In this post, you'll learn everything there is to know about on-page SEO. Follow these techniques whenever you publish a new post and improve your search engine rankings.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO (aka on-site SEO) is the process of optimizing the content of a webpage for higher rankings in the SERPs. The ultimate goal of on-page SEO is to help search engines understand the meaning and context of your pages and provide users with helpful content that will satisfy their search intent.
Why Is On-Page SEO Important?
On-page SEO is important because it gives search engines several signals to help them understand your content.
During the indexing and ranking processes, search engines try to associate web pages with keywords users type in the search box. Through on-page SEO techniques, you can guide them as to which keywords you want your pages to rank.
What Is The Difference Between SEO, Off-Page SEO and On-Page SEO?
SEO is a general term that includes everything you need to do to improve your website’s ranking in search engines. Includes technical SEO, on-page SEO, and Off-Site SEO. On-site SEO is a subset of SEO.
Off-page SEO is about link building and other factors you can use to convince search engines about the quality and usefulness of your website. It has to do with promotion methods outside the boundaries of your website.
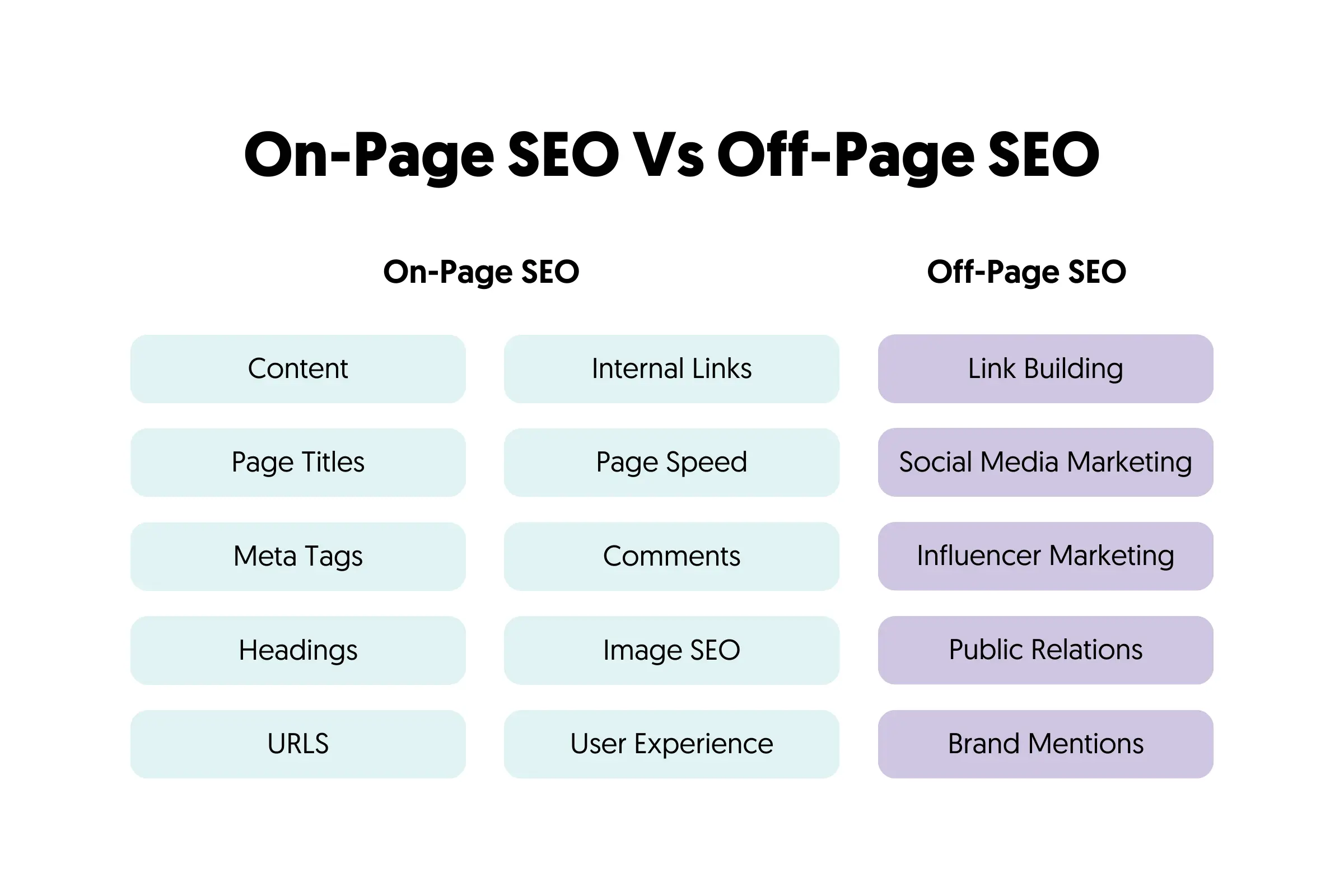
To get the best possible outcome, all SEO processes have to work together, but the main job of on-site SEO is to optimize the content and structure of a page.
