semrush to see how many people are searching for each keyword, how competitive it is, and what other related keywords people are searching for. This will help you to narrow down your list of potential keywords.
4. Analyze search intent: Analyze the search intent behind each keyword. This will help you understand why people search for that keyword and what content they want. For example, if someone searches for "how to lose weight", their intent might be to find tips and advice on weight loss.
5. Research your competitors: Using a keyword research tool, you can analyze the keywords used by your competitors and get more ideas for keywords you can use on your website.
6. Choose your target keywords: Based on the search volume, competition, and search intent, choose a set of target keywords that you want to rank for. These should be keywords that are relevant to your business, have high search volume, and are not too competitive.
7. Be realistic: Unfortunately, due to the competitiveness of the Internet, it's impossible to rank for all the keywords you want. If you're starting now, you'll have to compete with big websites that have gained Google's trust, making it challenging to rank for high-volume keywords. Instead, you should set realistic goals and go after keywords you can rank for. These are known as long-tail keywords.
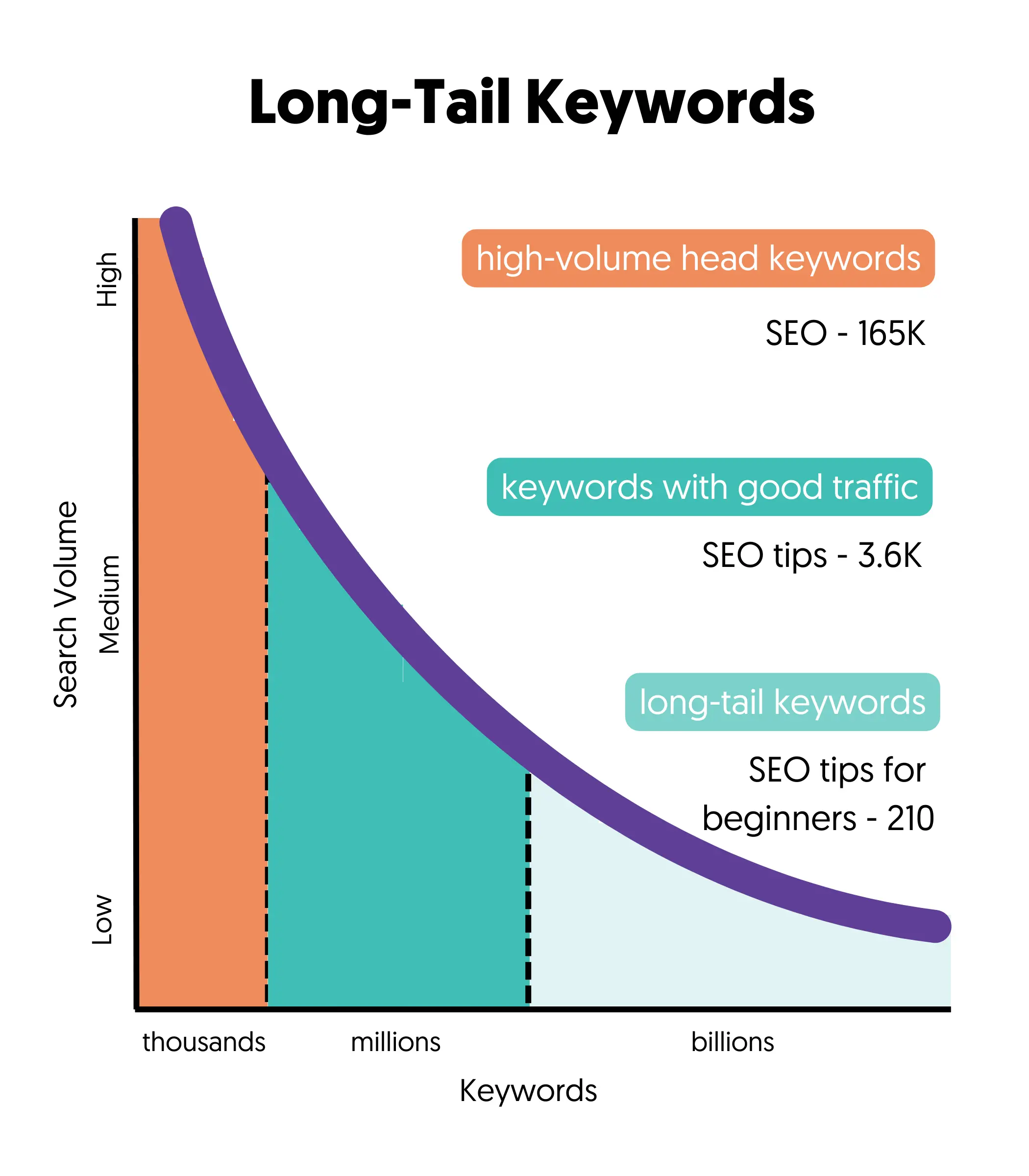
Step 2: Content Quality
Once you have a list of keywords you can potentially rank for, the next step is to create SEO-friendly content around those keywords. SEO-Friendly content meets the following criteria:
- It's high-quality.
- Matches the search intent.
- Optimized for featured snippets.
High-Quality Content
Any content you create for your site doesn't have to be superb, but it has to be better than what is already available on Google.
In simple terms, this means:
- It is unique for the particular website and has not been published online.
- It’s thorough and explains a topic in detail.
- It’s unbiased and tells both sides of a story.
- It’s authoritative based on experience, research studies, and data.
- Demonstrates high levels of E-E-A-T.
Matches The Search Intent
Your content must provide real value to the users and satisfy their search intent. A user's search intent is what searchers want to see for a particular search query.
Consider these examples:
- If you want to rank for "best yoga mats", your content should include a list comparing different yoga mats.
- If you want to rank for "SEO Fundamentals", your content should include the SEO basics in a format suited for beginners.
- If you want to rank for "how to fix a zipper", your content should include the steps to fix a broken zipper.
The easiest way to figure out the search intent for a keyword is to look at the top 5 ranking websites on Google.