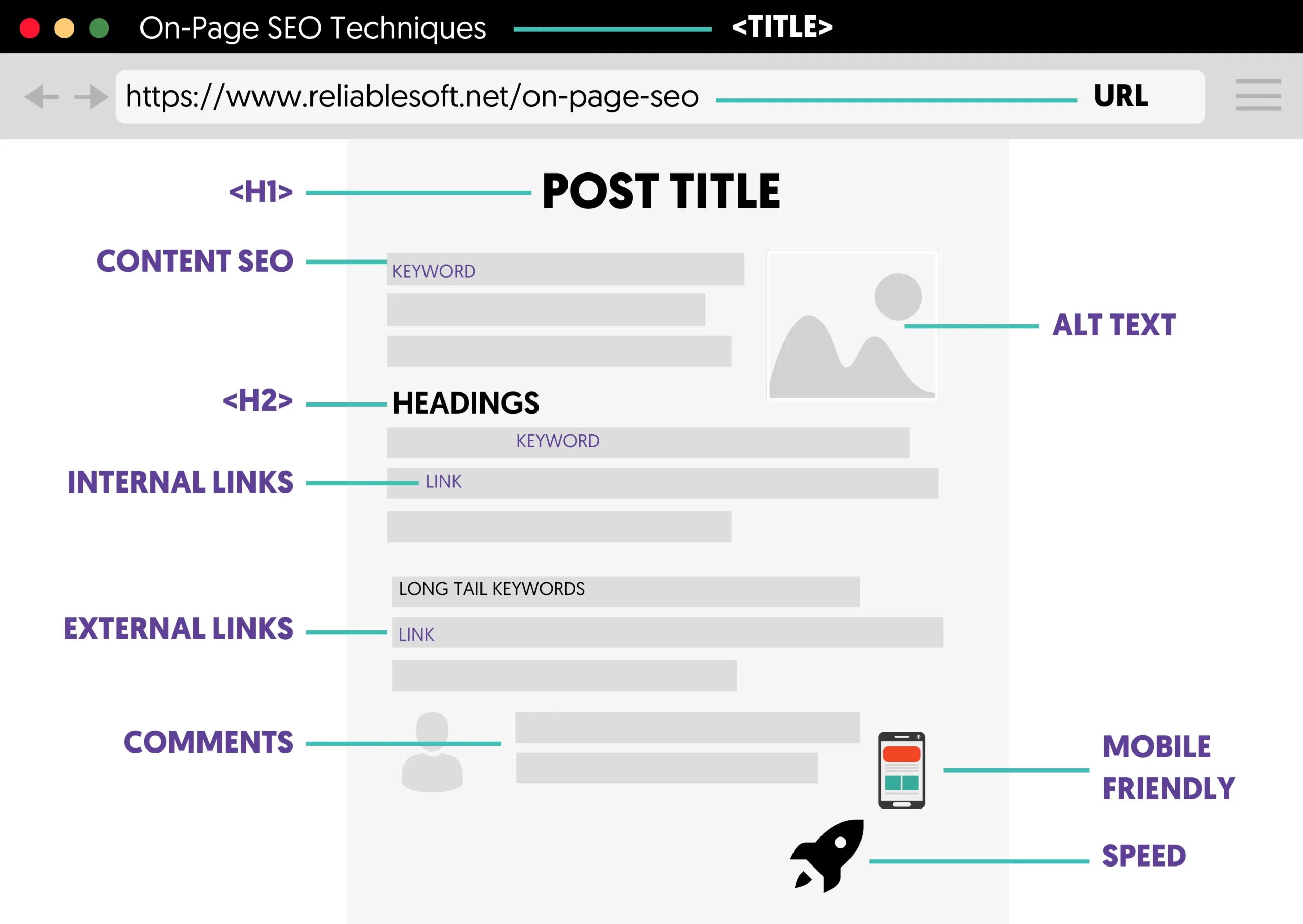
15 On-Page SEO Techniques
Here is a list of the basic and advanced on-page SEO elements:
- Publish High-Quality Content
- Optimize Page Titles
- Optimize Meta Descriptions
- Optimize Page Content
- Headings and Page Structure
- Optimize Your Images
- URL Optimization
- Add Internal Links
- Use External Links
- Optimize Page Experience
- Optimize For Featured Snippets
- Optimize For E-E-A-T
- Add Structured Data
- Enable User Comments
- Content Freshness
1. Publish High-Quality Content
When dealing with SEO, you always need to remember the following: A website with brilliant content can do great with or without SEO. A website with bad content will not survive with or without SEO. A website with good content can become even better with SEO!

So, what is considered good content? High-quality content has the following characteristics:
- Original content (articles, text, images, videos, comments, etc.) – No copies or rewrites of existing articles.
- Content exclusive for your website – Even if it’s your own content, if you have already published it on another website, it’s not good for your site.
- Content that includes text elements – Always use text to accompany your non-text content. For example, if you post videos on your website, try to add a text description as well. If you add images, try to describe in words what the image is all about.
- Create helpful, people-first content– Don’t publish content for the sake of publishing. Before hitting the publish button, make sure that what goes live adds value to your website and readers.
- Content that is well researched – Users don’t want to read quickly prepared posts, and neither do search engines.
- Unbiased content - If you are writing about a certain topic or answering a question, make sure that what you write is justified and covers both sides of a story.
Besides the above characteristics, you must ensure your content satisfies the search intent. Before publishing any content on your website, you need to understand what type of content users want to see for a given search query.

In general, the search intent can be categorized into four types:
- Informational - 'how many calories are in an egg?’
- Navigational - ‘Facebook’
- Transactional - 'buy coffee maker’
- Commercial -'best SEO courses'
The easiest way to find out what type of content to create is to take advantage of Google because they already did a great job of understanding what users like for different searches.
So, the first step is to go to Google and search for your target keywords. Navigate and carefully examine the top 10 results. Take note of things like:
- The type of content
- The level of detail
- How they use images and video
- Page design
Your goal is to use this information to build better content. Better in this context means a number of things like:
- More thorough and informative
- Easier to read
- Better user experience
- Possibly presenting a different view of the subject that is not already covered by the existing content.
Failure to create content that satisfies the search intent will eventually lead to lower rankings. Even if you manage to rank high on Google, this will be only temporary because Google uses different signals to measure whether or not users are happy with the websites shown at the top of the results.
So, before thinking about on-page SEO, make sure that the content you create is what a Google searcher wants.
Resources to learn more
- Content Writing - learn how to produce high-quality content for your website.
- Content Marketing Courses - the best courses to learn content marketing.
2. Optimize Page Titles
This is SEO 101, but it is crucial for on-page SEO. When search engines access your pages, among other things, they check the title tag.
They do so because they need to understand what the page is all about, and then, based on other factors (off-page SEO, domain authority, competition, etc.), they will rank your page (for various keywords) in a position in their search results.
Each page must have a unique title that will help search engines, and users understand what the page is about.
A page with the title On-Page SEO Tips for Beginners is better than a page with the title index.html.
The most important page title optimization tips are:
Add keywords to the beginning of your page titles – When possible, add your target keywords to the beginning of your page title. This helps search engines understand right from the beginning what the page content is about.
That does not mean you should cross the line and start doing keyword stuffing. If you cannot have a keyword at the beginning, it’s not the end of the world. Just make sure that your target keyword is part of the title.
Write short and descriptive titles – A page title shouldn’t be long. The general recommendation is to keep it below 70 characters because this is the average number of characters Google displays in the search results.
Include numbers and power words – Having numbers in the title and power words like “Ultimate, actionable, amazing, checklist, etc.” make titles more attractive and increase their CTR (Click-through rate).
No need to include your domain in the title - There is no need to include your domain name in the title because this is added automatically by Google. You can make use of the 70 characters to provide an accurate description of the page. An exception to this rule is when you have a strong brand that people can easily recognize.
Resources to learn more
- Page Title Optimization - best practices to optimize page titles (includes examples).
3. Optimize Meta Descriptions
The page meta description is shown on the search engine results page (SERPS). It has to be descriptive, up to 200 characters, and unique for each page.
It’s your opportunity to advertise your page and convince users to click your link and visit your website rather than selecting one of the other links.
It should be noted that Google does not always show the custom meta description, but they often use an automated description if they believe it is more useful for the searcher.
The most important meta-description optimization tips are:
Avoid auto-generated descriptions – Even though Google may not use your description, it’s always a best practice to avoid using auto-generated descriptions that sometimes don’t make sense.
Add your target keyword(s) in the description – Google still highlights the search terms both in the title and description so adding your target keywords, makes descriptions more relevant and appealing to the searcher.
Resources to learn more
- Meta Description Optimization - learn how to optimize your meta descriptions for SEO.
4. Optimize Page Content
Content SEO is part of on-page SEO and involves optimizing the content for your target keywords.
Before publishing content (text, images, audio, or video), the first step is to do keyword research.
This is necessary to determine what search terms users are typing in the search box and create content that satisfies their intent.
Once you decide on your target keywords, you should create a list of related keywords and longtail keywords and use them in your titles, descriptions, headings, and page content.
Why? Google search algorithms have become more intelligent, and besides keyword relevancy in content, they are also looking for topic relevancy.
This means that to make your content more relevant to broad topics, you need to enrich your content with related keywords.
There are various ways to find out which keywords are considered by Google relevant to your target keywords.
The easiest and fastest way is to take advantage of three features provided by Google: Google suggests, People also ask for, and Related Searches.
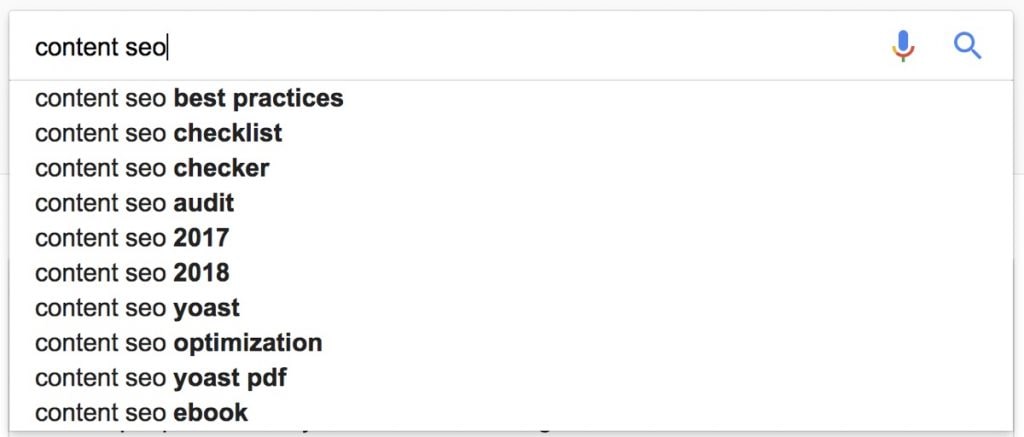
Google Suggest
When you start typing a query in Google Search, you are presented with a list of possible phrases to use in your search. These are great keyword candidates to mention in your content.
People Also Ask
When you click search, Google shows you the results, and among them, a section called "People also ask". These are good candidates to use in your sub-headings.

Related Searches
At the bottom of the search results, Google shows you a list of related searches.

All you have to do is mention some of the above words in your content (without doing keyword stuffing).
5. Headings and Page Structure
A page needs to be properly formatted. Think of it as a report which needs to have a heading (h1) and subheadings (h2, h3).
The H1 Tag
Each page needs to have only one H1 tag. In all CMS, by default, the title of a page is wrapped into H1 tags.
You can either choose to have the same <title> and <h1> tag or provide an alternative title for the heading.
Remember that search engines display in the results what they find in the title tag, not the h1 tag. If you're confused, read the differences between the two.

As far as the other headings are concerned (h2, h3), the things you need to have in mind are the following:
- Avoid using a single word for a heading, but make your headings interesting and useful for users who like to skim-read an article.
- Use headings hierarchically, i.e., the first heading tag is the <h1> and then the <h2> and then <h3>, <h4>, etc.
- The subheadings are a great place to use related keywords in your content.
Content Formatting
Do not just throw text on a page, but ensure it is readable.
- Use bold, underlined, or italics to highlight the important parts of a page.
- Use a good size font for desktop and mobile (at least 16px).
- Split the text into small paragraphs (max 3-4 lines).
- Use enough spacing between the paragraphs to make the text easier to read.
- Use CSS to create sections that stand out and break the text into smaller, more manageable parts.
6. Optimize Your Images

Images are important for presentation purposes. They make a page more interesting and easier to understand.
The biggest problems with images are that search engines don't understand them and that they add to the loading speed of a page.
Best practices for SEO optimizing images
- Use original images. If you need to use an existing image from the web you need to reference the source.
- Optimize the size of the images – the smaller the size (in bytes) of the image the better.
- Use an ALT tag to describe the image – This helps search engines understand what the image is about.
- Use descriptive filenames – Don’t just name your image ‘image1.jpg’ but try to use descriptive filenames, for example, ‘man-doing-push-ups.jpg’.
- Use a Content Delivery Network – If you have a lot of images on a single page you can use a CDN service that will make your page load faster. In simple terms, your images will be hosted and served by a number of servers, and this speeds up the loading process.
Resources to learn more
- Image SEO - everything you need to know about optimizing your images for SEO.
7. URL Optimization
Optimizing your URLs is important for maximum SEO. It has two parts. The first part is URL optimization and the second is the URL structure.
A permanent link (also known as a slug) is the unique URL of each page.

Good URLs should be less than 255 characters and use hyphens to ‘-‘ separate the different parts.
Just like the page title, an SEO-friendly URL is short, descriptive, and includes your target keyword.
These are some examples of good URLs:
- https://www.reliablesoft.net/diy-seo-tutorial-for-beginners/
- https://www.reliablesoft.net/seo-tools
- https://www.reliablesoft.net/search-engine-marketing/
These are examples of bad URLs:
- https://www.reliablesoft.net/p?165 or
- https://www.reliablesoft.net/seotipsforbeginners/ or
- https://www.reliablesoft.net/123131/publish/data2/seo_Tips.html
Best practices for optimizing your URL structure
- Create a matching site Structure and URL structure - The URL structure should mimic the actual structure of a website.
- Group related content into categories - Group your pages into categories to help users and search engines find what they want faster. It’s like having a warehouse with many uncategorized items versus a warehouse with all the items assigned to a dedicated category.
- Add a Breadcrumb menu– A breadcrumb is helpful because it allows users to navigate your website in a structured way since they always know where they are and how far from the home page.