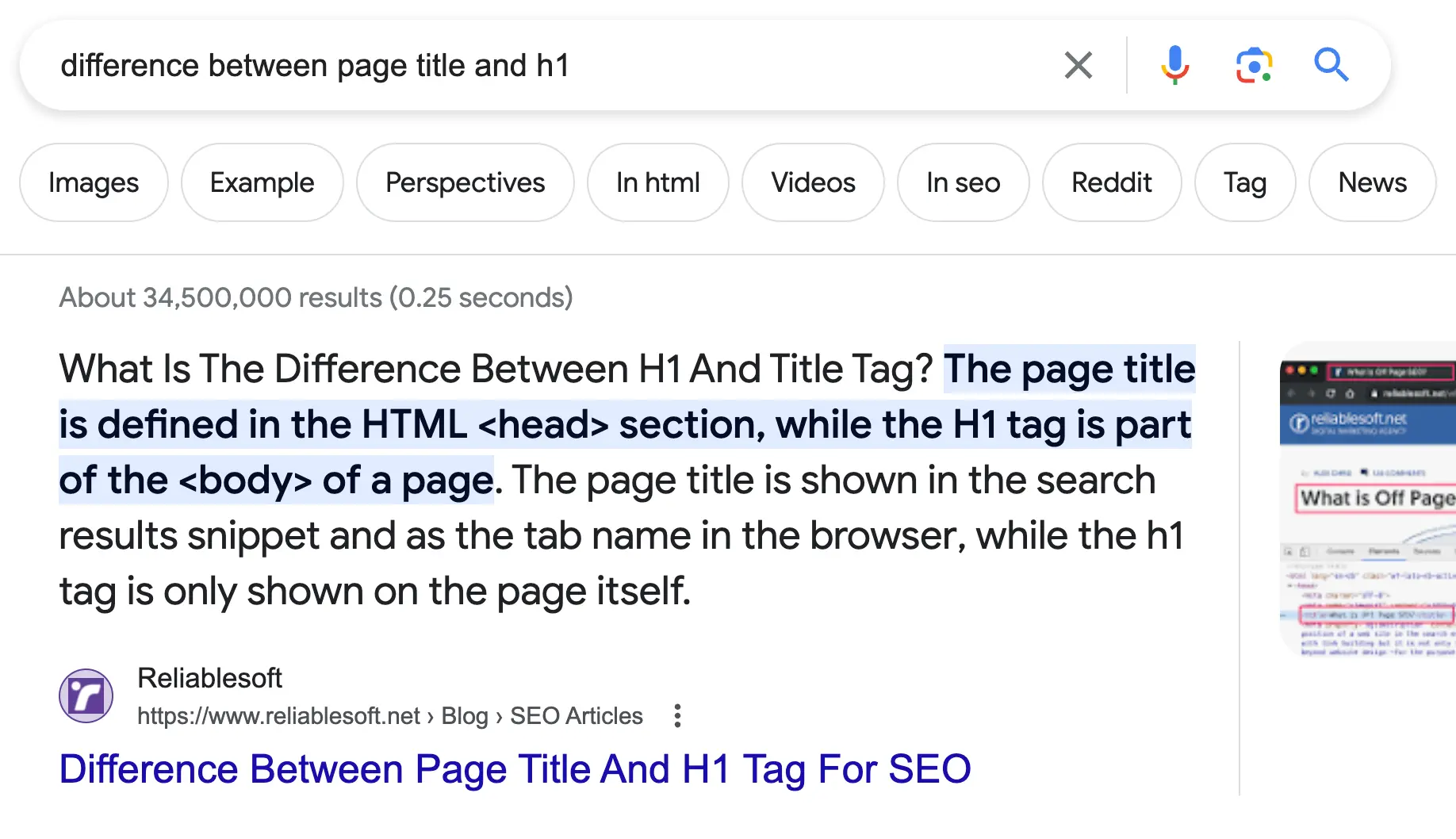
Optimized For Featured Snippets
Featured snippets appear on top of the organic results, giving users direct answers to their queries. Types of featured snippets include paragraphs, lists, videos, and images.
Featured snippets benefit from higher organic CTR, translating to more traffic from searches.
Here is an example:
Step 3: User Experience Factors
Besides publishing helpful content tailored to satisfy users' needs, you should also pay special attention to user experience (UX) factors.
Your goal is to keep users on your page and not return to the search results. This signals to Google that users are unhappy with your content and can negatively impact your rankings.
Here are a few SEO rules to make the user experience better:
Optimize The Above The Fold Area
Ensure that the part of your content that is visible without scrolling (known as above the fold) instantly grabs the reader's attention and communicates the value of your page.
Use engaging headlines and images to win the first impression and indicate to users that they are in the right place. Add keywords to your content to make it more relevant to the user's query.
Content Formatting
Organize your content into digestible chunks to enhance readability and retention. Use lists and bullet points to break down long text and make your content skimmable.
Break your content into short paragraphs, ideally 2-3 sentences each. Incorporate subheadings to guide readers through your article, and use bold or italic formatting to emphasize important points.
Step 4: On-Site Optimization
The next step is to deal with on-page SEO. This refers to techniques to help search engines understand your content better.
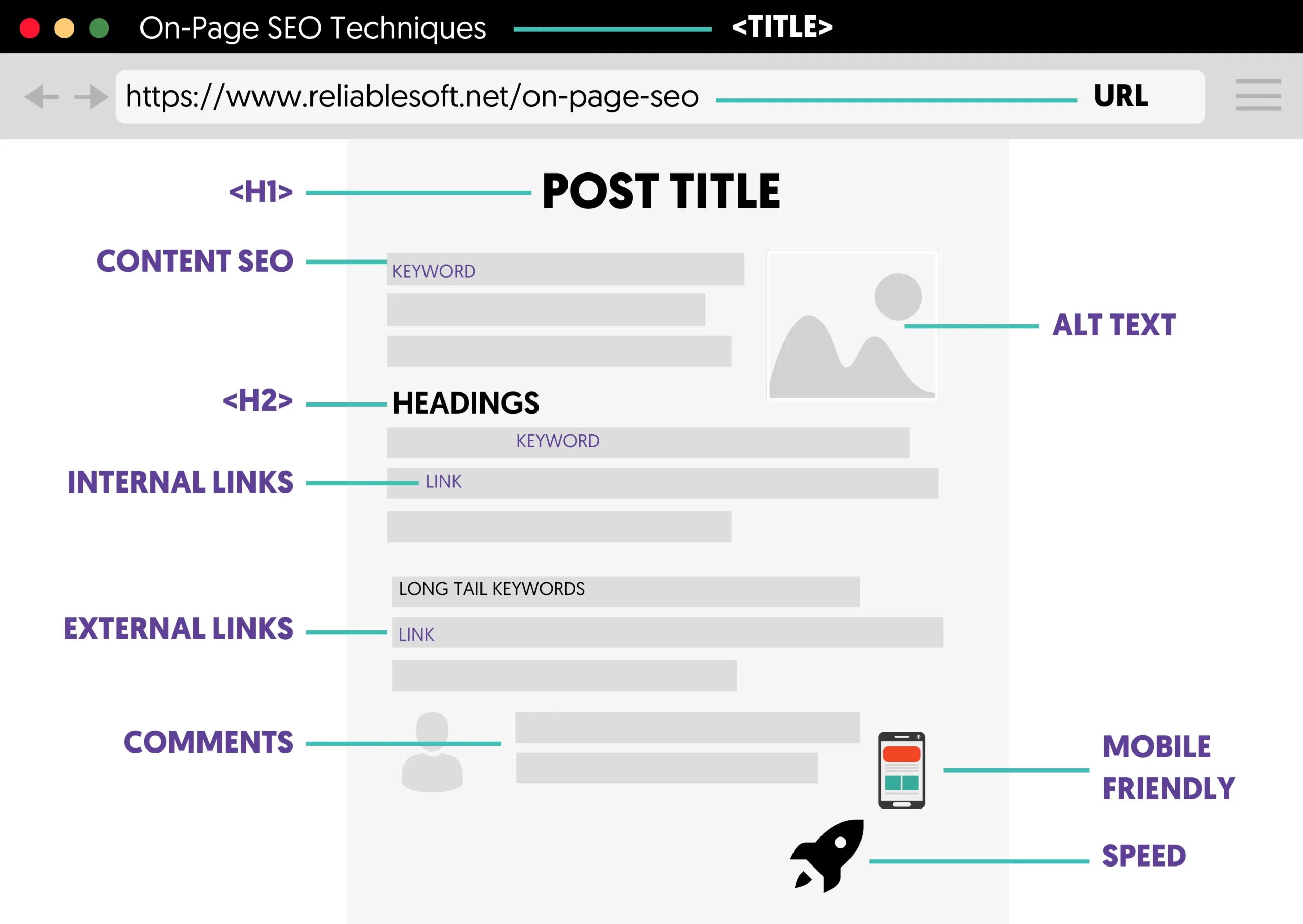
Page Title Tags
The page title is a critical SEO factor. It is shown in the SERPs, impacts your CTR, and is used by search engines during the ranking process.