Resources to learn more
- SEO Friendly URLs - how to create SEO-friendly URLs
- Site Structure Optimization - tips on how to optimize your site structure for SEO
8. Add Internal Links
Internal linking, i.e., linking to pages within your website, is a good SEO practice.
- It’s a way to let search engines know about your other pages.
- It’s a way to tell search engines your most important pages.
- It’s a way to increase the time users spend on your site.
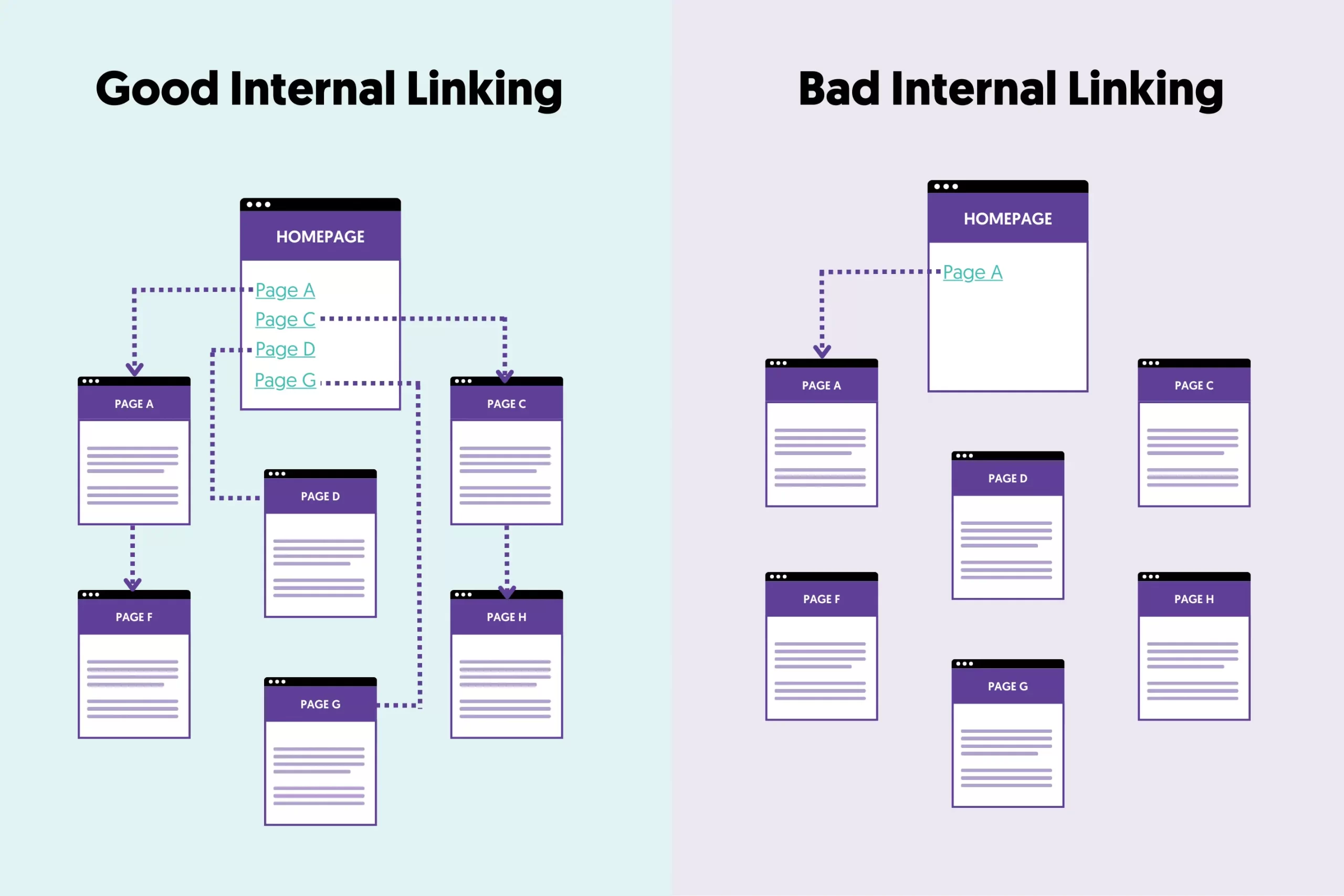
Best practices for internal linking:
- Add internal links when they are useful for your reader
- No more than 15 internal links per page (this is my opinion and not based on any research or studies)
- When possible, add the links in the main body of your webpage (not in the footer or sidebar)
- Link from older posts to newer posts and vice versa.
- The most important pages of your website should have a greater number of internal links.
- View the internal links report in Google Search Console to understand your internal linking structure.
9. Use External Links
An external link is a link pointing to a page outside your website, i.e., on a different domain. For the website that links out, it’s an external link and for the website that receives the link, it’s a backlink.
We know backlinks are important for SEO, but what about external links?
External links to related pages help Google figure out your page’s topic. It also shows Google that your page is a hub of quality info.
Adding external links to your content will not directly help you with SEO, it’s not a ranking factor but it can help you indirectly.
Let’s quickly review the best practices to follow when adding external links to your content.
- Link out only when it provides value to the reader.
- Link only to websites you trust.
- Link only to related websites that have unique and original content
- Use the 'nofollow' tag for external links going out to websites you don't fully trust.
10. Optimize Page Experience
Google's ranking systems look for several factors when evaluating the user experience on a page. Grouped together, these factors are called "Page Experience". The most important are:
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals is a set of KPIs for evaluating desktop and mobile site speed.
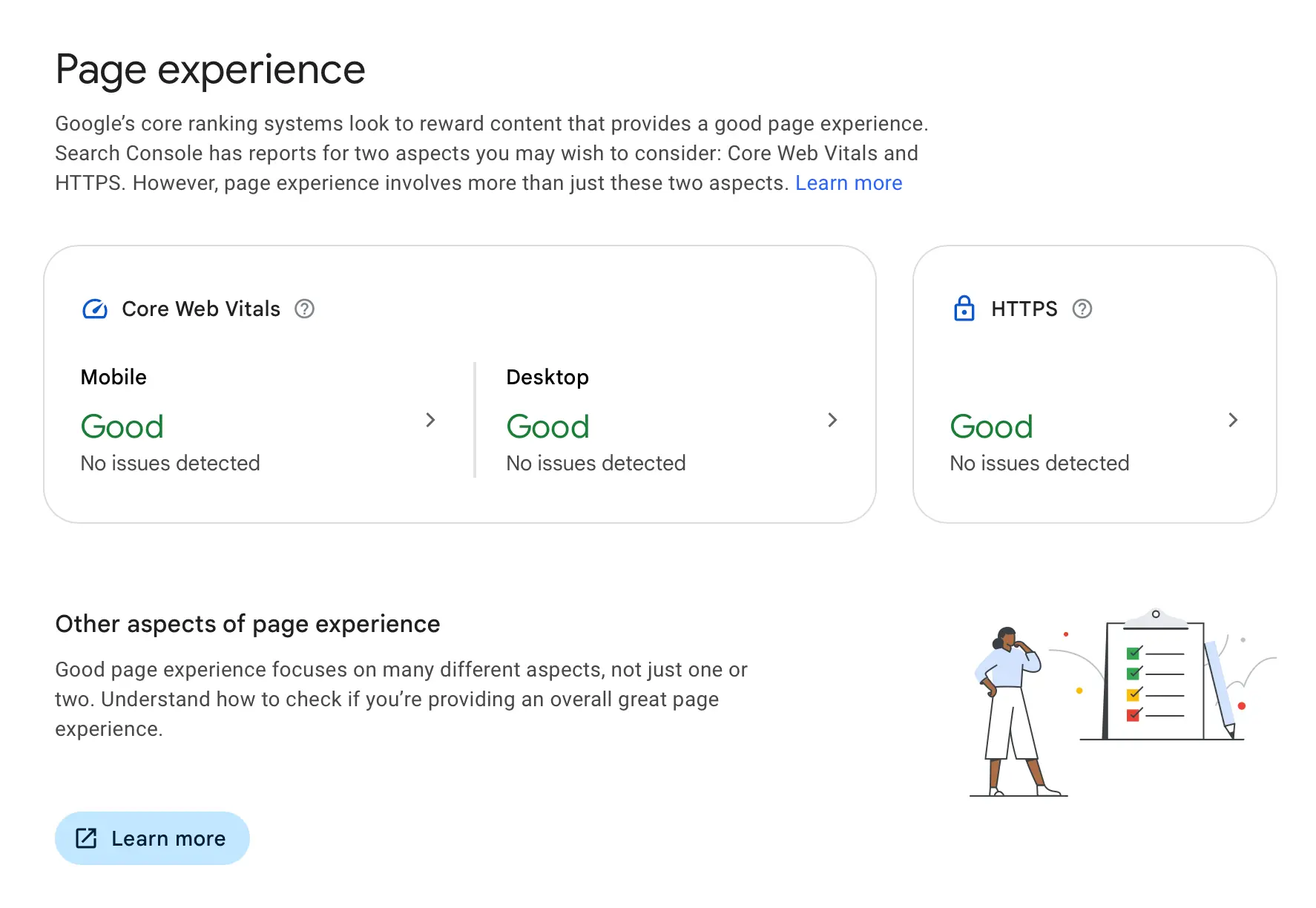
According to Google guidelines, websites should have these core web vitals values:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) –2.5 sec or less
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – 0.1 or less
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – 200 ms or less
The page experience report in Google Search Console will indicate if there is a problem with your core web vitals scores.
HTTPS
Having pages served securely by installing an SSL on your server and making your website HTTPS is a known ranking signal.
You can check that your installation is ok by visiting your website using https://yourdomain.com and clicking on the site information icon.
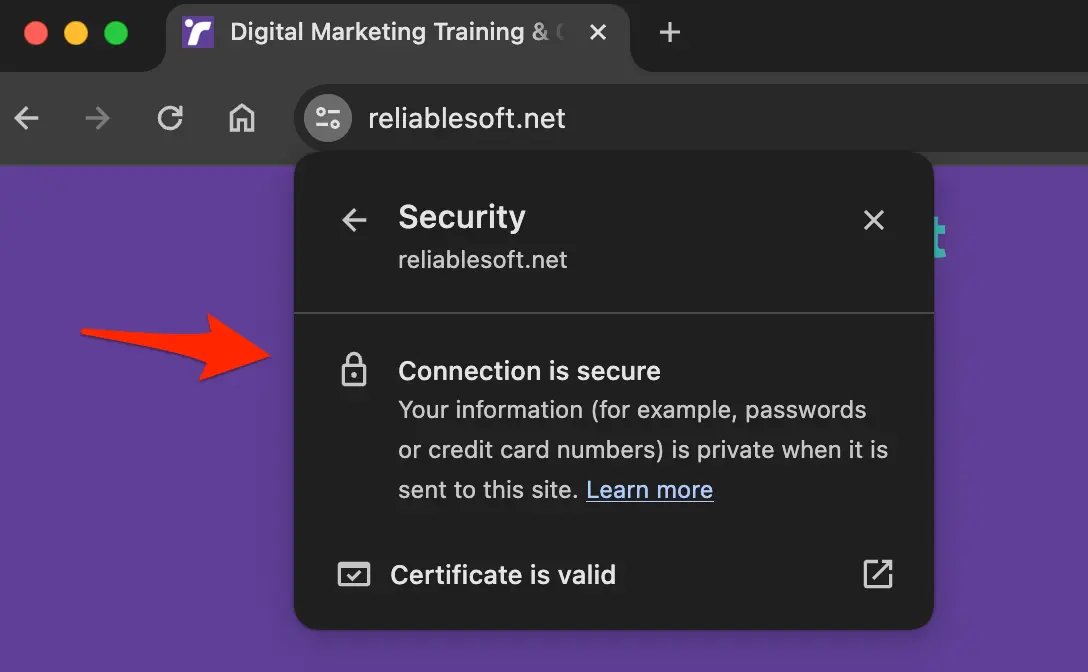
If you see the message "Connection is secure" and "Certificate is valid", then everything is configured ok.
Mobile Friendliness
With the introduction of mobile-first indexing by Google (a few years ago), the Google crawler uses the mobile version of the site’s content for indexing and ranking purposes.
This means that if your website is not optimized for mobile users, its rankings will suffer.
What should you do?
- As a first step, make sure that your website is mobile-friendly. In general, websites with a responsive design have nothing to worry about mobile-friendliness.
- Ensure that you have the same content on desktop and mobile.
- Format your content for mobile devices.
- Optimize your menus and navigation for mobile devices.
- For more tips, read our mobile SEO guide.
Ad Content
Websites with an excessive amount of ads offer a bad experience to users, and this is penalized by Google algorithms. If you're using ads on your website, ensure that:
- You're not using too many ads on a page.
- Ads are easily distinguished from the main content.
- Ads do not slow down your website, especially on mobile devices.