SEO-optimized title tags give crawlers a strong signal about the page content.
To optimize your page titles, follow these simple practices:
- Provide a unique title for all pages.
- Make titles relevant to the content.
- Keep the length between 50 and 60 characters.
- Add your target keyword, preferably at the beginning.
Here is an example of an SEO-friendly title:

Meta Descriptions
Another essential SEO element to optimize is the meta description. The meta description is a special HTML tag that gives users a short summary of what the page is about. It is shown below your page title and is another opportunity to advertise your page to users.
Although Google may pick up text from a page to create a description, writing unique meta descriptions for all your pages is a good SEO practice.
The SEO rules for optimizing your meta descriptions are simple:
- Keep the length between 150 and 160 characters.
- Include your primary keyword or related keywords.
- Tell users what to expect when they visit the page.
Here is an example of a meta description in Google SERPs:
Page URLs
Another SEO element that is very easy to optimize is the page URL.
Although this is no longer a strong signal, SEO-friendly URLs containing your target keyword (or related keywords) are better for users and search engines.
For example, the title of this article is “The Easy SEO Guide For Beginners,” and the URL is /seo-basics-guide/.
The shortest version tells you exactly what the article is about, is easier to remember, and includes the main target keyword.
Here is an example:
H1 Tag and Page Headings
Optimize your H1 Tags and other page headings.
A well-structured page should have one H1 Tag on top and several H2 or H3 tags for the page headings.

The value of the H1 tag can be the same as the page title or slightly different.
The value of the sub-headings should ideally include related keywords and be informative enough to help users while scrolling through the content.
Image Alt Text
A good piece of content can become even better with high-quality images.
When using images, make sure that you optimize their size so that they won’t slow down the website and that you provide a meaningful value to the ALT tag.
Read this guide on how to write ALT text for your images.

Internal Linking
Internal links are links pointing to pages on your website. By adding internal links to your content, you help search engines understand the structure of your website, and they make navigation easier for users.
It's also a great way to pinpoint to search engines which are the most important pages of your site.
Here is an example of an internal link:

When adding internal links, follow these rules:
- Link from new pages to older pages and vice versa.
- Use meaningful anchor text.
- Add links when they're useful to users.
- Link to your important pages only.
Read our internal linking best practices guide for more tips and examples.
Step 5: Technical SEO
The next step in the SEO process is to deal with some technical issues related to indexing errors, site speed, mobile responsiveness, site architecture, XML sitemaps, canonical URLs, and more.
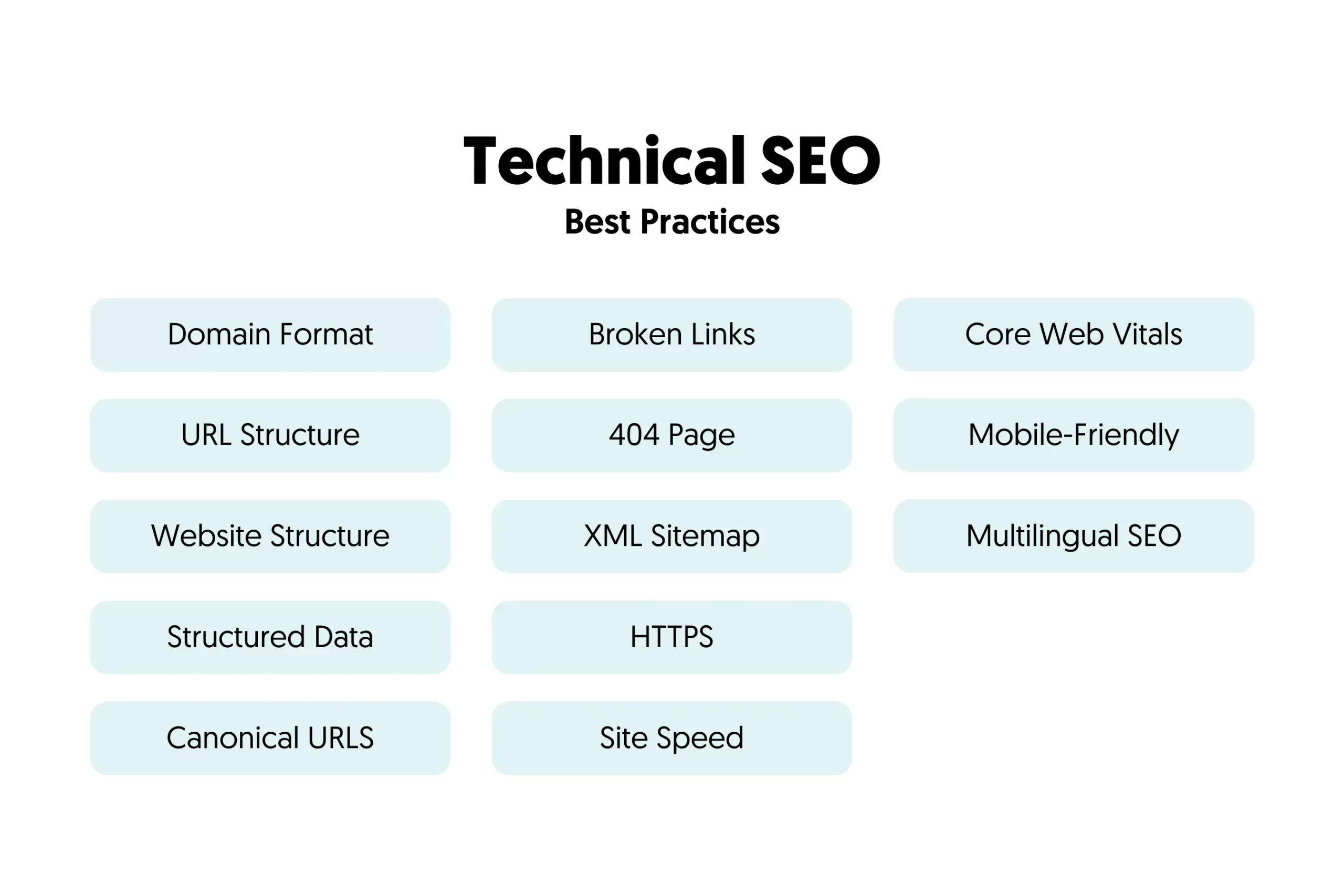
This stage is known as Technical SEO. The most important SEO concepts are:
Robots.Txt
You can use robots.txt file to tell search engines which page NOT to crawl and index. By default, all pages of your site will be indexable unless disallowed in the robots.txt file.