Popups and Intrusive Interstitials
Another element that is part of on-page SEO is intrusive interstitials and dialogs that block users' view of the content.
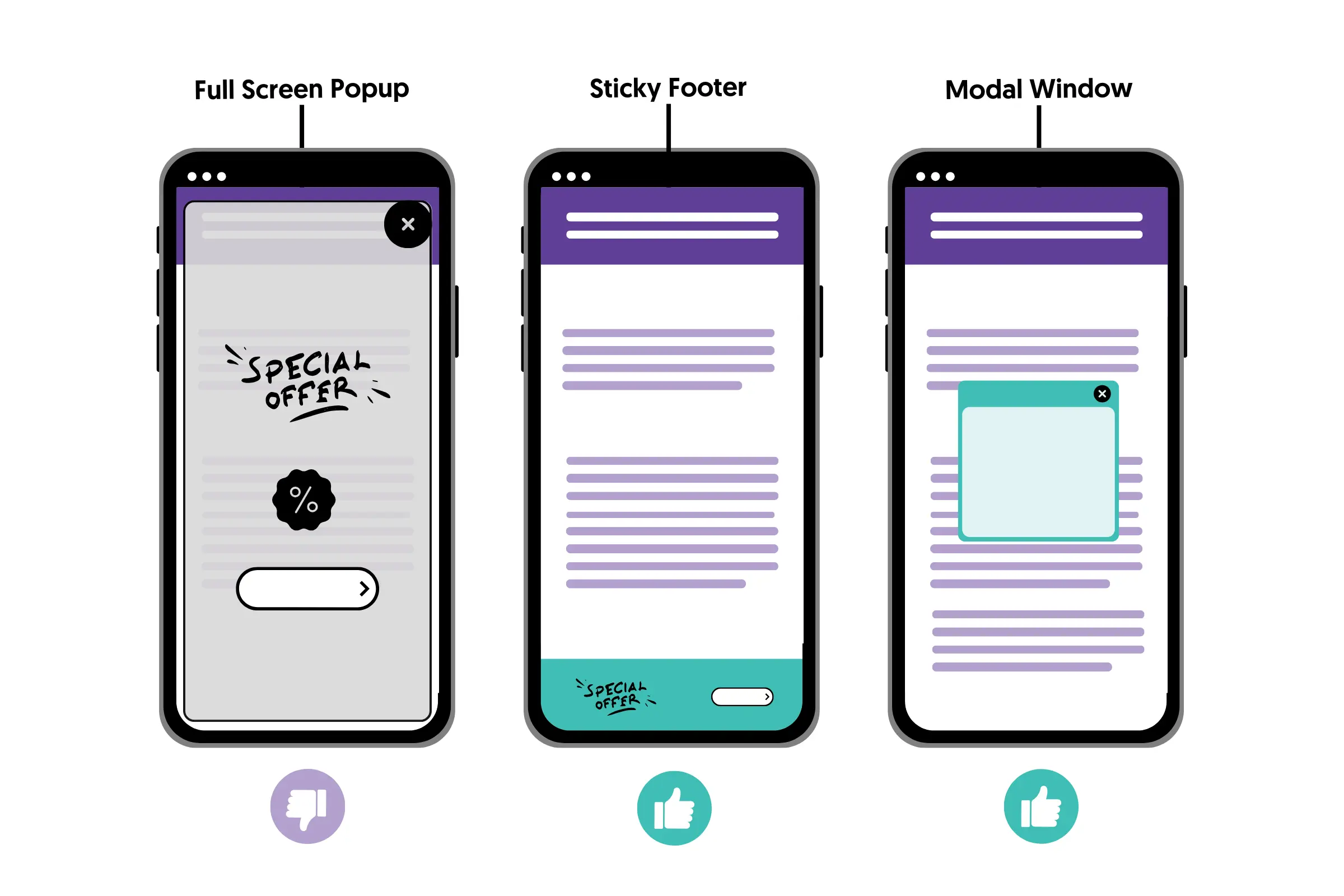
If you're using popups or dialogs on mobile that cover the whole page (or a large part of it) and appear as users scroll through the content, you should consider removing them. You can replace them with sticky footers.
11. Optimize For Featured Snippets
Featured snippets appear on the top of the Google organic results for certain queries. Here is an example:
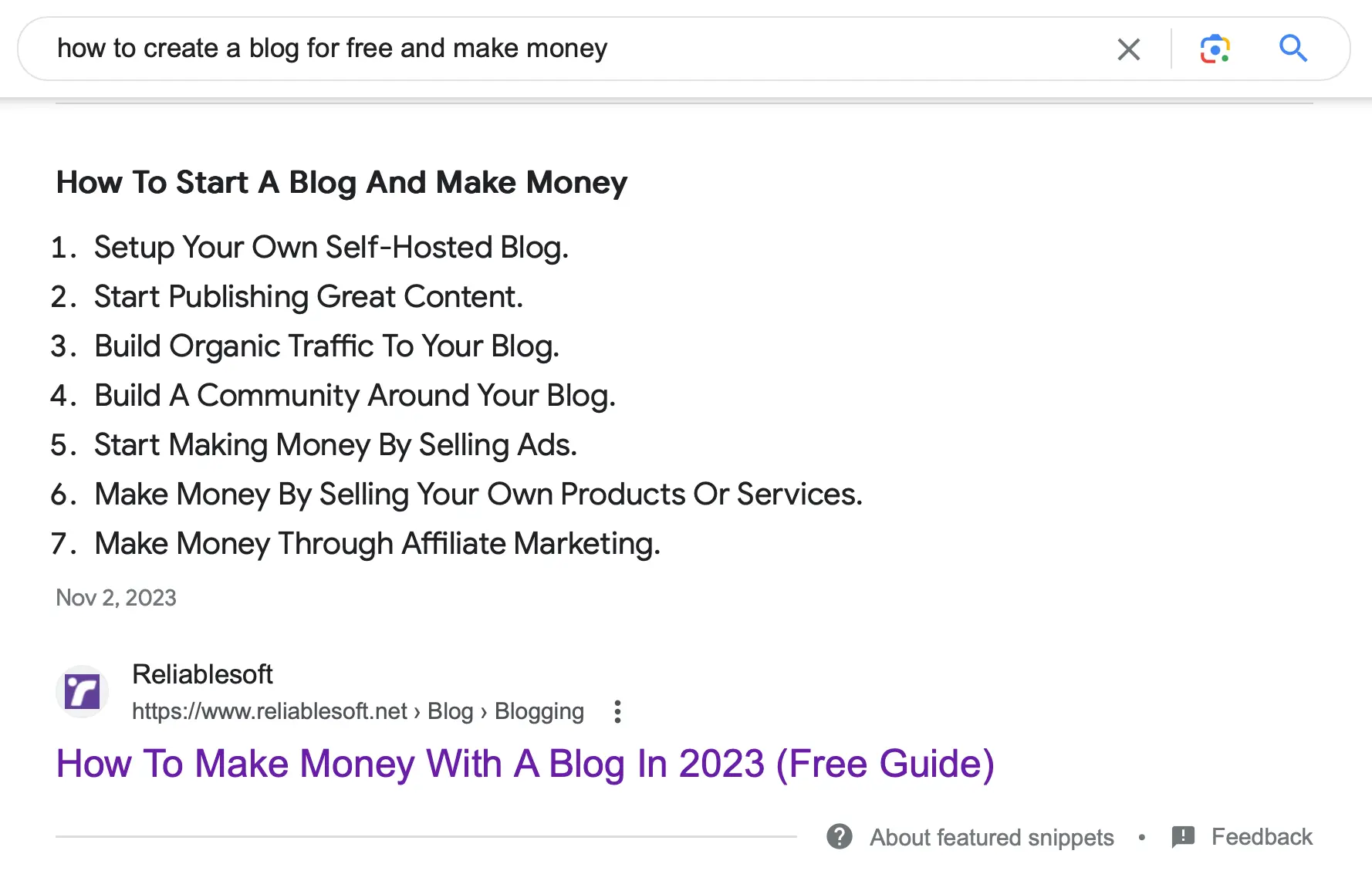
Getting a featured snippet means a substantially higher CTR and more traffic to your website. Google usually shows a featured snippet for:
- How-to queries that include a list of steps
- Best-of articles that include a list
- Definitions (what is....)
- Lists (digital marketing checklist, SEO checklist, etc).
To check if your website ranks for a featured snippet, use a tool like Ahrefs or Semrush and check the SERP Features Report.
To increase your chances of appearing in "position zero" of the SERPs, follow these tips:
- Summarize the answer to a question (or query) in one paragraph.
- Answer questions that "People also ask".
- Format your content with clear headings.
- Provide content that satisfies the user intent for the particular query.
For more techniques, read our How to Get a Google Featured Snippet guide.
12. Optimize For E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. These four pillars comprise a core component of Google’s Rater Guidelines for search quality.
Although all four factors are important for rankings, in the context of on-page SEO, you can optimize your content to demonstrate Experience and Expertise.

Experience
Experience allows Google to evaluate whether the content produced was created with a degree of actual experience. This is particularly important in today’s world of AI-generated content.
Expertise
Expertise determines whether authors of a topic have specific knowledge and skills in a particular topic.
Things you can do to improve "Experience and Expertise" in your content include:
- Creating a well-structured “About Us” page to demonstrate your company's credentials and qualifications.
- Use author bios on all your content, highlighting a writer’s credentials.
- Demonstrate experience in the content. For example, if you’re writing a review for a new smartphone, showcase how you interacted with each feature on the device by adding original images, studies, and other unique elements.
- Ensure all content is well-researched.
- Use authoritative citations by linking to credible sources.
For more information, read our Google E-E-A-T guide.
13. Add Structured Data
Structured data is code that helps Google to understand your content better. It is not a ranking factor, but it helps get rich snippets in Google Search Results.
Rich snippets are an enhanced version of a standard search snippet that usually includes graphical elements like images, review stars, and other visual enhancements.
Here is an example of a rich snippet:
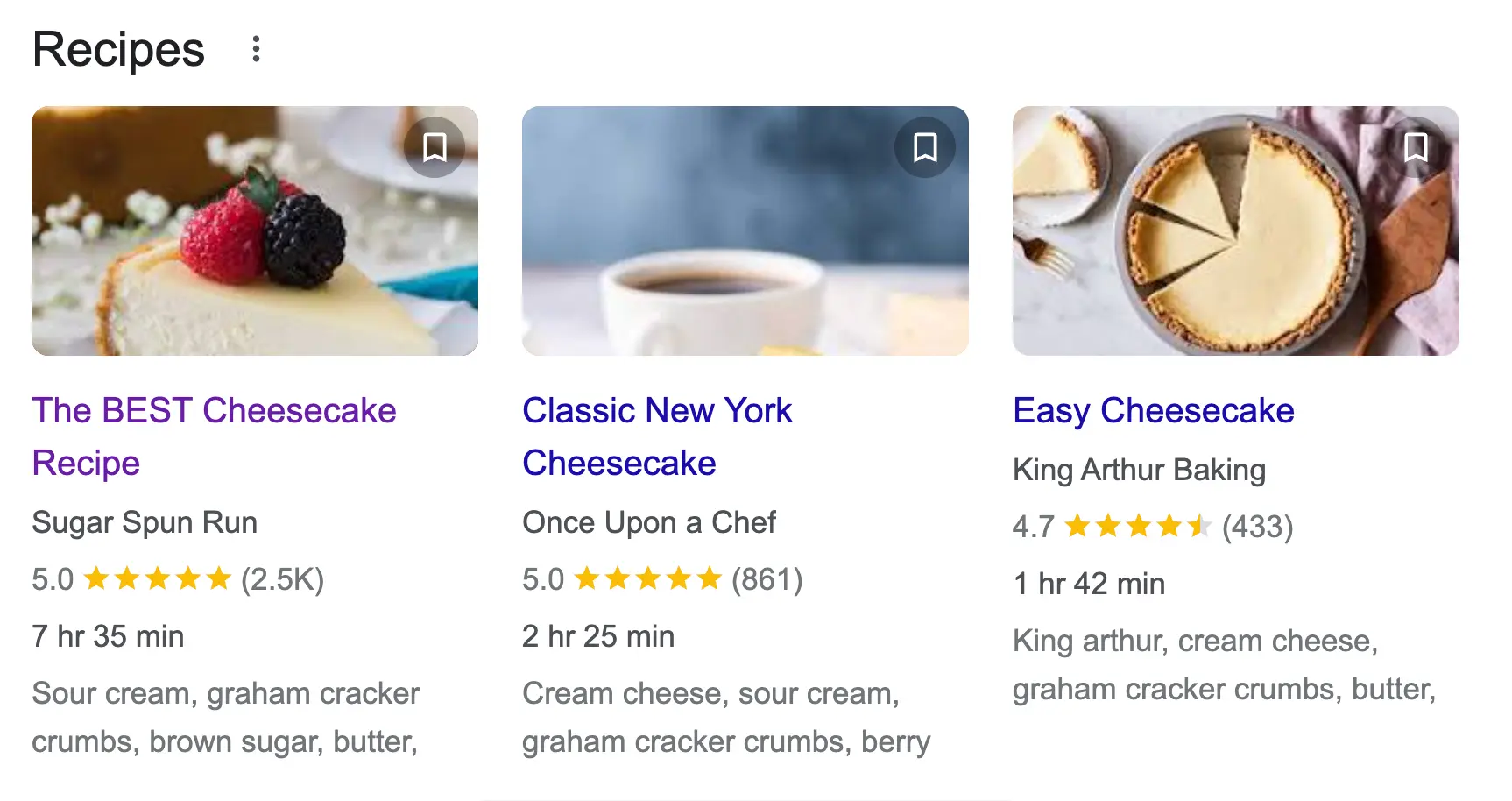
To be eligible for a rich snippet, follow these tips:
- Choose the right snippet type - view the list of all available snippets and choose the one that matches your content.