Here are a couple of examples of how the robot.txt file looks like:
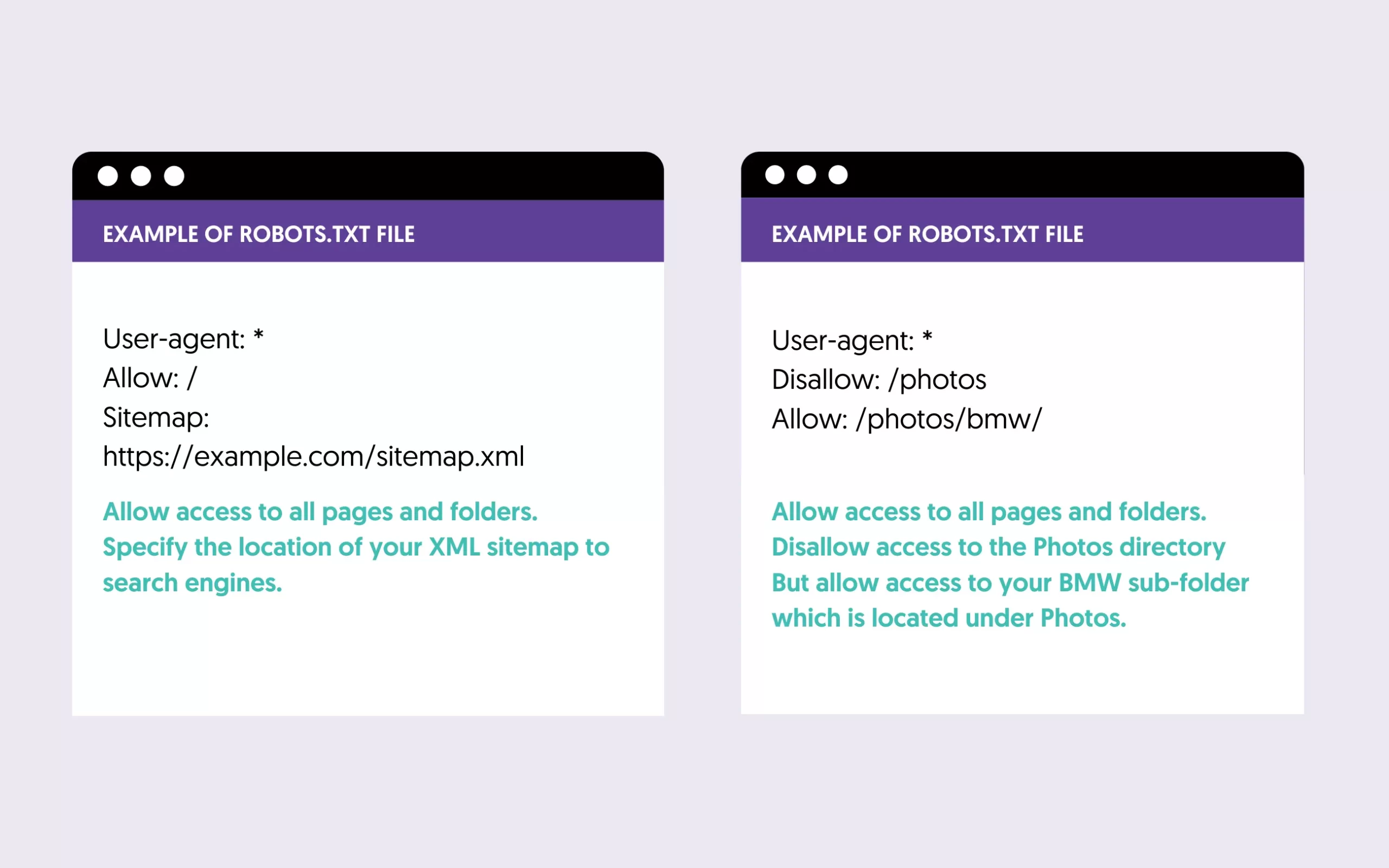
Check that your robots.txt does not block search engines from accessing important content, and use these guidelines to optimize it.
Page Experience (Core Web Vitals, HTTPS)
Page Experience Signals are a set of factors that Google has identified that contribute to a positive user experience.
The Page Experience Signals include:
- Core Web Vitals: these are a set of specific metrics related to page speed and user interaction with a website.
- HTTPS: this refers to whether a web page uses a secure connection. Pages that use HTTPS encryption provide a more secure browsing experience for users.
If there are any issues, you can use the Page Experience Report in Google Search Console to see which pages are affected and what actions are recommended.
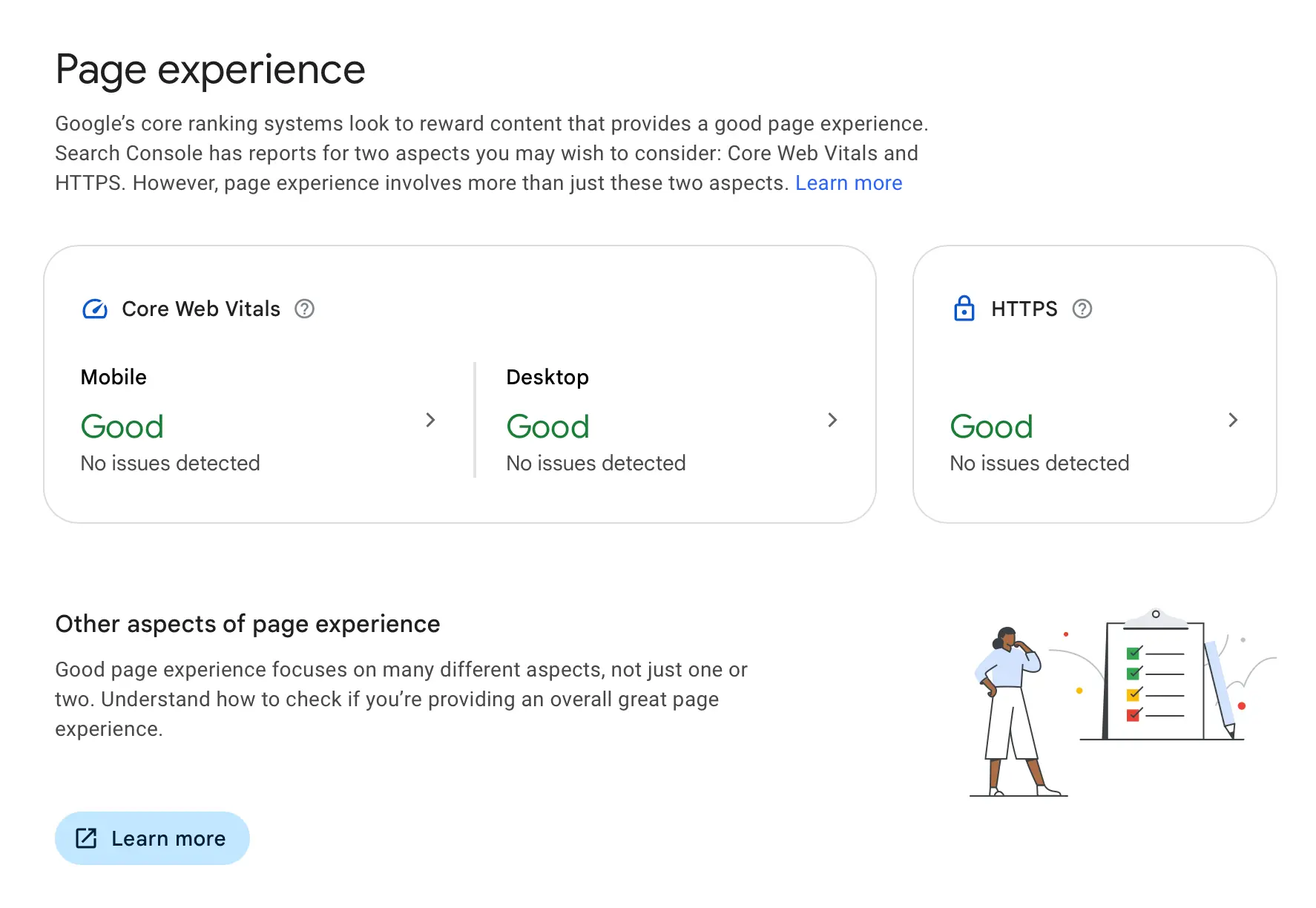
Read our Best SEO Practices guide for instructions on how to deal with page speed and core web vital problems.
XML Sitemaps
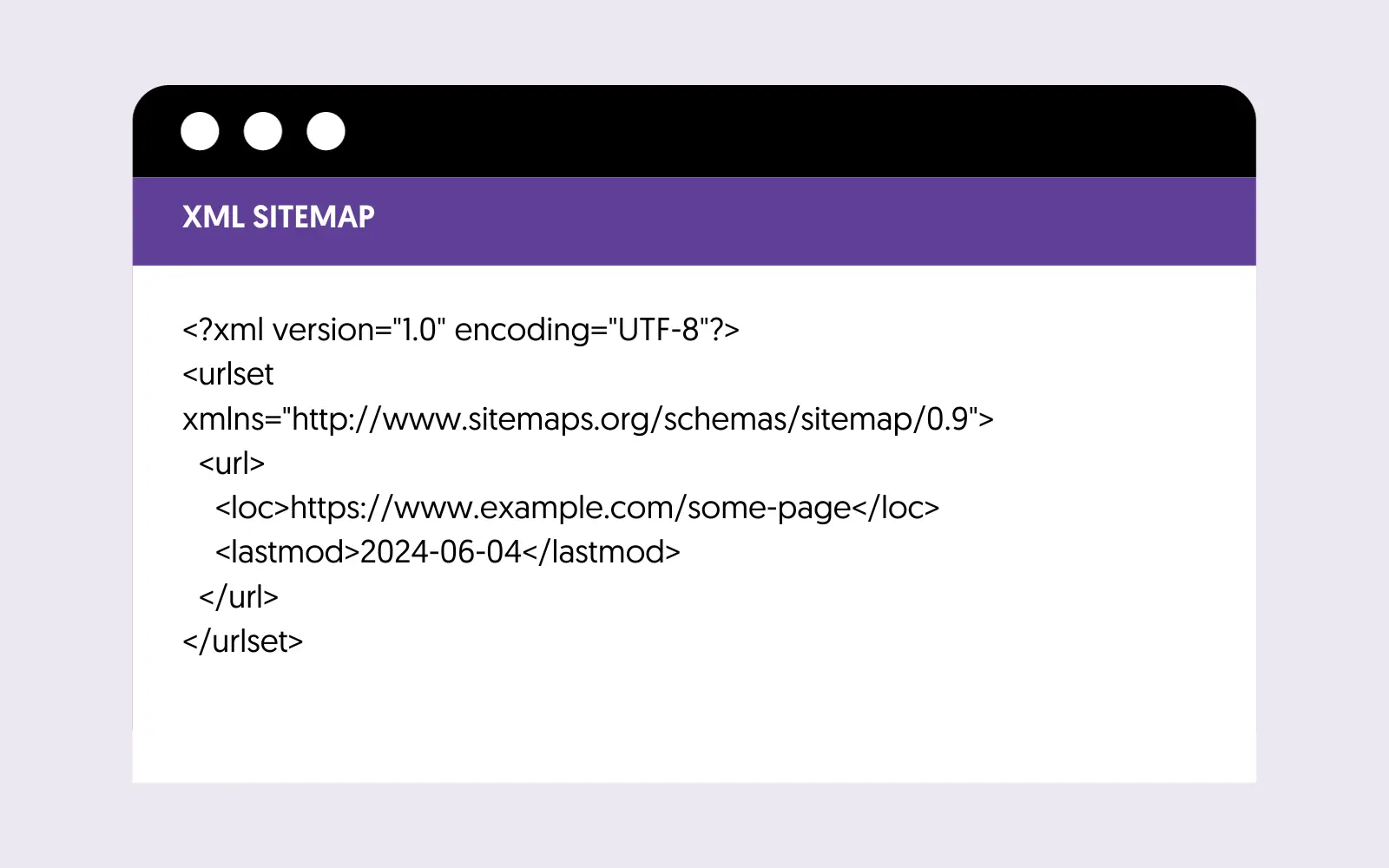
XML sitemaps help search engines discover all website pages you want to appear in their index. Think of an XML sitemap as a list of all the pages/posts on your site that you want search engines to know about.
Optimizing and submitting an XML sitemap to search engines is a straightforward process you must do only once. Depending on your CMS, the sitemaps are automatically updated when new pages are added or changed.
This is what an XML Sitemap looks like:
Structured Data
Another element that is very important for ranking websites on top of search engine results is structured data. In simple terms, structured data (also known as schema markup) is a way to describe your content to search engines in a language they can understand.
You can add small pieces of code within your HTML code that give crawlers extra information on your content. A good example is recipes that appear as rich snippets in Google search results.
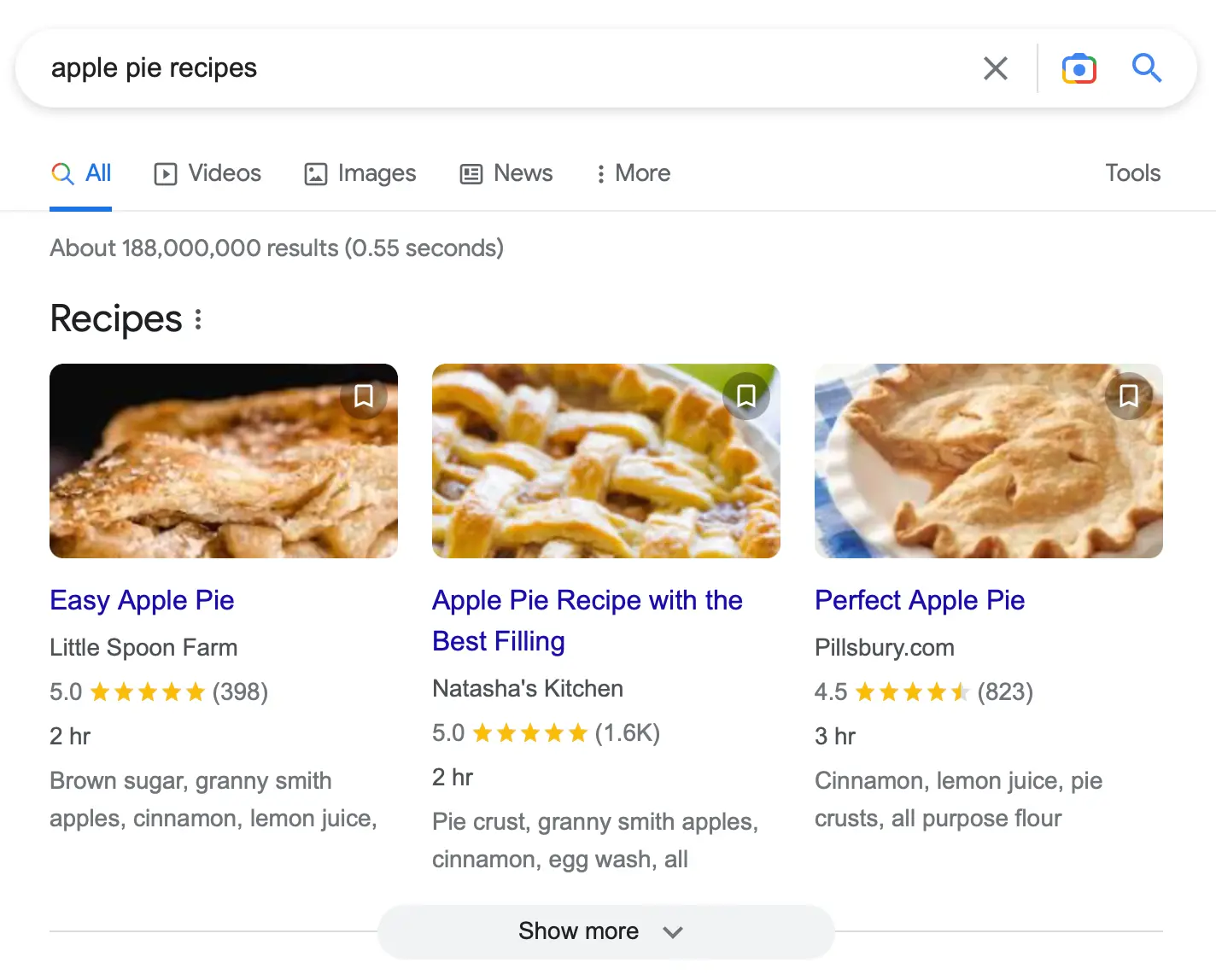
To help search engines identify the elements used in a rich snippet, like the image, name of the recipe, the number of reviews, and time to complete, you need to provide a script that looks like this:

This technical task may require playing with small pieces of code. If you’re using WordPress, some plugins automate this process for you. For other CMS, you can check their documentation or get the help of a developer to do this for you.
Step 6: Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO is the SEO process of getting higher rankings using promotion tactics that go beyond website content.

One of the most effective off-page SEO techniques is link-building. By acquiring high-quality backlinks from other websites, you gain Google's trust, which can lead to higher rankings.
You can do this by using different link-building methods like:
- Guest posting - publishing content on other websites with links pointing to your site.
- Getting links from suppliers and partners - getting links from websites you have real-life connections.
- Using HARO - this service helps you connect with reporters and get links from media websites.
- Creating link magnets - publishing content like case studies, statistics, and original data that can naturally attract links from other websites.
- Replicating your competitor's link-building practices - by analyzing your competitor's link profile, you can find and contact websites linking to them and secure an incoming link for your website.
Other off-site SEO techniques include influencer marketing, social media marketing, and digital PR.
Step 7: Mobile SEO
Mobile SEO is a type of SEO that gives special attention to the user experience on mobile devices. This is extremely important because:
- Mobile-first indexing - Google uses the mobile version of websites for indexing and ranking purposes. This means your mobile version should have the same content as the desktop and be optimized for smaller screens.
- Mobile usage is more than desktop - most of your traffic comes from mobile, and if you don’t optimize your website for mobile users, your conversions, bounce rate, and other important metrics will be negatively affected.
The most critical SEO guidelines for mobile users are:
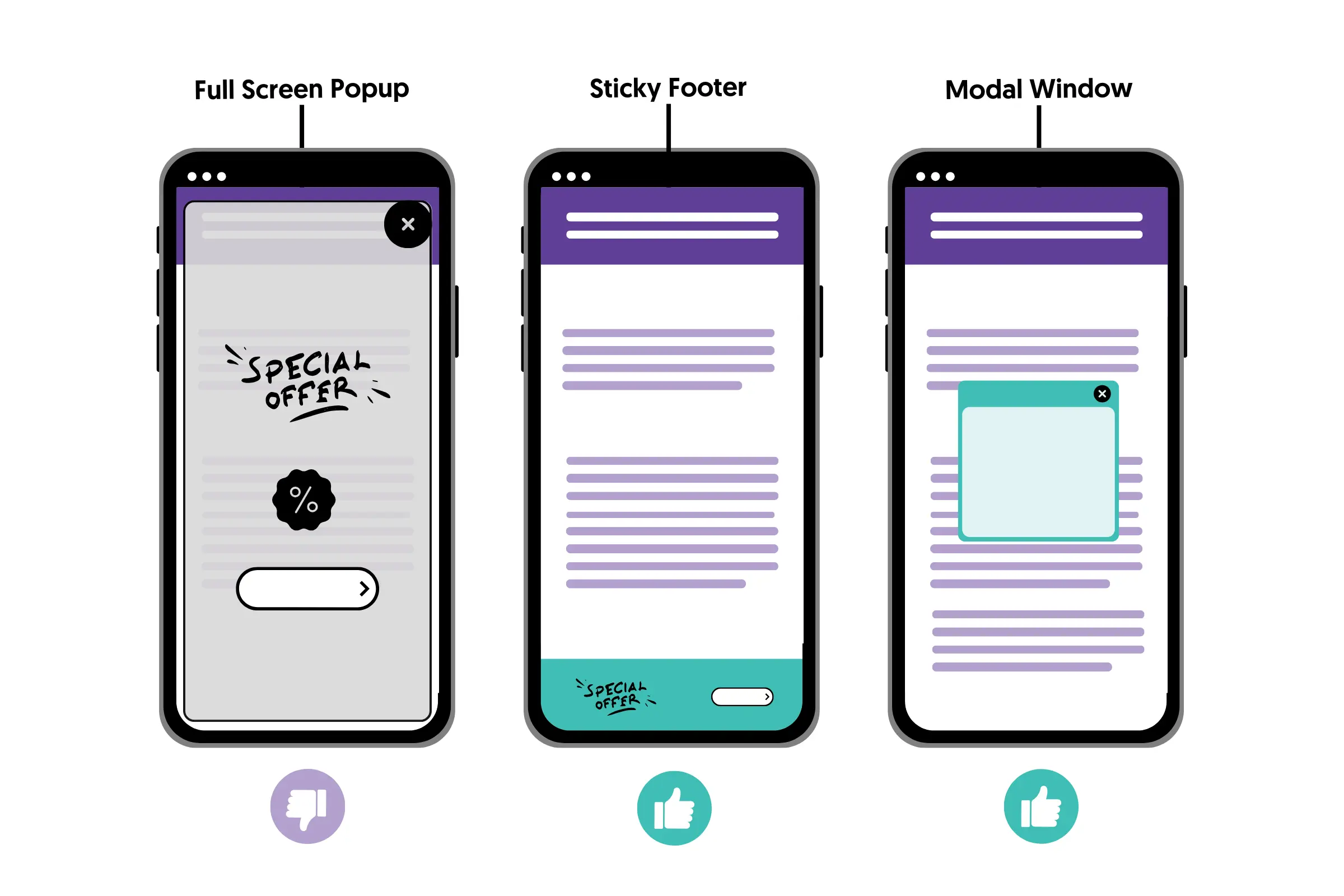
- Use a responsive design.
- Format content for mobile viewing.
- Give special attention to your mobile page speed.
- Avoid using popups and other intrusive elements.
- Optimize your navigation for mobile users.
- Optimize your call-to-action buttons and other CRO elements for mobile devices.
For more tips, read our mobile SEO guide.
Step 8: Local SEO
Local SEO is a set of SEO rules applicable to local businesses. With local SEO, you can optimize your website to appear in the local results on Google Search and Google Maps and get visits to your brick-and-mortar store.
The most effective local SEO strategies are:
- Optimize your Google Business Profile - Google Business is Google’s free local business directory. You’ll have to set up your Google Business Profile for your business to appear in local search results. You can add your business address, operating hours, contact information, and more helpful information.
- Get links from other local businesses - incoming links from local press or other local businesses can help your Google rankings.
- Positive reviews - online reviews can positively influence your rankings and help potential customers make a buying decision.
- Local directories listings - getting listed in quality directories related to your niche or local market is good for your SEO efforts.
For more actionable tips, view our local SEO checklist.
Step 9: SEO Performance
A critical aspect of running successful SEO campaigns is your ability to measure SEO performance accurately. Tracking the right SEO metrics will help you make data-driven decisions when adjusting your SEO strategy.
The most important SEO KPIs to monitor are:
Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is the number of visitors coming to your website from search engines. You can measure this using the Search Results report of Google Search Console and by installing Google Analytics.
The Search Results report in GSC will give you more information on how your website performs on Google. You can see which search queries your website was shown in Google and how many people clicked on your search snippets and visited your site.
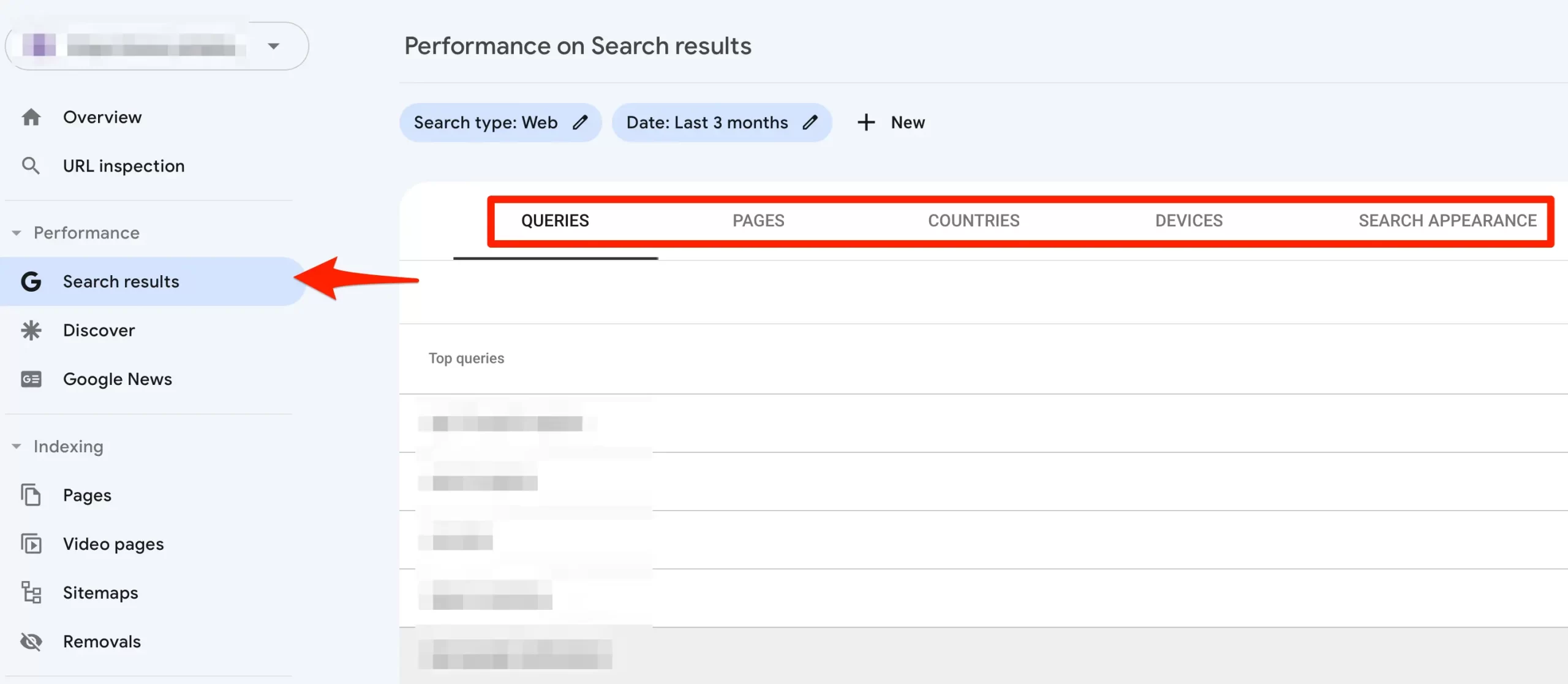
To get a holistic view of all the traffic sources that generated traffic to your site and how users interacted with your pages, you should install Google Analytics.
Through Google Analytics, you can access several reports to measure the effectiveness of your SEO campaigns and see what's working in terms of engagement and conversions.
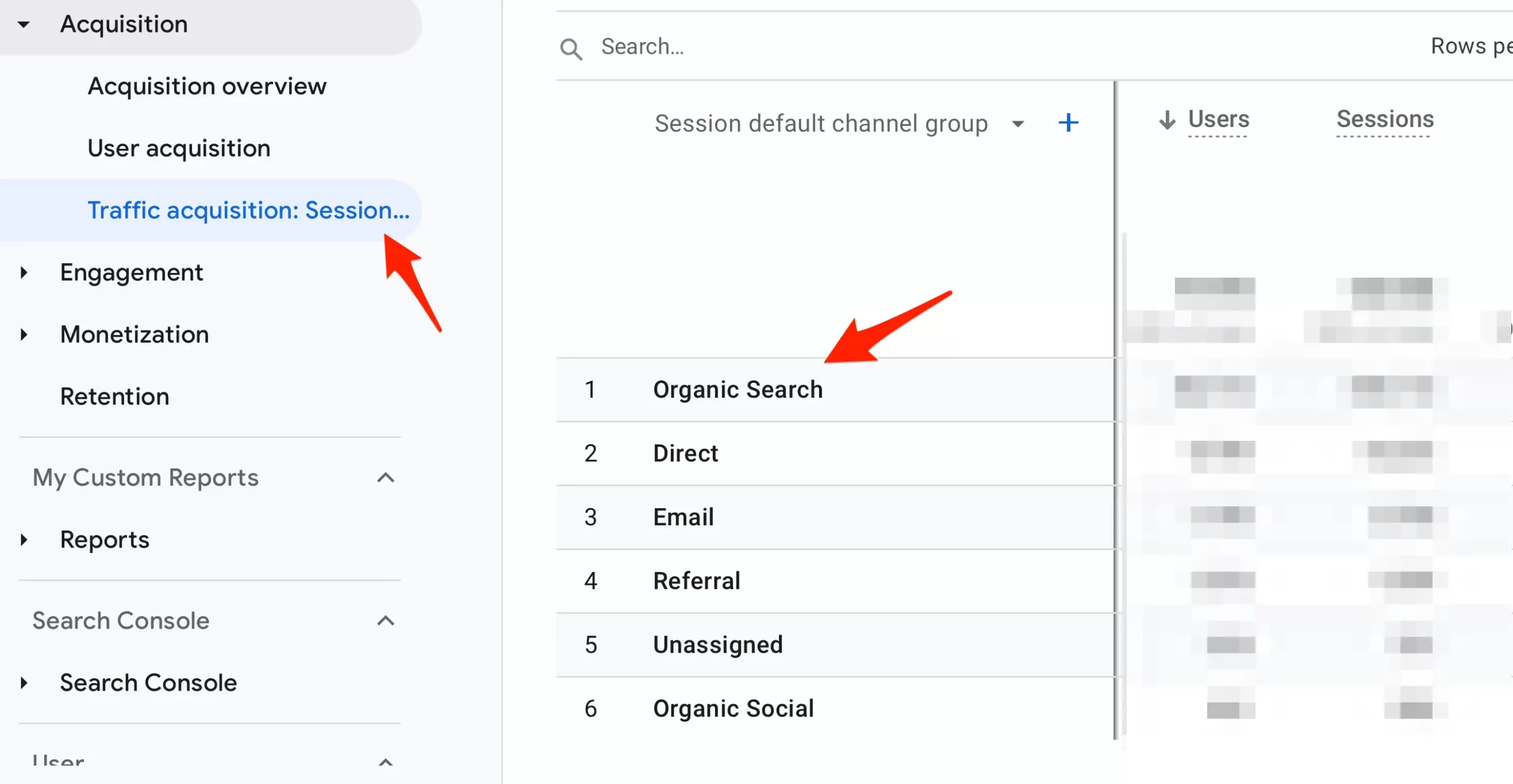
Rankings
Another element that you should monitor closely is your Google rankings. Using a keyword ranking tool, you can see your ranking position in Google for all your keywords. While your goal is to rank in the top position, this won't happen overnight, so monitoring your rankings and tracking your process is necessary.
With a ranking tool, you can:
- Track the ranking position of all keywords.
- Get reports on ranking changes.
- See for which SERP features your site ranks.
- Compare your rankings with competitors.
Conversions
A successful website generates conversions. Whether this is getting leads or making sales, you can use Google Analytics conversion tracking features to find out from where your customers are coming.
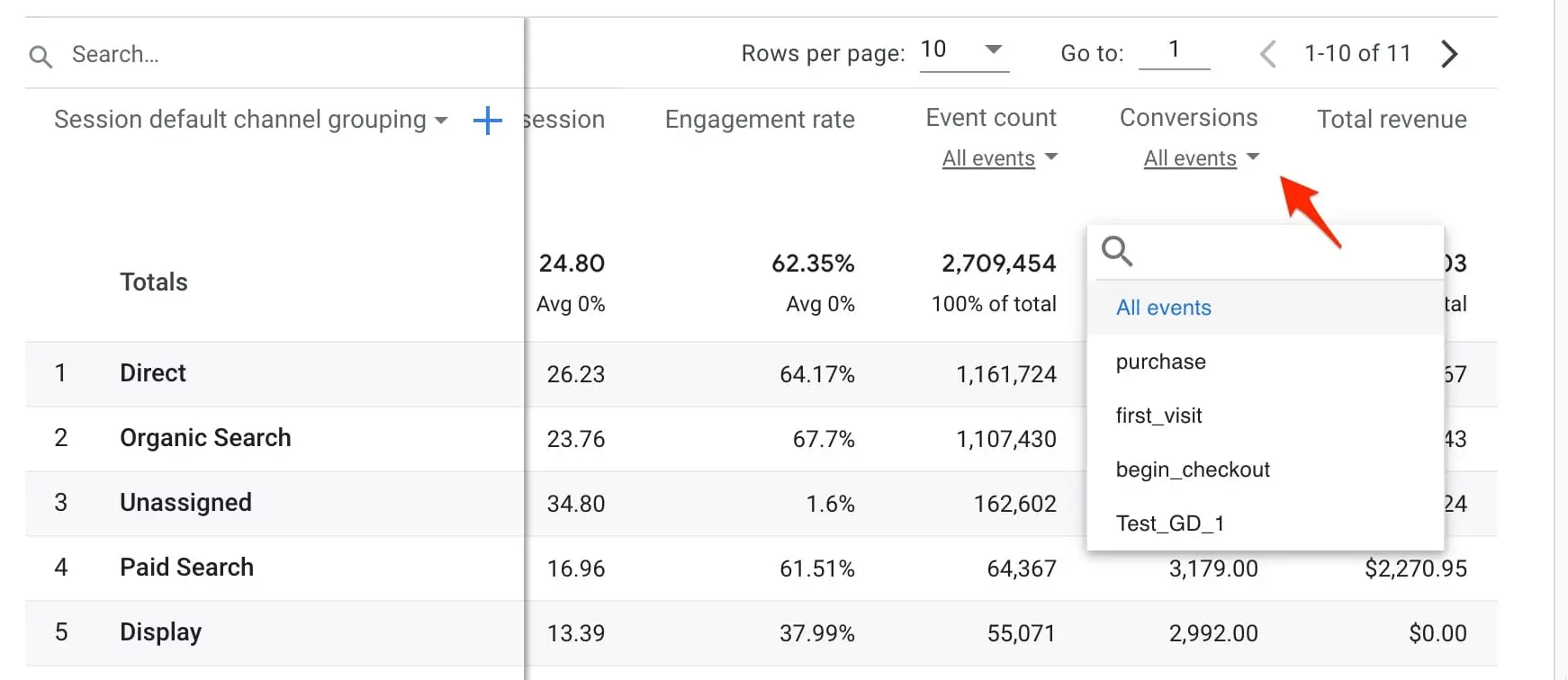
To become an expert on SEO analytics, use our Google Analytics 4 Course.
Get Started With SEO
From what you have learned in this guide about SEO, one thing is certain. There is a learning curve to go through for beginners. There are many concepts to master, requiring a lot of practice.
The best way to continue your SEO learning journey is the following:
1. Start With An SEO Course - This will help you master the basics and determine if SEO is the right career for you.
2. Get an SEO Certification - Going through the process of getting an SEO Certification will help you learn everything there is to know about SEO and put your knowledge to the test. You’ll also get a certification that can prove useful when applying to work as an SEO.
Let me know in the comments if you have any questions about SEO.