- Write the code - use Google tools or third-party software to write the structured data markup code.
- Test your script - test your code using the rich results testing tool.
- Add the scripts to your website.
For more information, read our Rich Snippets guide.
14. Enable User Comments
Many people believe that with the rise of social media, blog comments are no longer critical, but that's not true. Blog comments are still important.
As stated many times by Google, user comments indicate that people like your content and interact with the page, which can boost your SEO.
Look, for example, the number of comments on this post. More than 200 people found the content useful and submitted their comments.
Before posting a new comment users will probably read the existing comments before posting a new comment, which is an additional way to increase the time spent on the page and your website.
To make the best use of comments, follow these simple rules:
- Always moderate comments before publishing
- Avoid publishing comments that are too general
- Only approve comments that are relevant to the page content and add value
- Don’t approve comments when users don’t use a real name
- Always reply to comments. This will encourage more people to comment.
15. Content Freshness
One of the big SEO mistakes many publishers make is creating new content without going back to review and update their existing content. You should monitor your rankings and perform regular content updates as part of your on-page SEO audit. Content freshness is a known ranking factor.
- Twice (at least) per year, monitor your Google rankings to find your top-performing pages.
- Find for which keywords a page is ranking. You can use Google Search Console or your favorite SEO tool.
- Search on Google and analyze the content of the top-ranking pages for those keywords.
- Find missing topics/features included in the top pages and adjust your content accordingly.
- Refresh your visuals.
- Check your outbound and internal links.
- Ensure that your content matches the user intent.
- Optimize your content for Google features (featured and rich snippets).
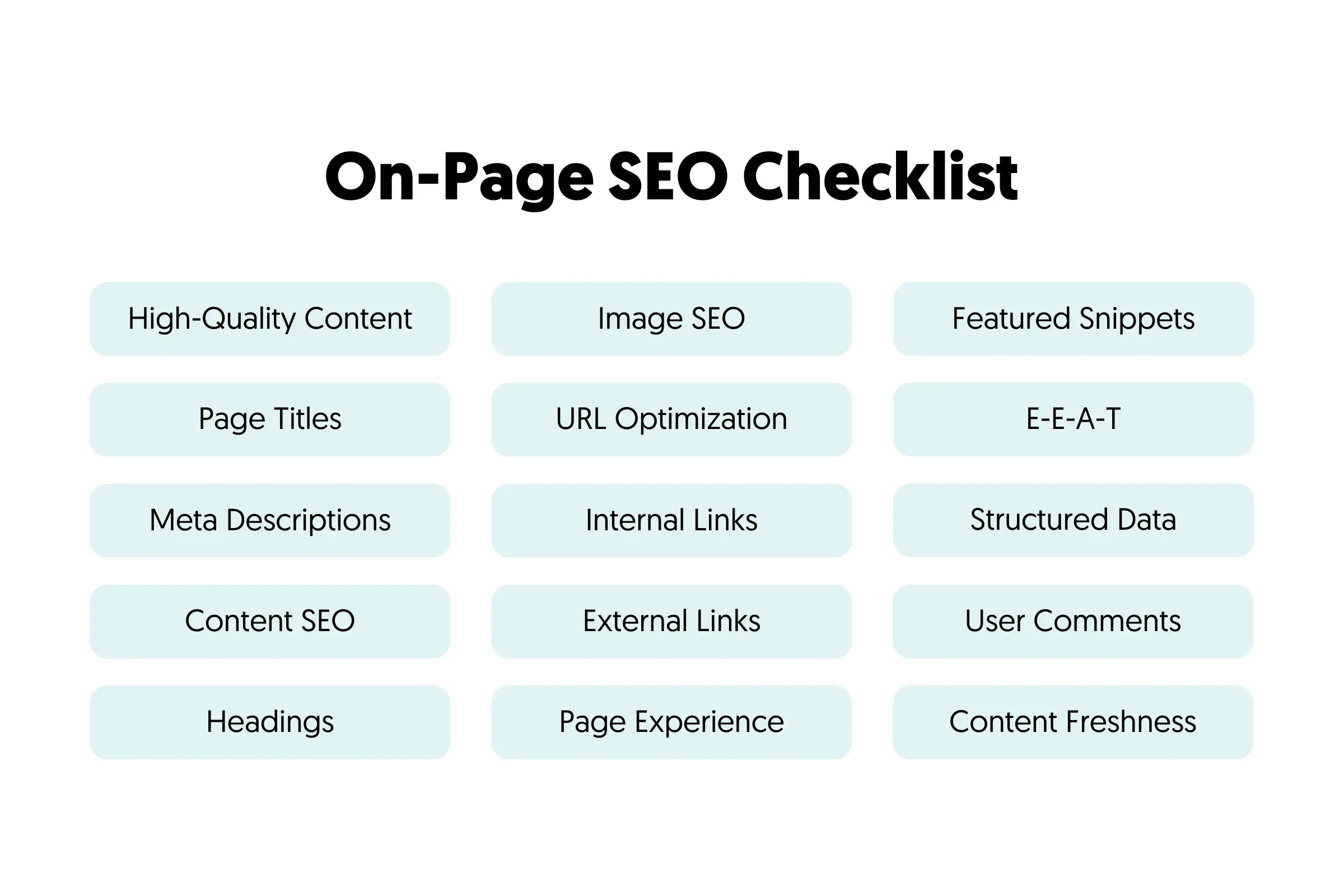
On-Page SEO Checklist
Here is your complete on-page SEO checklist, which includes both basic and advanced SEO factors.
Learn More About On-Page SEO
Use the following resources to learn more about on-site SEO and become an expert:



